|
Dębowiec, Podkarpackie Voivodeship
Dębowiec is a village in Jasło County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Dębowiec. It lies approximately south of Jasło and south-west of the regional capital Rzeszów. The village has an approximate population of 2,000. Debowiec has a long and rich history. For centuries it was a town, located in southeastern corner of the historic province of Lesser Poland. Until the Partitions of Poland, Debowiec belonged to Biecz County of Krakow Voivodeship. In the early Middle Ages, Debowiec was a gord, located in sparsely inhabited areas of Carpathian foothills. In the 11th century, Benedictine monks from Tyniec encouraged settlers to come to this corner of Lesser Poland. Debowiec was a village, destroyed in 1241, during the Mongol invasion of Poland. Asiatic hordes returned in 1259–1260 and 1287–1288, bringing further destruction. On August 15, 1349, King Kazimierz Wielki granted Magdebu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Mongol Invasion Of Poland
The Mongol Invasion of Poland from late 1240 to 1241 culminated in the Battle of Legnica, where the Mongols defeated an alliance which included forces from fragmented Poland and their allies, led by Henry II the Pious, the Duke of Silesia. The first invasion's intention was to secure the flank of the main Mongolian army attacking the Kingdom of Hungary. The Mongols neutralized any potential help to King Béla IV being provided by the Poles or any military orders. Background The Mongols invaded Europe with three armies. One of the three armies was tasked with distracting Poland, before joining the main Mongol force invading Hungary. The Mongol general in charge, Subutai, did not want the Polish forces to be able to threaten his flank during the primary invasion of Hungary. Thus, the Mongol goal was to use a small detachment to prevent the Poles from assisting Hungary until the Hungarians were defeated. That army, under Baidar, Kadan and Orda Khan, began scouting operations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marina Mniszech
Marina Mniszech, ( pl, Maryna Mniszech; russian: Марина Мнишек, Marina Mnishek, ) also known in Russian lore as Marinka the Witch ( 1588 – 24 December 1614) was a Polish noblewoman Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many e ... who became the Tsaritsa of Tsardom of Russia , Russia during the Time of Troubles. A devout Catholic, she hoped to convert Russia's population to Catholicism. Life Marina Mniszech family, Mniszech was a daughter of Jadwiga Tarło family, Tarło and Poland, Polish Voivode-Governor of Sandomierz Jerzy Mniszech, who was one of the organizers of the Polish–Muscovite War (1605–18), Dimitriads, which were instigated by the appearance of a man who claimed to be Ivan the Terrible's son. Marina Mniszech's marriage to False Dmitriy I provided a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Dmitriy I
False Dmitry I ( rus, Лжедмитрий I, Lzhedmitriy I) (or Pseudo-Demetrius I) reigned as the Tsar of Russia from 10 June 1605 until his death on 17 May 1606 under the name of Dmitriy Ivanovich ( rus, Дмитрий Иванович). According to historian Chester S.L. Dunning, Dmitry was "the only Tsar ever raised to the throne by means of a military campaign and popular uprisings". He was the first, and most successful, of three "pretenders" (russian: самозванцы (sing.: самозванец), samozvanets) who claimed during the Time of Troubles to be the youngest son of Ivan the Terrible, tsarevich Dmitry Ivanovich, who supposedly escaped a 1591 assassination attempt when he was eight years old. It is generally believed that the real Dmitry of Uglich died in Uglich in 1591. False Dmitry claimed that his mother, Maria Nagaya, anticipated the assassination attempt ordered by Boris Godunov and helped him escape to a monastery in the Tsardom of Russia, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerzy Mniszech
Jerzy Mniszech (c. 1548 – 1613) was a Poles, Polish Szlachta, nobleman and diplomat in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Member of the Mniszchowie, House of Mniszech. Krajczy koronny in 1574, castellan of Radom in 1583, voivode of Sandomierz Voivodship in 1590, żupnik ruski, starost of Lwów in 1593, starost of Samborzec, Sambor, Sokal, Sanok, Rohatyn. Biography Father of Marina Mniszech (c. 1588—1614). Dealt with providing courtisans for the courts of some Commonwealth magnates. He is known for meddling in the Tsardom of Russia, Muscovy Times of Troubles, as he wed his daughter Marina to the False Dmitri I and later convinced her to marry the False Dmitri II. He had several other children. His daughter Urszula Mniszech, born in 1603, married prince Konstanty Wiśniowiecki, voivode of Russia (1564–1641). Anna Mniszech married Piotr Szyszkowski, castellan of Wojno. Eufrozyna Mniszech married Hermolaus Jordan. Mikołaj Mniszech (1587–1613) became starost of Łukó ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starosta
The starosta or starost (Cyrillic: ''старост/а'', Latin: ''capitaneus'', german: link=no, Starost, Hauptmann) is a term of Slavic origin denoting a community elder whose role was to administer the assets of a clan or family estates. The Slavic root of starost translates as "senior". Since the Middle Ages, it has meant an official in a leadership position in a range of civic and social contexts throughout Central and Eastern Europe. In terms of a municipality, a ''starosta'' was historically a senior royal administrative official, equivalent to the County Sheriff or the outdated Seneschal, and analogous to a gubernator. In Poland, a ''starosta'' would administer crown territory or a delineated district called a '' starostwo''. In the early Middle Ages, the ''starosta'' could head a settled urban or rural community or other communities, such as a church starosta, or an ''artel'' starosta, etc. The starosta also functioned as the master of ceremonies. Poland Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Golden Age
The Polish Golden Age was the Renaissance period in Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, roughly corresponding to the period of rule of the King Sigismund I the Old and his son, Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellonian Dynasty monarchs, until his death in 1572. Some historians reckon the Polish Golden Age to have continued to the mid-17th century, when the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was ravaged by the Khmelnytsky Uprising (1648–57) and by the Swedish and Russian invasion. During its Golden Age, the Commonwealth became one of the largest kingdoms of Europe, stretching from modern Estonia in the north to Moldavia in the east and Bohemia in the west. In the 16th century the Commonwealth grew to almost 1 million km2, with a population of 11 million. It prospered from its enormous grain, wood, salt, and cloth exports to Western Europe via the Baltic Sea ports of Gdańsk, Elbląg, Riga, Memel, and Königsberg. The Commonwealth's major cities included Poznań, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia is traditionally divided into two sections, Muntenia (Greater Wallachia) and Oltenia (Lesser Wallachia). Dobruja could sometimes be considered a third section due to its proximity and Dobruja#Wallachian rule, brief rule over it. Wallachia as a whole is sometimes referred to as Muntenia through identification with the larger of the two traditional sections. Wallachia was founded as a principality in the early 14th century by Basarab I of Wallachia, Basarab I after a rebellion against Charles I of Hungary, although the first mention of the territory of Wallachia west of the river Olt River, Olt dates to a charter given to the voivode Seneslau in 1246 by Béla IV of Hungary. In 1417, Wallachia was fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
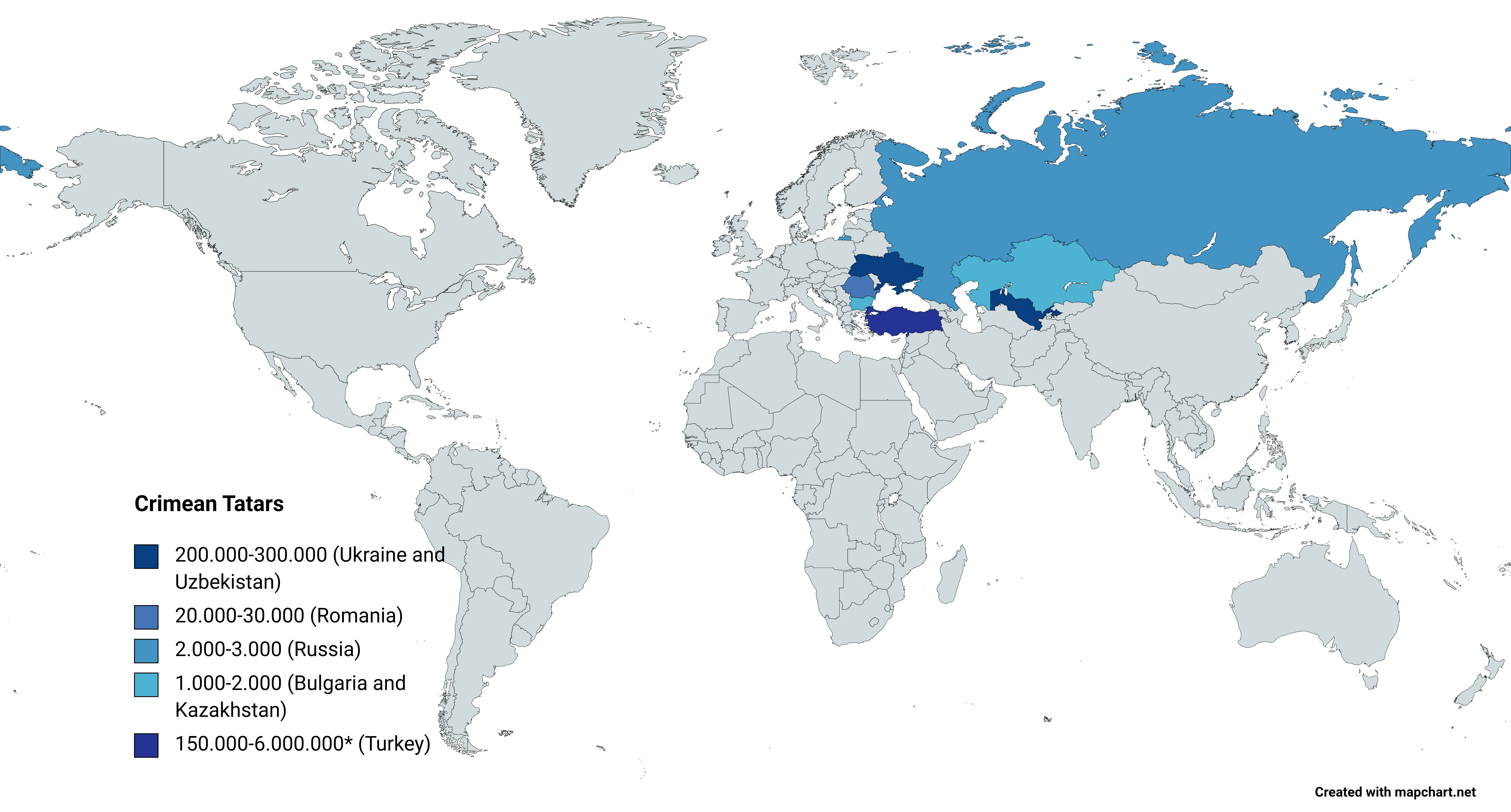
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Varna
The Battle of Varna took place on 10 November 1444 near Varna in eastern Bulgaria. The Ottoman Army under Sultan Murad II (who did not actually rule the sultanate at the time) defeated the Hungarian–Polish and Wallachian armies commanded by Władysław III of Poland (also King of Hungary), John Hunyadi (acting as commander of the combined Christian forces) and Mircea II of Wallachia. It was the final battle of the Crusade of Varna. Background The Hungarian Kingdom fell into crisis after the death of King Sigismund in 1437. His son-in-law and successor, King Albert, ruled for only two years and died in 1439, leaving his widow Elizabeth with an unborn child, Ladislaus the Posthumous. The Hungarian noblemen then called the young King Władysław III of Poland to the throne of Hungary, expecting his aid in defense against the Ottomans. After his Hungarian coronation, he never went back to his homeland again, assuming rule of the Hungarian Kingdom next to the influential noblem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcin Of Wrocimowice
Marcin of Wrocimowice ( pl, Marcin z Wrocimowic, ; died 1442) was a Polish knight and diplomat from the Półkozic clan. He served as Starosta (prefect) of Łowicz and as Standard-Bearer of the Territory of Kraków. In the latter capacity, he carried the banner of the Territory of Kraków – which was, at the same time, the Banner of the Kingdom of Poland – under which a unit consisting of Poland's elite knights, including such chivalrous celebrities as Zawisza the Black, went to the Battle of Grunwald (Tannenberg) on 15 July 1410. According to Jan Długosz, during the course of the battle, the national banner slipped out of Marcin's hand and fell on the ground, but it was quickly picked up and saved from destruction by Polish army's most valiant knights, which gave the Poles even more motivation to strive for victory over the Teutonic Knights. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |