|
Dynamic Network Analysis
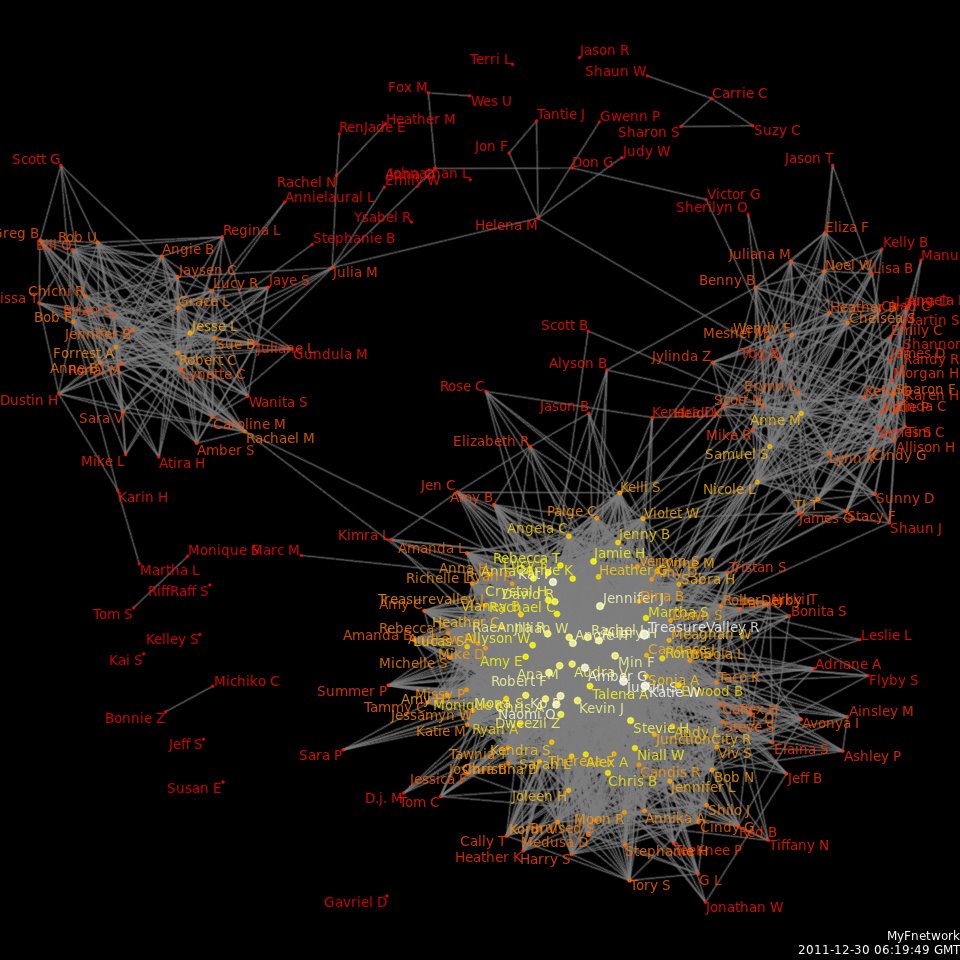
Dynamic network analysis (DNA) is an emergent scientific field that brings together traditional social network analysis (SNA), link analysis (LA), social simulation and multi-agent systems (MAS) within network science and network theory. Dynamic networks are a function of time (modeled as a subset of the real numbers) to a set of graphs; for each time point there is a graph. This is akin to the definition of dynamical systems, in which the function is from time to an ambient space, where instead of ambient space time is translated to relationships between pairs of vertices. Overview There are two aspects of this field. The first is the statistical analysis of DNA data. The second is the utilization of simulation to address issues of network dynamics. DNA networks vary from traditional social networks in that they are larger, dynamic, multi-mode, multi-plex networks, and may contain varying levels of uncertainty. The main difference of DNA to SNA is that DNA takes interactions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Network Analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of ''nodes'' (individual actors, people, or things within the network) and the ''ties'', ''edges'', or ''links'' (relationships or interactions) that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, memes spread, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, social networks, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through ''sociograms'' in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attributes of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static
Static may refer to: Places *Static Nunatak, a nunatak in Antarctica United States * Static, Kentucky and Tennessee *Static Peak, a mountain in Wyoming **Static Peak Divide, a mountain pass near the peak Science and technology Physics *Static electricity, a net charge of an object **Triboelectric effect, due to frictional contact between different materials *Static spacetime, a spacetime having a global, non-vanishing, timelike Killing vector field which is irrotational *Statics, a branch of physics concerned with physical systems in equilibrium **Fluid statics, the branch of fluid mechanics that studies fluids at rest Engineering *Static pressure, in aircraft instrumentation and fluid dynamics ** Static port, a proprietary sensor used on aircraft to measure static pressure *White noise or static noise, a random signal with a flat power spectral density **Noise (radio), in radio reception **Noise (video), the random black-and-white image produced by televisions attempting to disp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Statistics
Social statistics is the use of statistical measurement systems to study human behavior in a social environment. This can be accomplished through polling a group of people, evaluating a subset of data obtained about a group of people, or by observation and statistical analysis of a set of data that relates to people and their behaviors. Statistics in the social sciences History Adolph Quetelet was a proponent of social physics. In his book ''Physique sociale'' he presents distributions of human heights, age of marriage, time of birth and death, time series of human marriages, births and deaths, a survival density for humans and curve describing fecundity as a function of age. He also developed the Quetelet Index. Francis Ysidro Edgeworth published "On Methods of Ascertaining Variations in the Rate of Births, Deaths, and Marriages" in 1885 which uses squares of differences for studying fluctuations and George Udny Yule published "On the Correlation of total Pauperism with Prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Network Analysis
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices like smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links bill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huan Liu
Huan Liu is a Chinese-born computer scientist. Education and teaching career Liu studied computer science and engineering at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and specialized in computer science while completing his master's and doctoral degrees at the University of Southern California. Liu began his teaching career in the 1990s at the National University of Singapore, and joined the Arizona State University faculty in 2000. Honors Liu was named a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2012 for his contributions to feature selection in data mining and knowledge discovery. He was elected as an ACM Fellow in 2018 for "contributions in feature selection for data mining and knowledge discovery and in social computing". Publications Books * Liu H, Motoda H. ''Feature selection for knowledge discovery and data mining''. Springer Science & Business Media; 1998 *Liu H, Motoda H, editors. ''Computational methods of feature selection''. CRC Press; 2007 *Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mia Bloom
Mia M. Bloom is a Canadian academic, author, and Professor of Communication at Georgia State University. She was formerly an associate Professor of International Studies at the Pennsylvania State University in University Park and a fellow at the International Center for the Study of Terrorism at Penn State. Bloom received a PhD in political science from Columbia University, a Master's in Arab Studies from Georgetown University and a Bachelor's from McGill University in Russian, Islamic studies and Middle East Studies. Her studies specialize in ethnic conflict, rape in war, child soldiers, female terrorists, and terrorist communications. Bloom was a term member of the Council on Foreign Relations The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank A think tank, or policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, mi ... in 2003–2008. Bloom has also taught ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequential Dynamical System
Sequential dynamical systems (SDSs) are a class of graph dynamical systems. They are discrete dynamical systems which generalize many aspects of for example classical cellular automata, and they provide a framework for studying asynchronous processes over graphs. The analysis of SDSs uses techniques from combinatorics, abstract algebra, graph theory, dynamical systems and probability theory. Definition An SDS is constructed from the following components: * A finite ''graph'' ''Y'' with vertex set v 'Y''= . Depending on the context the graph can be directed or undirected. * A state ''xv'' for each vertex ''i'' of ''Y'' taken from a finite set ''K''. The ''system state'' is the ''n''-tuple ''x'' = (''x''1, ''x''2, ... , ''xn''), and ''x'' 'i''is the tuple consisting of the states associated to the vertices in the 1-neighborhood of ''i'' in ''Y'' (in some fixed order). * A ''vertex function'' ''fi'' for each vertex ''i''. The vertex function maps the state of vertex ''i'' at time '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Science
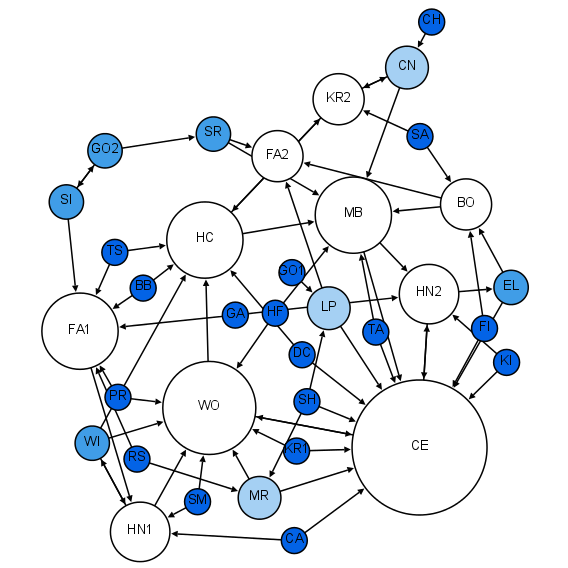
Network science is an academic field which studies complex networks such as telecommunication networks, computer networks, biological networks, cognitive and semantic networks, and social networks, considering distinct elements or actors represented by ''nodes'' (or ''vertices'') and the connections between the elements or actors as ''links'' (or ''edges''). The field draws on theories and methods including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, data mining and information visualization from computer science, inferential modeling from statistics, and social structure from sociology. The United States National Research Council defines network science as "the study of network representations of physical, biological, and social phenomena leading to predictive models of these phenomena." Background and history The study of networks has emerged in diverse disciplines as a means of analyzing complex relational data. The earliest known paper in this f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Dynamics
Network dynamics is a research field for the study of Network theory, networks whose status changes in time. The dynamics may refer to the structure of connections of the units of a network, to the collective internal state of the network, or both. The networked systems could be from the fields of biology, chemistry, physics, sociology, economics, computer science, etc. Networked systems are typically characterized as complex systems consisting of many units coupled by specific, potentially changing, interaction topologies. For a dynamical systems' approach to discrete network dynamics, see sequential dynamical system. See also References Networks {{combin-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathleen M
Kathleen may refer to: People * Kathleen (given name) * Kathleen (singer), Canadian pop singer Places * Kathleen, Alberta, Canada * Kathleen, Georgia, United States * Kathleen, Florida, United States * Kathleen High School (Lakeland, Florida), United States * Kathleen, Western Australia, Western Australia * Kathleen Island, Tasmania, Australia * Kathleen Lumley College, South Australia * Mary Kathleen, Queensland, former mining settlement in Australia Other * ''Kathleen'' (film), a 1941 American film directed by Harold S. Bucquet * ''The Countess Kathleen and Various Legends and Lyrics'' (1892), second poetry collection of William Butler Yeats * Kathleen Ferrier Award, competition for opera singers * Kathleen Mitchell Award, Australian literature prize for young authors * Plan Kathleen, plan for a German invasion of Northern Ireland sanctioned by the IRA Chief of Staff in 1940 * Tropical Storm Kathleen (other) * "Kathleen" (song), a song by Catfish and the Bottl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Network For Social Network Analysis
The International Network for Social Network Analysis (INSNA) is a professional academic association of researchers and practitioners of social network analysis. Members have interests in social networks as a new theoretical paradigm, in methodological developments, and in a variety of applications of different types of social networks approaches, social network software, and social networking. History INSNA was founded in 1977 by Barry Wellman, a sociologist. A key function of the organization was to provide a sense of identity for a set of researchers who were widely dispersed geographically and across scientific disciplines. Wellman served as "coordinator" of INSNA until 1988, when he passed the baton to Al Wolfe, an anthropologist at the University of South Florida. Wolfe in turn passed the leadership to Steve Borgatti, who served from 1993 to 1999. Borgatti incorporated INSNA as a legal entity, creating bylaws and establishing the positions of President, Vice-President and Tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Dynamical System
In mathematics, the concept of graph dynamical systems can be used to capture a wide range of processes taking place on graphs or networks. A major theme in the mathematical and computational analysis of GDSs is to relate their structural properties (e.g. the network connectivity) and the global dynamics that result. The work on GDSs considers finite graphs and finite state spaces. As such, the research typically involves techniques from, e.g., graph theory, combinatorics, algebra, and dynamical systems rather than differential geometry. In principle, one could define and study GDSs over an infinite graph (e.g. cellular automata or probabilistic cellular automata over \mathbb^k or interacting particle systems when some randomness is included), as well as GDSs with infinite state space (e.g. \mathbb as in coupled map lattices); see, for example, Wu. In the following, everything is implicitly assumed to be finite unless stated otherwise. Formal definition A graph dynamical system is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |