|
Earth-to-Earth Spaceflight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly spacecraft into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in orbit around Earth, but also includes space probes for flights beyond Earth orbit. Such spaceflight operates either by telerobotic or autonomous control. The more complex human spaceflight has been pursued soon after the first orbital satellites and has reached the Moon and permanent human presence in space around Earth, particularly with the use of space stations. Human spaceflight programs include the Soyuz, Shenzhou, the past Apollo Moon landing and the Space Shuttle programs, with currently the International Space Station as the main destination of human spaceflight missions while China's Tiangong Space Station is under construction. Spaceflight is used for placing in Earth's orbit communications satellites, reconnaissance satellites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour Approaches The International Space Station (iss065e002231)
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrodynamics
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and the Newton's law of universal gravitation, law of universal gravitation. Orbital mechanics is a core discipline within space exploration, space-mission design and control. Celestial mechanics treats more broadly the orbital dynamics of systems under the influence of gravity, including both spacecraft and natural astronomical object, astronomical bodies such as star systems, planets, Natural satellite, moons, and comets. Orbital mechanics focuses on spacecraft trajectory, trajectories, including orbital maneuvers, orbital plane (astronomy), orbital plane changes, and interplanetary transfers, and is used by mission planners to predict the results of spacecraft propulsion, propulsive maneuvers. General relativity is a more exact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Launch
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Signific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Launch
Space launch is the earliest part of a flight that reaches space. Space launch involves liftoff, when a rocket or other space launch vehicle leaves the ground, floating ship or midair aircraft at the start of a flight. Liftoff is of two main types: rocket launch (the current conventional method), and non-rocket spacelaunch (where other forms of propulsion are employed, including airbreathing jet engines or other kinds). Issues with reaching space Definition of outer space Energy Therefore, by definition for spaceflight to occur, sufficient altitude is necessary. This implies a minimum gravitational potential energy needs to be overcome: for the Kármán line this is approximately 1 MJ/kg. W=mgh, m=1 kg, g=9.82 m/s2, h=105m. W=1*9.82*105≈106J/kg=1MJ/kg In practice, a higher energy than this is needed to be expended due to losses such as airdrag, propulsive efficiency, cycle efficiency of engines that are employed and gravity drag. In the past fifty years spacefl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Tourism
Space tourism is human space travel for recreational purposes. There are several different types of space tourism, including orbital, suborbital and lunar space tourism. During the period from 2001 to 2009, seven space tourists made eight space flights aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraft to the International Space Station, brokered by Space Adventures in conjunction with Roscosmos and RSC Energia. The publicized price was in the range of US$20–25 million per trip. Some space tourists have signed contracts with third parties to conduct certain research activities while in orbit. By 2007, space tourism was thought to be one of the earliest markets that would emerge for commercial spaceflight. Russia halted orbital space tourism in 2010 due to the increase in the International Space Station crew size, using the seats for expedition crews that would previously have been sold to paying spaceflight participants. Orbital tourist flights were set to resume in 2015 but the planned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
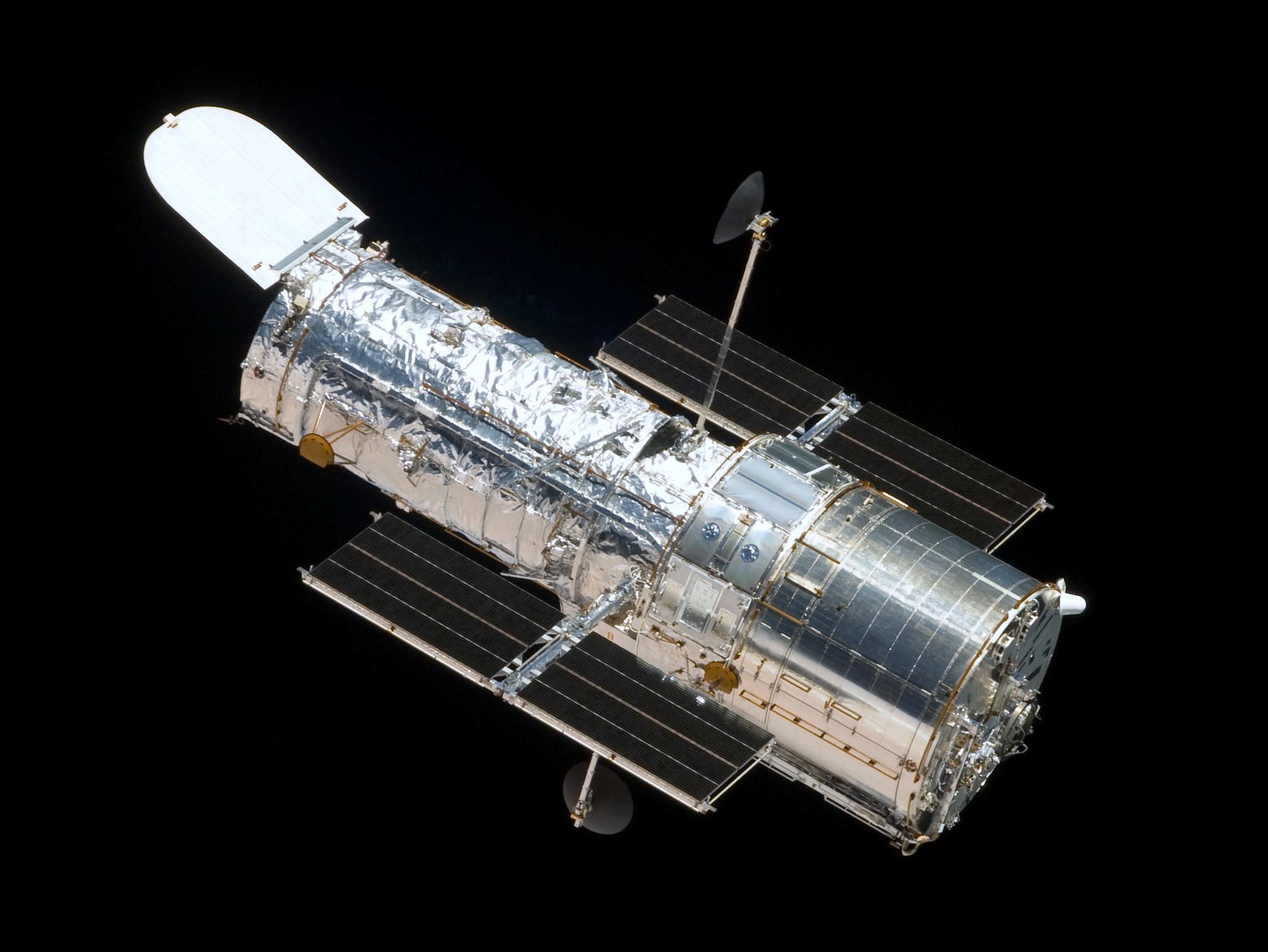
Space Observatory
A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope aboard space station Salyut 1 in 1971. Space telescopes avoid the filtering and distortion ( scintillation) of electromagnetic radiation which they observe, and avoid light pollution which ground-based observatories encounter. They are divided into two types: Satellites which map the entire sky (astronomical survey), and satellites which focus on selected astronomical objects or parts of the sky and beyond. Space telescopes are distinct from Earth imaging satellites, which point toward Earth for satellite imaging, applied for weather analysis, espionage, and other types of information gathering. History Wilhelm Beer and Johann Heinrich Mädler in 1837 discussed the advantages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Exploration
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration though is conducted both by robotic spacecraft, uncrewed robotic space probes and human spaceflight. Space exploration, like its classical form astronomy, is one of the main sources for space science. While the observation of objects in space, known as astronomy, predates reliable recorded history, it was the development of large and relatively efficient rockets during the mid-twentieth century that allowed physical space exploration to become a reality. The world's first large-scale experimental rocket program was Opel-RAK under the leadership of Fritz von Opel and Max Valier during the late 1920s leading to the first crewed rocket cars and rocket planes, which paved the way for the Nazi era V2 program and US and Soviet activities from 1950 onwards. The Opel-RAK program and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Observation Satellite
An Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, cartography and others. The most common type are Earth imaging satellites, that take satellite images, analogous to aerial photographs; some EO satellites may perform remote sensing without forming pictures, such as in GNSS radio occultation. The first occurrence of satellite remote sensing can be dated to the launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957. Sputnik 1 sent back radio signals, which scientists used to study the ionosphere. The United States Army Ballistic Missile Agency launched the first American satellite, Explorer 1, for NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on January 31, 1958. The information sent back from its radiation detector led to the discovery of the Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
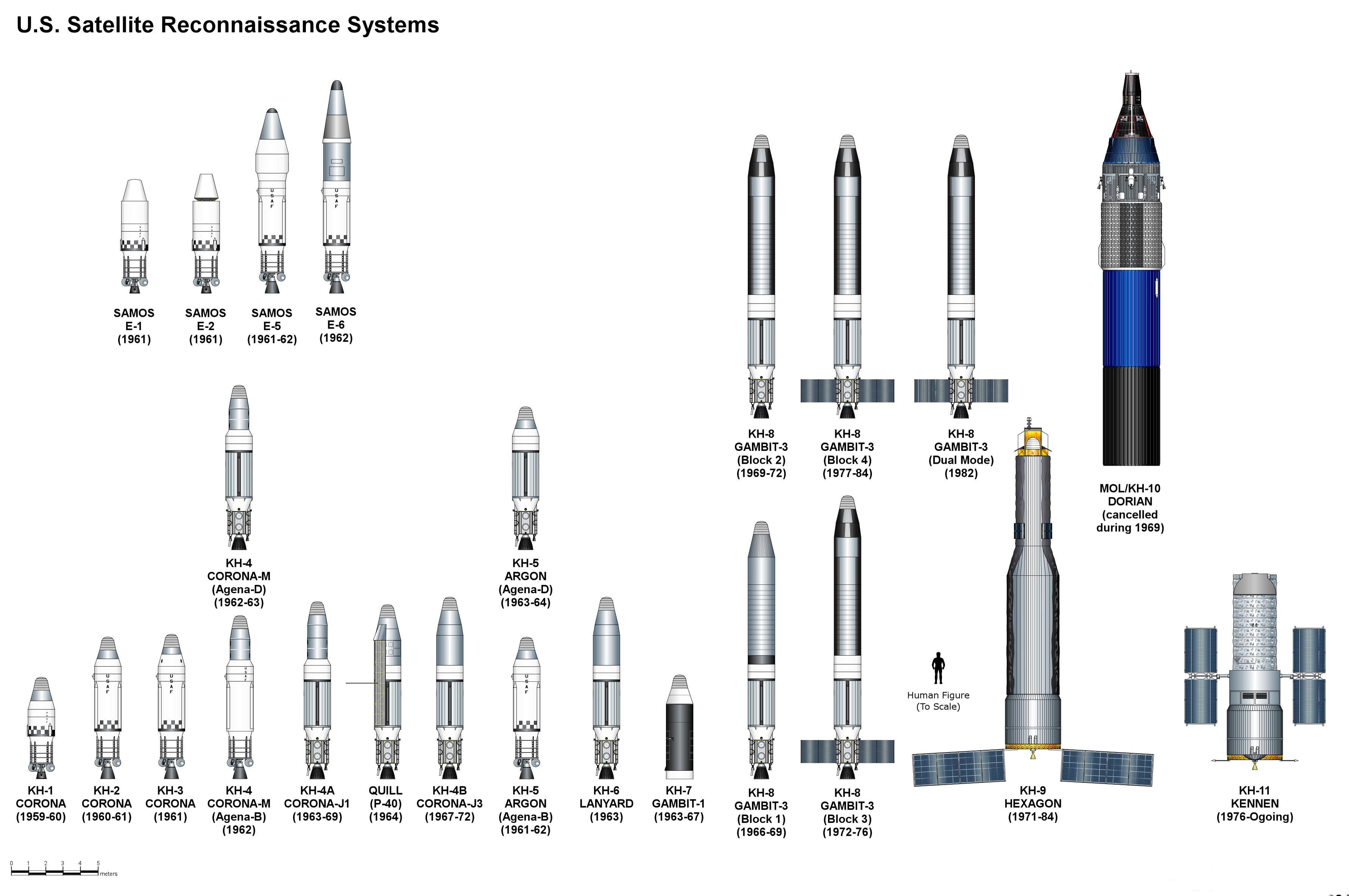
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassified o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


.jpg)


.jpg)