|
Dyar Site
The Dyar site ( 9GE5) is an archaeological site in Greene County, Georgia, in the north central Piedmont physiographical region. The site covers an area of 2.5 hectares. It was inhabited almost continuously from 1100 to 1600 by a local variation of the Mississippian culture known as the South Appalachian Mississippian culture. Although submerged under Lake Oconee, the site is still important as one of the first explorations of a large Mississippian culture mound. The Dyar site is thought to have been one of the principal towns of the paramount chiefdom of Ocute, perhaps Cofaqui. Site description The platform mound located at the site was described in 1975 as being in the shape of a truncated cone approximately high and with a base in diameter. On the eastern edge of the mound in the central area of the site was a plaza surrounded by domestic structures making up an oval shaped village of 2.13 hectares. Mound Platform mounds are built up in a series of stages that can span ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greensboro, Georgia
Greensboro is a town in and the county seat of Greene County, Georgia, United States. Its population was 3,648 as of the 2020 census. The city is located approximately halfway between Atlanta and Augusta on Interstate 20. History Greensboro was founded circa 1780; in 1787, it was designated seat of the newly formed Greene County. It was incorporated as a town in 1803 and as a city in 1855. The city was named for Major General Nathanael Greene, commander of the rebel American forces at the Battle of Guilford Court House on March 15, 1781. Geography Greensboro is located at the center of Greene County at (33.571528, -83.180921). U.S. Route 278 passes through the city center as Broad Street, leading east to Union Point and west to Madison. Georgia State Route 44 leads southwest from Greensboro to Eatonton. State Route 15 leads north to Athens and southeast to Sparta. The city limits extend southwest along SR 44 for so as to include Exit 130 on Interstate 20. I-20 leads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construction Waste
Construction waste or debris is any kind of debris from the construction process. Different government agencies have clear definitions. For example, the United States Environmental Protection Agency EPA defines construction and demolition materials as “debris generated during the construction, renovation and demolition of buildings, roads, and bridges.” Additionally, the EPA has categorized Construction and Demolition (C&D) waste into three categories: non-dangerous, hazardous, and semi-hazardous. Of total waste in the United States, 90% comes from the demolition of structures, while waste generated during construction accounts for less than 10%. Construction waste frequently includes materials that are hazardous if disposed of in landfills. Such items inculude fluorescent lights, batteries, and other electrical equipment. When waste is created, options of disposal include exportation to a landfill, incineration, direct site reuse through integration into construction or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
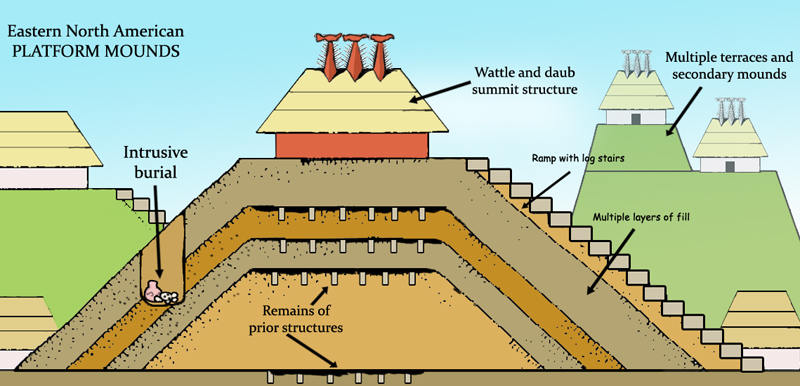
List Of Mississippian Sites
This is a list of Mississippian sites. The Mississippian culture was a mound-building Native American culture that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, inland-Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1500 CE, varying regionally. Its core area, along the Mississippi River and its major tributaries, stretched from sites such as Cahokia in modern Illinois, the largest of all the Mississippian sites, to Mound Bottom in Tennessee, to the Winterville site in the state of Mississippi. The typical form were earthwork platform mounds, with flat tops, often the sites for temples or elite residences. Other mounds were built in conical or ridge-top forms. The culture reached peoples in settlements across the continent: Temple mound complexes were constructed also in areas ranging from Aztalan in Wisconsin to Crystal River in Florida, and from Fort Ancient, now in Ohio, to Spiro in Oklahoma. Mississippian cultural influences extended as far north and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Georgia
, mottoeng = "To teach, to serve, and to inquire into the nature of things.""To serve" was later added to the motto without changing the seal; the Latin motto directly translates as "To teach and to inquire into the nature of things." , established = , endowment = $1.8 billion (2021)As of June 30, 2021. , type = Public flagship land-grant research university , parent = University System of Georgia , accreditation = SACS , academic_affiliation = , president = Jere W. Morehead , provost = S. Jack Hu , city = Athens , state=Georgia , country = United States , coordinates = , faculty = 3,119 , students = 40,118 (fall 2021) , undergrad = 30,166 (fall 2021) , postgrad = 9,952 (fall 2021) , free_label2 = Newspaper , free2 = '' The Red & Black'' , campus = Midsize city / College town , campus_size = (main campus) (total) , colors = , sports_nickname = Bulldogs , sporting_affiliations = NCAA Division I FBS – SEC , mascot = Uga X (live English Bulldo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia Power
Georgia Power is an electric utility headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. It was established as the Georgia Railway and Power Company and began operations in 1902 running streetcars in Atlanta as a successor to the Atlanta Consolidated Street Railway Company. Georgia Power is the largest of the four electric utilities that are owned and operated by Southern Company. Georgia Power is an investor-owned, tax-paying public utility that serves more than 2.4 million customers in all but four of Georgia's 159 counties. It employs approximately 9,000 workers throughout the state. The Georgia Power Building, its primary corporate office building, is located at 241 Ralph McGill Boulevard in downtown Atlanta. In 2006, the Savannah Electric & Power Company, a separate subsidiary of Southern Company, was merged into Georgia Power. History Originally the Georgia Railway and Power Company, it began in 1902 as a company running the streetcars in Atlanta and was the successor t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavation (archaeology)
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be conducted over a few weeks to several years. Excavation involves the recovery of several types of data from a site. This data includes artifacts (portable objects made or modified by humans), features (non-portable modifications to the site itself such as post molds, burials, and hearths), ecofacts (evidence of human activity through organic remains such as animal bones, pollen, or charcoal), and archaeological context (relationships among the other types of data).Kelly&Thomas (2011). ''Archaeology: down to earth'' (4th ed.). Belmont, Calif.: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. Before excavating, the presence or absence of archaeological remains can often be suggested by, non-intrusive remote sensing, such as ground-penetrating radar. Basic informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Phase
A bell is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be made by an internal "clapper" or "uvula", an external hammer, or—in small bells—by a small loose sphere enclosed within the body of the bell (jingle bell). Bells are usually cast from bell metal (a type of bronze) for its resonant properties, but can also be made from other hard materials. This depends on the function. Some small bells such as ornamental bells or cowbells can be made from cast or pressed metal, glass or ceramic, but large bells such as a church, clock and tower bells are normally cast from bell metal. Bells intended to be heard over a wide area can range from a single bell hung in a turret or bell-gable, to a musical ensemble such as an English ring of bells, a carillon or a Russian zvon which are tuned to a common scale and instal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Horse Phase
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |