|
Dynamic Demand (electric Power)
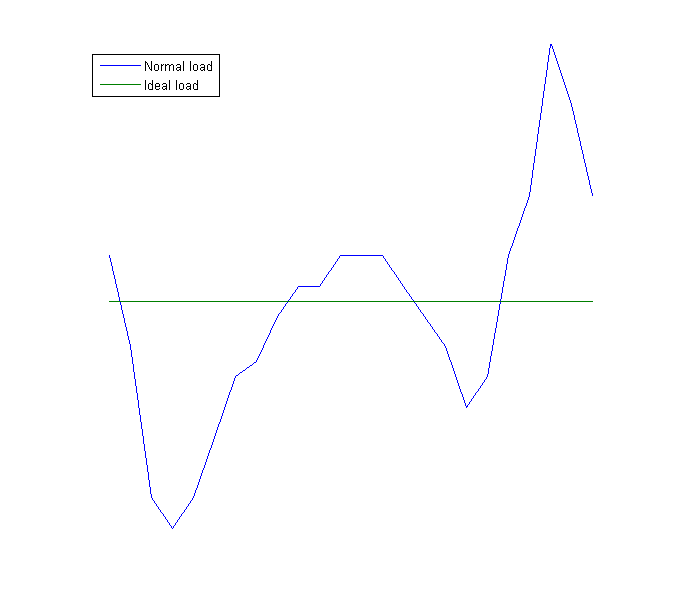
Dynamic Demand is the name of a semi-passive technology to support demand response by adjusting the load demand on an electrical power grid. It is also the name of an independent not-for-profit organization in the UK supported by a charitable grant from the Esmée Fairbairn Foundation, dedicated to promoting this technology. The concept is that by monitoring the frequency of the power grid, as well as their own controls, intermittent domestic and industrial loads switch themselves on/off at optimal moments to balance the overall grid load with generation, reducing critical power mismatches. As this switching would only advance or delay the appliance operating cycle by a few seconds, it would be unnoticeable to the end user. This is the foundation of dynamic demand control. In the United States, in 1982, a (now-lapsed) patent for this idea was issued to power systems engineer Fred Schweppe. Other patents have been issued based on this idea. Dynamic demand is similar to demand resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand Response
Demand response is a change in the power consumption of an electric utility customer to better match the demand for power with the supply. Until the 21st century decrease in the cost of pumped storage and batteries electric energy could not be easily stored, so utilities have traditionally matched demand and supply by throttling the production rate of their power plants, taking generating units on or off line, or importing power from other utilities. There are limits to what can be achieved on the supply side, because some generating units can take a long time to come up to full power, some units may be very expensive to operate, and demand can at times be greater than the capacity of all the available power plants put together. Demand response seeks to adjust the demand for power instead of adjusting the supply. Utilities may signal demand requests to their customers in a variety of ways, including simple off-peak metering, in which power is cheaper at certain times of the day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megawatt Hour
A kilowatt-hour ( unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common billing unit for electrical energy delivered to consumers by electric utilities. Definition The kilowatt-hour is a composite unit of energy equal to one kilowatt (kW) sustained for (multiplied by) one hour. Expressed in the standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI), the joule (symbol J), it is equal to 3,600 kilojoules or 3.6 MJ."Half-high dots or spaces are used to express a derived unit formed from two or more other units by multiplication.", Barry N. Taylor. (2001 ed.''The International System of Units.'' (Special publication 330). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. 20. Unit representations A widely used representation of the kilowatt-hour is "kWh", derived from its compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancillary Services (electric Power)
Ancillary services are the services necessary to support the transmission of electric power from generators to consumers given the obligations of control areas and transmission utilities within those control areas to maintain reliable operations of the interconnected transmission system. Ancillary services are specialty services and functions provided by actors within the electric grid that facilitate and support the continuous flow of electricity, so that the demand for electrical energy is met in real time. The term ancillary services is used to refer to a variety of operations beyond generation and transmission that are required to maintain grid stability and security. These services generally include active power control or frequency control and reactive power control or voltage control, on various timescales. Traditionally, ancillary services have been provided by large production units such as generators. With the integration of more intermittent generation and the developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peaking Power Plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand. Although historically peaking power plants were frequently used in conjunction with coal baseload plants, peaking plants are now used less commonly. Combined cycle gas turbine plants have two or more cycles, the first of which is very similar to a peaking plant, with the second running on the waste heat of the first. That type of plant is often capable of rapidly starting up, albeit at reduced efficiency, and then over some hours transitioning to a more efficient baseload generation mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the nominal frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in a wide area synchronous grid transmitted from a power station to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains electricity by country. During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late-19th and early-20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controller (control Theory)
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects which are also studied are controllability and observability. Control theory is used in control syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Outlet
AC power plugs and sockets connect electric equipment to the alternating current (AC) mains electricity power supply in buildings and at other sites. Electrical plugs and sockets differ from one another in voltage and current rating, shape, size, and connector type. Different standard systems of plugs and sockets are used around the world. Plugs and sockets for portable appliances became available in the 1880s, to replace connections to light sockets with wall-mounted outlets. A proliferation of types developed for both convenience and protection from electrical injury. Today there are about 20 types in common use around the world, and many obsolete socket types are found in older buildings. Coordination of technical standards has allowed some types of plug to be used across large regions to facilitate trade in electrical appliances, and for the convenience of travellers and consumers of imported electrical goods. Some multi-standard sockets allow use of several types of plug; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigeration
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, https://www.ashrae.org/technical-resources/free-resources/ashrae-terminology Refrigeration can be considered an artificial, or human-made, cooling method. Refrigeration refers to the process by which energy, in the form of heat, is removed from a low-temperature medium and transferred to a high-temperature medium. This work of energy transfer is traditionally driven by mechanical means, but can also be driven by heat, magnetism, electricity, laser, or other means. Refrigeration has many applications, including household refrigerators, industrial freezers, cryogenics, and air conditioning. Heat pumps may use the heat output of the refrigeration process, and also may be designed to be reversible, but are otherwise similar to air conditionin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Pump
A heat pump is a device that can heat a building (or part of a building) by transferring thermal energy from the outside using a refrigeration cycle. Many heat pumps can also operate in the opposite direction, cooling the building by removing heat from the enclosed space and rejecting it outside. Units that only provide cooling are called air conditioners. When in heating mode, a refrigerant at outside temperature is being compressed. As a result, the refrigerant becomes hot. This thermal energy can be transferred to an indoor unit. After being moved outdoors again, the refrigerant is decompressed — evaporated. It has lost some of its thermal energy and returns colder than the environment. It can now take up the surrounding energy from the air or from the ground before the process repeats. Compressors, fans, and pumps run with electric energy. Common types are air-source heat pumps, ground-source heat pumps, water-source heat pumps and exhaust air heat pumps. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Heating
Water heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses. Domestically, water is traditionally heated in vessels known as ''water heaters'', ''kettles'', ''cauldrons'', ''pots'', or ''coppers''. These metal vessels that heat a batch of water do not produce a continual supply of heated water at a preset temperature. Rarely, hot water occurs naturally, usually from natural hot springs. The temperature varies with the consumption rate, becoming cooler as flow increases. Appliances that provide a continual supply of hot water are called ''water heaters'', ''hot water heaters'', '' hot water tanks'', ''boilers'', '' heat exchangers'', ''geysers'' (Southern Africa and the Arab world), or ''calorifiers''. These names depend on region, and whether they heat potable or non-potabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Conditioner
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling the humidity of internal air. Air conditioning can be achieved using a mechanical 'air conditioner' or alternatively a variety of other methods, including passive cooling or ventilative cooling. Air conditioning is a member of a family of systems and techniques that provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Heat pumps are similar in many ways to air conditioners, but use a reversing valve to allow them to both heat and also cool an enclosed space. Air conditioners, which typically use vapor-compression refrigeration, range in size from small units used within vehicles or single rooms to massive units that can cool large buildings. Air source heat pumps, which can be used for heating as well as cooling, are becoming incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
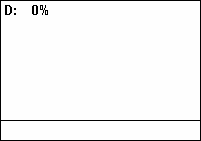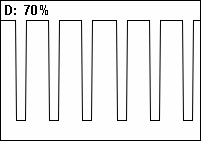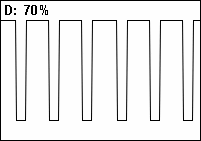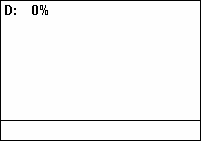
Duty Cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as: :D = \frac \times 100\% Equally, a duty cycle (ratio) may be expressed as: :D = \frac where D is the duty cycle, PW is the pulse width (pulse active time), and T is the total period of the signal. Thus, a 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time but off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period. Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply or the firing of action potentials by a living system such as a neuron. The duty factor for periodic signal expresses the same notion, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |