|
EIA-485
RS-485, also known as TIA-485(-A) or EIA-485, is a standard defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in serial communications systems. Electrical signaling is balanced, and multipoint systems are supported. The standard is jointly published by the Telecommunications Industry Association and Electronic Industries Alliance (TIA/EIA). Digital communications networks implementing the standard can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear, multidrop bus. These characteristics make RS-485 useful in industrial control systems and similar applications. Overview RS-485 supports inexpensive local networks and multidrop communications links, using the same differential signaling over twisted pair as RS-422. It is generally accepted that RS-485 can be used with data rates up to 10 Mbit/s or, at lower speeds, distances up to . As a rule of thumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS-422
RS-422, also known as TIA/EIA-422, is a technical standard originated by the Electronic Industries Alliance that specifies electrical characteristics of a digital signaling circuit. It was meant to be the foundation of a suite of standards that would replace the older RS-232C standard with standards that offered much higher speed, better immunity from noise, and longer cable lengths. RS-422 systems can transmit data at rates as high as 10 Mbit/s, or may be sent on cables as long as at lower rates. It is closely related to RS-423, which uses the same signaling systems but on a different wiring arrangement. RS-422 specifies differential signaling, with every data line paired with a dedicated return line. It is the voltage difference between these two lines that define the mark and space, rather than, as in RS-232, the difference in voltage between a data line and a local ground. As the ground voltage can differ at either end of the cable, this required RS-232 to use signals wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multidrop Bus
A multidrop bus (MDB) is a computer bus in which all components are connected to the electrical circuit. A process of arbitration determines which device sends information at any point. The other devices listen for the data they are intended to receive. Multidrop buses have the advantage of simplicity and extensibility, but their differing electrical characteristics make them relatively unsuitable for high frequency or high bandwidth applications. In computing Since 2000, multidrop standards such as PCI and Parallel ATA are increasingly being replaced by point-to-point systems such as PCI Express and SATA SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host adapter, host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) .... Modern SDRAM chips exemplify the problem of electrical impedance discontinuity. Fully Buffered DIMM is an alternative appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fail-safe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that in the event of a specific type of failure, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safety to a particular hazard, a system being "fail-safe" does not mean that failure is impossible or improbable, but rather that the system's design prevents or mitigates unsafe consequences of the system's failure. That is, if and when a "fail-safe" system fails, it remains at least as safe as it was before the failure. Since many types of failure are possible, failure mode and effects analysis is used to examine failure situations and recommend safety design and procedures. Some systems can never be made fail-safe, as continuous availability is needed. Redundancy, fault tolerance, or contingency plans are used for these situations (e.g. multiple independently controlled and fuel-fed engines). Examples Mechanical or physical Examples i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multidrop Bus
A multidrop bus (MDB) is a computer bus in which all components are connected to the electrical circuit. A process of arbitration determines which device sends information at any point. The other devices listen for the data they are intended to receive. Multidrop buses have the advantage of simplicity and extensibility, but their differing electrical characteristics make them relatively unsuitable for high frequency or high bandwidth applications. In computing Since 2000, multidrop standards such as PCI and Parallel ATA are increasingly being replaced by point-to-point systems such as PCI Express and SATA SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host adapter, host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) .... Modern SDRAM chips exemplify the problem of electrical impedance discontinuity. Fully Buffered DIMM is an alternative appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanced Line
In telecommunications and professional audio, a balanced line or balanced signal pair is a circuit consisting of two conductors of the same type, both of which have equal impedances along their lengths and equal impedances to ground and to other circuits. The chief advantage of the balanced line format is good rejection of common-mode noise and interference when fed to a differential device such as a transformer or differential amplifier.G. Ballou, ''Handbook for Sound Engineers'', Fifth Edition, Taylor & Francis, 2015, p. 1267–1268. As prevalent in sound recording and reproduction, balanced lines are referred to as balanced audio. Common forms of balanced line are twin-lead, used for radio frequency signals and twisted pair, used for lower frequencies. They are to be contrasted to unbalanced lines, such as coaxial cable, which is designed to have its return conductor connected to ground, or circuits whose return conductor actually is ground (see earth-return telegraph). Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-state Logic
In digital electronics, a tri-state or three-state buffer is a type of digital buffer that has three stable states: a high output state, a low output state, and a high-impedance state. In the high-impedance state, the output of the buffer is disconnected from the output bus, allowing other devices to drive the bus without interference from the tri-state buffer. This can be useful in situations where multiple devices are connected to the same bus and need to take turns accessing it. Tri-state buffers are commonly used in bus-based systems, where multiple devices are connected to the same bus and need to share it. For example, in a computer system, multiple devices such as the CPU, memory, and peripherals may be connected to the same data bus. To ensure that only one device can transmit data on the bus at a time, each device is equipped with a tri-state buffer. When a device wants to transmit data, it activates its tri-state buffer, which connects its output to the bus and allows it t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Bus Topology
A bus network is a network topology in which nodes are directly connected to a common half-duplex link called a bus. A host A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it. Host may also refer to: Places * Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County People *Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman * Michel Host ... on a bus network is called a ''station''. In a bus network, every station will receive all network traffic, and the traffic generated by each station has equal transmission priority. A bus network forms a single network segment and collision domain. In order for nodes to share the bus, they use a medium access control technology such as carrier-sense multiple access (CSMA) or a bus master. References {{Network topologies Network architecture Network topology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Network
A star network is an implementation of a spoke–hub distribution paradigm in computer networks. In a star network, every host is connected to a central hub. In its simplest form, one central hub acts as a conduit to transmit messages. The star network is one of the most common computer network topologies. The hub and hosts, and the transmission lines between them, form a graph with the topology of a star. Data on a star network passes through the hub before continuing to its destination. The hub manages and controls all functions of the network. It also acts as a repeater for the data flow. The star topology reduces the impact of a transmission line failure by independently connecting each host to the hub. Each host may thus communicate with all others by transmitting to, and receiving from, the hub. The failure of a transmission line linking any host to the hub will result in the isolation of that host from all others, but the rest of the network will be unaffect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Network
A ring network is a network topology in which each node connects to exactly two other nodes, forming a single continuous pathway for signals through each node – a ring. Data travels from node to node, with each node along the way handling every packet. Rings can be unidirectional, with all traffic travelling either clockwise or anticlockwise around the ring, or bidirectional (as in SONET/SDH). Because a unidirectional ring topology provides only one pathway between any two nodes, unidirectional ring networks may be disrupted by the failure of a single link. A node failure or cable break might isolate every node attached to the ring. In response, some ring networks add a "counter-rotating ring" (C-Ring) to form a redundant topology: in the event of a break, data are wrapped back onto the complementary ring before reaching the end of the cable, maintaining a path to every node along the resulting C-Ring. Such "dual ring" networks include the ITU-T's PSTN telephony systems network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Termination Resistor
In electronics, electrical termination is the practice of ending a transmission line with a device that matches the characteristic impedance of the line. Termination prevents signals from reflecting off the end of the transmission line. Reflections at the ends of unterminated transmission lines cause distortion which can produce ambiguous digital signal levels and mis-operation of digital systems. Reflections in analog signal systems cause such effects as video ghosting, or power loss in radio transmitter transmission lines. Transmission lines Signal termination often requires the installation of a terminator at the beginning and end of a wire or cable to prevent an RF signal from being reflected back from each end, causing interference, or power loss. The terminator is usually placed at the end of a transmission line or daisy chain bus (such as in SCSI), and is designed to match the AC impedance of the cable and hence minimize signal reflections, and power losses. Less co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
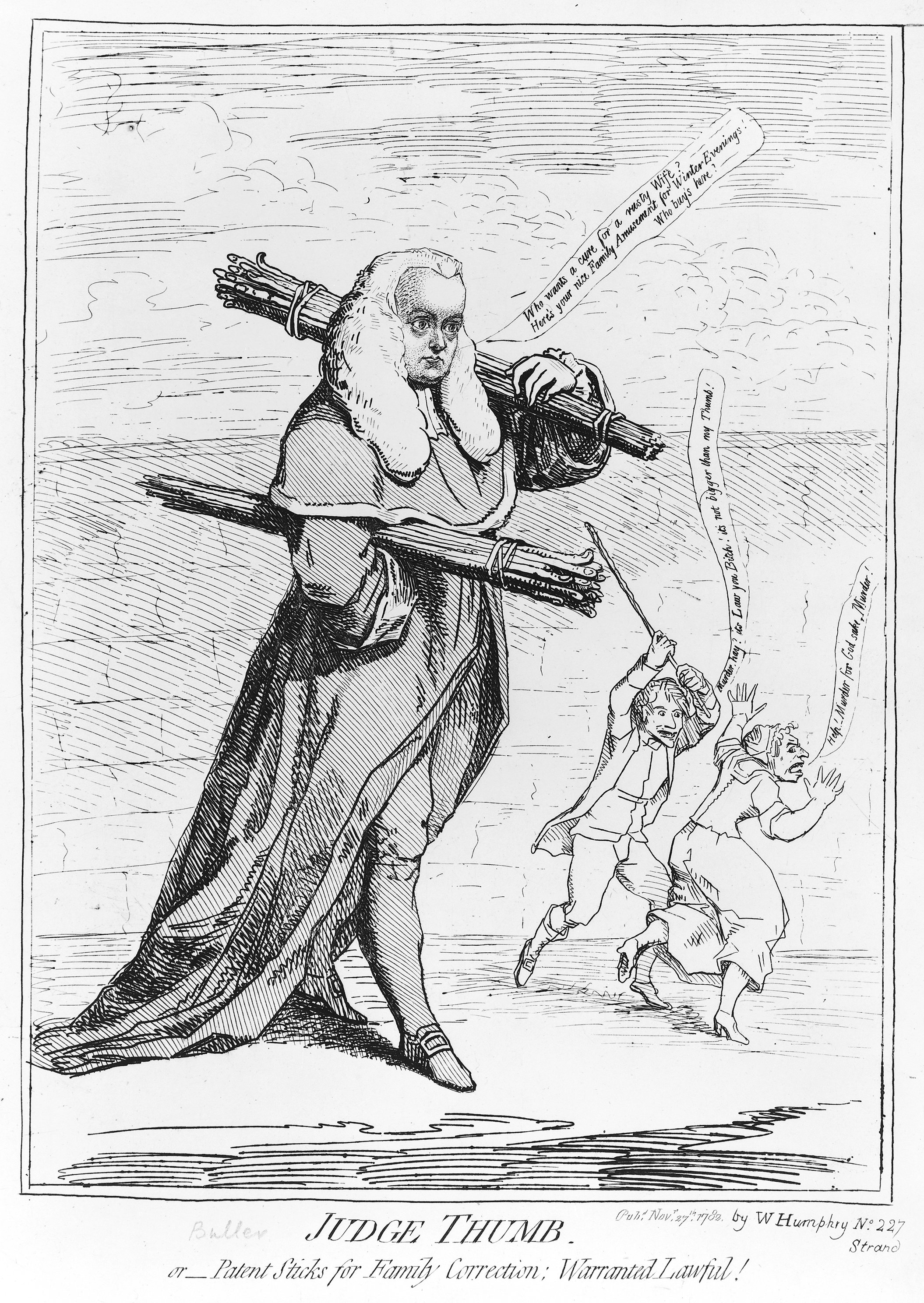
Rule Of Thumb
In English, the phrase ''rule of thumb'' refers to an approximate method for doing something, based on practical experience rather than theory. This usage of the phrase can be traced back to the 17th century and has been associated with various trades where quantities were measured by comparison to the width or length of a thumb. A modern folk etymology holds that the phrase is derived from the maximum width of a stick allowed for wife-beating under English common law, but no such law ever existed. This belief may have originated in a rumored statement by 18th-century judge Sir Francis Buller that a man may beat his wife with a stick no wider than his thumb. The rumor produced numerous jokes and satirical cartoons at Buller's expense, but there is no record that he made such a statement. English jurist Sir William Blackstone wrote in his '' Commentaries on the Laws of England'' of an "old law" that once allowed "moderate" beatings by husbands, but he did not mention thumbs or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |