|
EIA-530
Currently known as TIA-530-A, but often called EIA-530, or RS-530, is a balanced line, balanced serial interface standard that generally uses a 25-pin connector, originally created by the Telecommunications Industry Association. Finalized in 1987 (revision A finalized in 1992), the specification defines the cable between the Data terminal equipment, DTE and Data circuit-terminating equipment, DCE devices. It is to be used in conjunction with EIA-422 and EIA-423, which define the electrical signaling characteristics. Because TIA-530 calls for the more common 25 pin connector, it displaced the similar EIA-449, which also uses EIA-422/423, but a larger 37-pin connector. Two types of interchange circuits ("signals" or "leads") between the DCE and DTE are defined in TIA-530: Category I, which uses the balanced characteristics of EIA-422, and Category II, which is the unbalanced EIA-423. Most of the interchange circuits are Category I, with the exception of Local Loopback (pin 18), Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIA-422
RS-422, also known as TIA/EIA-422, is a technical standard originated by the Electronic Industries Alliance that specifies electrical characteristics of a digital signaling circuit. It was meant to be the foundation of a suite of standards that would replace the older RS-232C standard with standards that offered much higher speed, better immunity from noise, and longer cable lengths. RS-422 systems can transmit data at rates as high as 10 Mbit/s, or may be sent on cables as long as at lower rates. It is closely related to RS-423, which uses the same signaling systems but on a different wiring arrangement. RS-422 specifies differential signaling, with every data line paired with a dedicated return line. It is the voltage difference between these two lines that define the mark and space, rather than, as in RS-232, the difference in voltage between a data line and a local ground. As the ground voltage can differ at either end of the cable, this required RS-232 to use signals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIA-423
RS-423, also known as TIA/EIA-423, is a technical standard originated by the Electronic Industries Alliance that specifies electrical characteristics of a digital signaling circuit. Although it was originally intended as a successor to RS-232C offering greater cable lengths, it is not widely used. RS-423 systems can transmit data on cables as long as . It is closely related to RS-422, which used the same signaling systems but on a different wiring arrangement. RS-423 differed primarily in that it had a single return pin instead of one for each data pin. RS-423 specifies an unbalanced ( single-ended) interface, similar to RS-232, with a single, unidirectional sending driver, and allowing for up to 10 receivers. It is normally implemented in integrated circuit technology and can also be employed for the interchange of serial binary signals between DTE & DCE. Standard scope RS-423 is the common short form title of American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard ''ANSI/TIA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
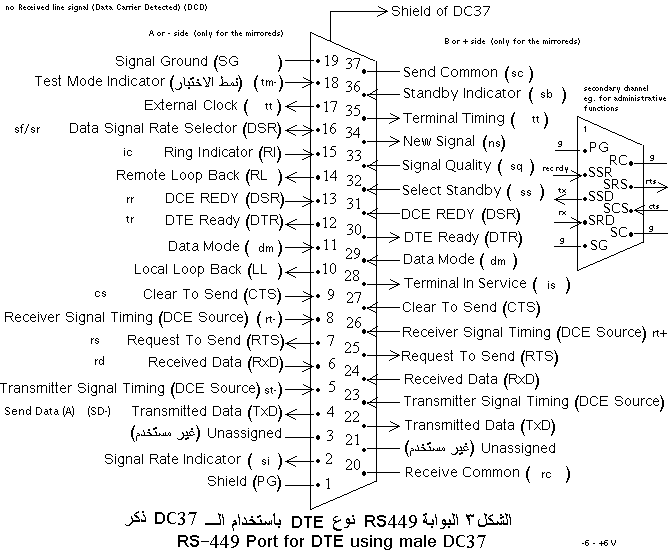
EIA-449
The RS-449 specification, also known as EIA-449 or TIA-449, defines the functional and mechanical characteristics of the interface between data terminal equipment, typically a computer, and data communications equipment, typically a modem or terminal server. The full title of the standard is ''EIA-449 General Purpose 37-Position and 9-Position Interface for Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange''. 449 was part of an effort to replace RS-232C, offering much higher performance and longer cable lengths while using the same DB-25 connectors. This was initially split into two closely related efforts, RS-422 and RS-423. As feature creep set in, the number of required pins began to grow beyond what a DB-25 could handle, and the RS-449 effort started to define a new connector. 449 emerged as an unwieldy system using a large DC-37 connector along with a separate DE-9 connector if the 422 protocol was used. The resulting cabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanced Line
In telecommunications and professional audio, a balanced line or balanced signal pair is a circuit consisting of two conductors of the same type, both of which have equal impedances along their lengths and equal impedances to ground and to other circuits. The chief advantage of the balanced line format is good rejection of common-mode noise and interference when fed to a differential device such as a transformer or differential amplifier.G. Ballou, ''Handbook for Sound Engineers'', Fifth Edition, Taylor & Francis, 2015, p. 1267–1268. As prevalent in sound recording and reproduction, balanced lines are referred to as balanced audio. Common forms of balanced line are twin-lead, used for radio frequency signals and twisted pair, used for lower frequencies. They are to be contrasted to unbalanced lines, such as coaxial cable, which is designed to have its return conductor connected to ground, or circuits whose return conductor actually is ground (see earth-return telegraph). Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Interface
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel. Throughout most of the history of personal computers, data has been transferred through serial ports to devices such as modems, terminals, various peripherals, and directly between computers. While interfaces such as Ethernet, FireWire, and USB also send data as a serial stream, the term ''serial port'' usually denotes hardware compliant with RS-232 or a related standard, such as RS-485 or RS-422. Modern consumer personal computers (PCs) have largely replaced serial ports with higher-speed standards, primarily USB. However, serial ports are still frequently used in applications demanding simple, low-speed interfaces, such as industrial automation systems, scientific instruments, point of sale systems and some industrial and consumer produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Industry Association
The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) to develop voluntary, consensus-based industry standards for a wide variety of Information and Communication Technologies (Information and communication technologies, ICT) products, and currently represents nearly 400 companies. TIA's Standards and Technology Department operates twelve engineering committees, which develop guidelines for private radio equipment, cellular towers, data terminals, satellites, telephone terminal equipment, accessibility, VoIP devices, structured cabling, data centers, mobile device communications, multimedia multicast, vehicular telematics, healthcare ICT, Machine to machine, machine to machine communications, and smart grid, smart utility networks. Active participants include communications equipment manufacturers, service providers, government agencies, academic institutions, and end-users are engaged in TIA's standards setting proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Terminal Equipment
Data terminal equipment (DTE) is an end instrument that converts user information into signals or reconverts received signals. These can also be called tail circuits. A DTE device communicates with the data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE). The DTE/DCE classification was introduced by IBM. A DTE is the functional unit of a data station that serves as a data source or a data sink and provides for the data communication control function to be performed in accordance with the link protocol. Usually, the DTE device is the terminal (or a computer emulating a terminal), and the DCE is a modem or another carrier-owned device. The data terminal equipment may be a single piece of equipment or an interconnected subsystem of multiple pieces of equipment that perform all the required functions necessary to permit users to communicate. A user interacts with the DTE (e.g. through a human-machine interface), or the DTE may be the user. Connections Two different types of devices are as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Circuit-terminating Equipment
A data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) is a device that sits between the data terminal equipment (DTE) and a data transmission circuit. It is also called data communication(s) equipment and data carrier equipment. Usually, the DTE device is the terminal (or computer), and the DCE is a modem. In a ''data station'', the DCE performs functions such as signal conversion, coding, and line clocking and may be a part of the DTE or intermediate equipment. Interfacing equipment may be required to couple the DTE into a transmission circuit or channel and from a transmission circuit or channel into the DTE. Usage Although the terms are most commonly used with RS-232, several data communication standards define different types of interfaces between a DCE and a DTE. The DCE is a device that communicates with a DTE device in these standards. Standards that use this nomenclature include: * Federal Standard 1037C, MIL-STD-188 * RS-232 * Certain ITU-T standards in the V series (notably V.24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Buses
Serial may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media The presentation of works in sequential segments * Serial (literature), serialised literature in print * Serial (publishing), periodical publications and newspapers * Serial (radio and television), series of radio and television programs that rely on a continuing plot * Serial film, a series of short subjects, with a continuing story, originally shown in theaters, in conjunction with feature films, particularly in the 1930s and 1940s * Indian serial, a type of Indian television program Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Serial'' (1980 film), based on McFadden's novel, starring Martin Mull and Tuesday Weld * ''Serial'' (podcast), a podcast spinoff of the radio series ''This American Life'' * ''The Serial: A Year in the Life of Marin County'', a 1977 novel by Cyra McFadden Computing and technology * SerDes, a Serializer/Deserializer (pronounced sir-deez) * Serial ATA * Serial attached SCSI * Serial bus, e.g., **IÂ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


