|
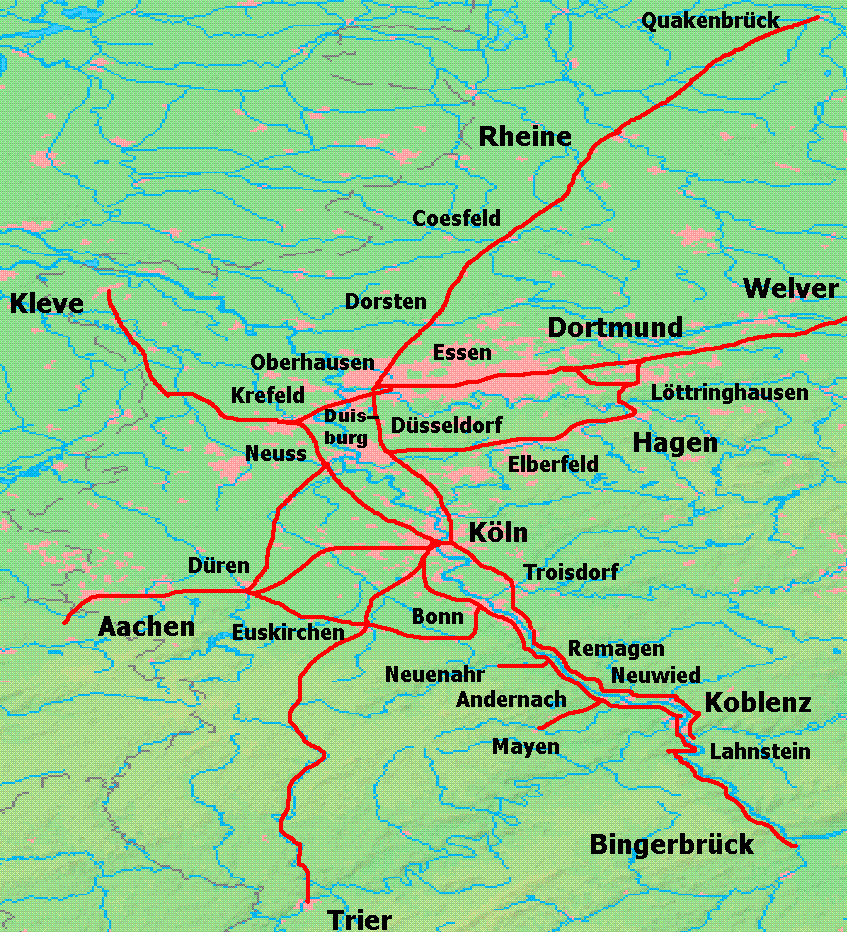
Düren–Neuss Railway
The Düren–Neuss railway is a line in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The non-electrified main line originally ran from Düren to Neuss, but the Düren–Bedburg section has been closed and dismantled. History The Neuss–Duren section was opened on 1 September 1869 by the Rhenish Railway Company (''Rheinische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', RhE), which was nationalised in 1880. It formed the first cross connection between the two main lines to Aachen from Düsseldorf via Mönchengladbach and from Cologne, as the (Mönchengladbach –) Hochneukirch – Jülich – Stolberg (– Aachen) branch line was opened four years later and the current Mönchengladbach–Cologne main line was opened between 1889 and 1899. The later emergence of the now more important and electrified Mönchengladbach–Cologne line is also the reason for the location of Grevenbroich station, which was initially built on the north-south running Neuss–Düren line. This meant that east-west run ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a States of Germany, state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhabitants, it is the List of German states by population, most populous state of Germany. Apart from the city-states, it is also the List of German states by population density, most densely populated state in Germany. Covering an area of , it is the List of German states by area, fourth-largest German state by size. North Rhine-Westphalia features 30 of the 81 German municipalities with over 100,000 inhabitants, including Cologne (over 1 million), the state capital Düsseldorf, Dortmund and Essen (all about 600,000 inhabitants) and other cities predominantly located in the Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan area, the largest urban area in Germany and the fourth-largest on the European continent. The location of the Rhine-Ruhr at the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsdorf (Rheinland)
Elsdorf is a town in the Rhein-Erft-Kreis The Rhein-Erft-Kreis ( ksh, Rhing-Ärff-Kries) is a district in the west of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Neuss, district-free Cologne, Rhein-Sieg, Euskirchen, Düren. History The district in its current borders was ..., in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is situated approximately 5 km south-west of Bergheim and 30 km west of Cologne. Notable people * Eugen Langen (1833–1895), entrepreneur, engineer and inventor, co-founder of the Elsdorf sugar factory Pfeifer & Langen * Werner Marx (1746–1806), General Vicar of the Archbishop of Cologne References Rhein-Erft-Kreis {{RheinErftKreis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kevelaer
Kevelaer ( Low Rhenish: ''Käwela'') is a town in the district of Kleve, in North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. It is the largest Catholic pilgrimage location within north-western Europe. More than 1 million pilgrims, mostly from Germany and the Netherlands, visit Kevelaer every year to honour the Virgin Mary. The population in 2019 was 28,021. History Kevelaer is a center of veneration and pilgrimage to Our Lady, Comforter of the Afflicted (also known as Our Lady of Consolation. According to tradition, a merchant named Hendrik Busman, in the days before Christmas, 1641, three times heard a voice saying "Here thou shalt build me a chapel". He began to set money aside but feared his wife, Mechel, wouldn't approve. She, however, had a vision, around Pentecost, in which she saw a little chapel containing a print of Our Lady of Consolation, all bathed in light. The story was confirmed by two passing soldiers, who saw the house light up at night. Days before, two soldiers had trie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rommerskirchen
Rommerskirchen is the southernmost municipality in the Rhein-Kreis Neuss, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Notable places Rommerskirchen possesses rich historical inheritances, including numerous remains of the Roman Villae Rusticae, and those from several Frankish settlements. The town centre still contains several medieval Roman and Gothic churches and a castle. There are many buildings from even earlier modern times, as well as those from the time of the Napoleonic occupation. Many of these sites are currently closed while undergoing restoration. Infrastructure Rommerskirchen is the location of a large 380kV- substation of the RWE. The first 380kV-line in Germany went into service on October 5, 1957. It began between the transformer stations of Rommerskirchen and Ludwigsburg-Hoheneck. The strategic railway embankment begins at Rommerskirchen station, and Oekoven maintains a public railway facility. Rommerskirchen generally mean Roman Catholic Church. Famous people * Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mönchengladbach–Stolberg Railway
Euregiobahn in Eschweiler-Nothberg The Mönchengladbach–Stolberg railway was opened by the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company (german: Bergisch-Märkische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft, BME) and built in sections between 1870 and 1875. The only scheduled traffic on it now are passenger services operated as part of the Euregiobahn concept (which is aimed at improving regional rail passenger services in Aachen and southern Limburg) and freight operation to railway sidings on the southern part of the line, known as the Eschweiler Valley Railway (''Eschweiler Talbahn'') or Inde Valley Railway (''Indetalbahn''), as well as regional trains operated between Mönchengladbach Hauptbahnhof and Cologne on the short section of the line between Rheydt- Odenkirchen and Hochneukirch, which is now considered to be part of the Cologne–Mönchengladbach line. Occasional freight trains run between Mönchengladbach Hauptbahnhof and Rheydt-Geneicken. The northern sections of the line from Hochneukirch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenish Railway Company
The Rhenish Railway Company (German language, German: ''Rheinische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', RhE) was along with the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (CME) and the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company (BME) one of the railway companies that in the mid-19th century built the first railways in the Ruhr and large parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia. Foundation The industrialists of the Rhineland and the Bergisches Land, then part of Prussia, sought to avoid paying the high tolls for using the Rhine imposed by the Netherlands and very early in its development, saw the possibility of the new means of transport, the railway. As early as the 1830s committees were established the cities of the Rhineland to promote proposals for building railways. Some of the members of the Cologne committee under David Hansemann (1790–1864)—a merchant and banker from Aachen—and the Aachen Committee favoured a railway line through Belgium to the seaport of Antwerp via Liege. Belgium, which had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Düren Station
Düren station is located to the north of the centre of Düren and is the largest station in the city and the district of Düren. It is located at the intersection of the Cologne–Aachen high-speed line with the lines to Linnich, Heimbach and Euskirchen. Until 1992 it was also connected to the Erft Railway. The train is served by Regional-Express, Regionalbahn and S-Bahn trains. It is the terminus of line S19 Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn. The station was opened on 1 September 1841 by the Rhenish Railway Company on its original line from Cologne to Belgium. History Düren station was established on 1 September 1841 with the opening of the Aachen–Düren–Cologne line. The station became more and more important during the period of industrialisation. This resulted in the opening of the following lines: Due to its ever-improving accessibility Düren was served by increasing numbers of express trains on the various lines. Thus, there were express trains via Euskirchen to Bonn and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Börde Railway
A ''börde'' (plural: ''börden'') is a region of highly fertile lowland in North Germany, a "fertile plain". These landscapes often cover great areas and are particularly important for arable farming on account of their rich soils. These regions coincide closely with areas of flat, fertile loess soil and few trees. ''Börden'' are found in Germany, especially in the North German Old Drift region on the northern edges of Central Uplands. The resulting black earth soils are some of the best soils in Germany. Etymology These landscapes are restricted to, or concentrated on, those regions where the Eastphalian and Westphalian dialects are spoken. There are two opposing explanations for the name. According to one, the term is connected with the Old High German word ''giburida'' ("judicial district") or the plattdeutsch word ''bören'' ("to bear"). The ''börde'' in this context is seen as a district in which the inhabitants had to "bear" public charges, i.e. it was effectively a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne–Aachen High-speed Railway
The Cologne–Aachen high-speed line is the German part of the Trans-European transport networks project ''high-speed line Paris–Brussels–Cologne''. It is not a newly built railway line, but a project to upgrade the existing railway line which was opened in 1841 by the Rhenish Railway Company. When it was continued into Belgium in 1843, it became the world's first international railway line. The line inside Germany has a length of about . The first from Cologne to Düren have been rebuilt. Since 2002 the line allows for speeds up to . Separate tracks have been built parallel to the high-speed tracks for local S-Bahn traffic. The remaining line from Düren to Aachen allows speeds up to with some slower sections. Upgrades of Düren–Aachen are planned for the near future. In Belgium, the high-speed line is continued as HSL 3. Regional-Express services on the line are RE 1 (''NRW-Express'') and RE 9 (''Rhein-Sieg-Express'') with push-pull trains with six double-decker car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)