|
Duolun Road
Duolun Road (; Shanghainese: ''Dulen Lu''), formerly Darroch Road (), is a historic street in Hongkou District, Shanghai, China. Location Laid in 1911, the road is 550 metres long. Both ends of the L-shaped road join to North Sichuan Road near Lu Xun Park and Hongkou Stadium. The road is today reconstructed as a pedestrian street. History Darroch (Duolun) Road was built by the Shanghai Municipal Council, the municipal authority of the Shanghai International Settlement. It was an "extra-settlement road" (), built outside the boundaries of the International Settlement, but over which the Settlement authorities had extraterritorial jurisdiction. It was named after John Darroch, a British missionary to China who had been received by the Guangxu Emperor of the Qing Dynasty. A primarily residential street, the golden age of the road was in the 1920s and 30s, when it attracted writers and other prominent residents, giving it a reputation as a vibrant centre of thought and literature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
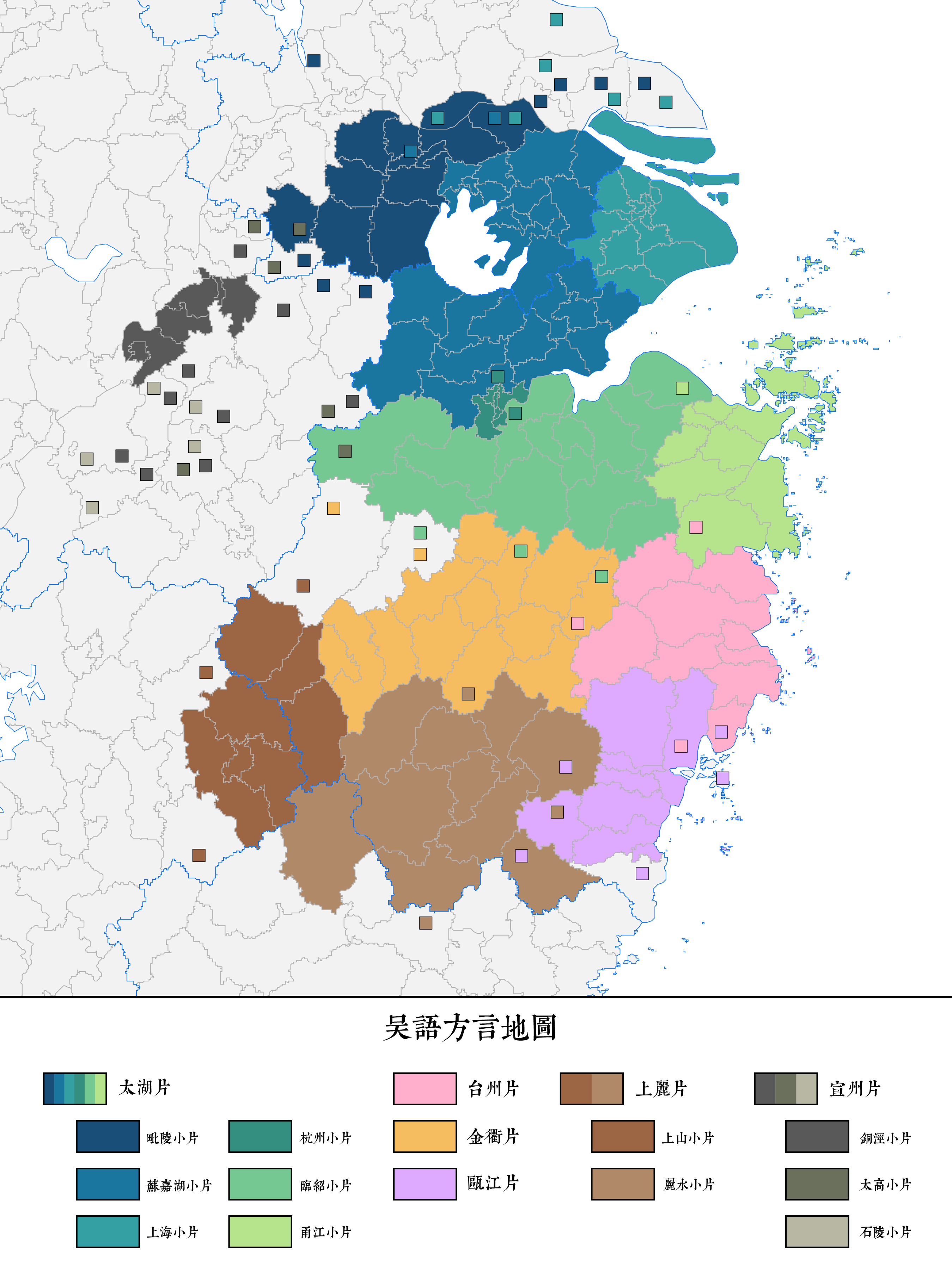
Shanghainese
The Shanghainese language, also known as the Shanghai dialect, or Hu language, is a variety of Wu Chinese spoken in the Districts of Shanghai, central districts of the Shanghai, City of Shanghai and its surrounding areas. It is classified as part of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Shanghainese, like the rest of the Wu language group, is mutually unintelligible with other varieties of Chinese, such as Mandarin. Shanghainese belongs a separate group of the Taihu Wu subgroup. With nearly 14 million speakers, Shanghainese is also the largest single form of Wu Chinese. Since the late 19th century it has served as the lingua franca of the entire Yangtze River Delta region, but in recent decades its status has declined relative to Mandarin, which most Shanghainese speakers can also speak. Like other Wu varieties, Shanghainese is rich in vowels and consonants, with around twenty unique vowel qualities, twelve of which are phonemic. Similarly, Shanghainese also has voiced obstruent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of . The main island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Taoyuan, Taichung, Tainan, and Kaohsiung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world. Taiwan has been settled for at least 25,000 years. Ancestors of Taiwanese indigenous peoples settled the island around 6,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Yi (Kuomintang)
Chen Yi (; courtesy names Gongxia (公俠) and later Gongqia (公洽), sobriquet Tuisu (退素); May 3, 1883 – June 18, 1950) was the chief executive and garrison commander of Taiwan Province after the Empire of Japan surrendered to the Republic of China. He acted on behalf of the Allied Powers to accept the Japanese Instrument of Surrender in Taipei Zhongshan Hall on October 25, 1945. He is considered to have mismanaged the tension between the Taiwanese and Mainland Chinese which resulted in the February 28 Incident in 1947, and was dismissed. In June 1948 he was appointed Chairman of Zhejiang Province, but was dismissed and arrested when his plan to surrender to the Chinese Communist Party was discovered. He was sentenced to death and executed by hanging in Taipei in 1950. Early biography and education Chen was born in Shaoxing, Zhejiang. After studying at Qiushi Academy (now Zhejiang University), in 1902 he went to a military academy in Japan for seven years. He joined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Enbo
Tang Enbo (, birth name was ,(1898–1954) was a Kuomintang, Nationalist general in the Republic of China. Life Early life and war with Japan Born in 1898 in Wuyi, Zhejiang, Tang Enbo was a graduate of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy, and therefore was familiar with the tactics of his Japanese enemy during the Second Sino-Japanese War. Tang's early resistance to the Japanese invasion was most ineffective, due to the political situation in China— Tang's superior Chiang Kai-shek was reluctant to devote his best troops to fight the Japanese invaders, wishing instead to use them to exterminate the Communists. Limited in troops and material, any commander would have had great difficulties in fighting such a superior enemy, and Tang Enbo was no exception. Furthermore, the battle plans though successful on paper rarely materialized on the battlefield during this stage because local Chinese warlords were only interested in maintaining their forces and largely ignored Chiang Kai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bai Chongxi
Bai Chongxi (18 March 1893 – 2 December 1966; , , Xiao'erjing: ) was a Chinese general in the National Revolutionary Army of the Republic of China (ROC) and a prominent Chinese Nationalist leader. He was of Hui ethnicity and of the Muslim faith. From the mid-1920s to 1949, Bai and his close ally Li Zongren ruled Guangxi province as regional warlords with their own troops and considerable political autonomy. His relationship with Chiang Kai-shek was at various times antagonistic and cooperative. He and Li Zongren supported the anti-Chiang warlord alliance in the Central Plains War in 1930, then supported Chiang in the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Chinese Civil War. Bai was the first defense minister of the Republic of China from 1946 to 1948. After losing to the Communists in 1949, he fled to Taiwan, where he died in 1966. Warlord era Bai was born in Guilin, Guangxi and given the courtesy name Jiansheng (). He was a descendant of a Persian merchant of the name Baider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qu Qiubai
Qu Qiubai (; 29 January 1899 – 18 June 1935) was a leader of the Chinese Communist Party in the late 1920s. He was born in Changzhou, Jiangsu, China. Early life Qu was born in Changzhou, Jiangsu. His family lived in Tianxiang Lou () located on Qingguo Lane (). Qu's father, Qu Shiwei (), was born in a family that was once powerful. He was good at painting and fencing and acquired much medical knowledge, but had no interest in politics and business. Qu's mother, Jin Xuan (), the daughter of an elite government official, was skilled in poetry. Qu had five brothers and one sister, he being the eldest. When Qu was young, his family lived in his uncle's house and was supported financially by relatives. Though Qu's father took a job as teacher, he was not able to support his family due to his addiction to opium. In 1915, Qu's mother, overcome by her life's mounting difficulties and debts, committed suicide. In 1916, Qu went to Hankou (today Wuhan) and entered Wuchang Foreign Lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sha Ding
Sha or SHA may refer to: Places * Sha County, Fujian, China * Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport, (IATA code) * Sia, Cyprus, also spelled ''Sha'' * Sagamihara Housing Area, an army installation in Japan * Vehicle registration plates in the district Schwäbisch Hall and the town Schwäbisch Hall, Germany People and language * Sha (surname) * Sha (singer) (born 1979), German singer * Sha Fei (1912–1950), Chinese photojournalist * Sha language * Sha (Cyrillic) (Ш, ш), a Cyrillic letter Government and organizations * Maryland State Highway Administration * Strategic health authorities, England * Saskatchewan Hockey Association, now known as Hockey Saskatchewan * Secondary Heads Association, now the Association of School and College Leaders * Society for Historical Archaeology * The Socialist Health Association, a left-wing English medical association affiliated with the Labour Party. History * ''Scriptores Historiae Augustae'' Science and technology * Secure Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ding Ling
Ding Ling (; October 12, 1904 – March 4, 1986), formerly romanized as Ting Ling, was the pen name of Jiang Bingzhi (), also known as Bin Zhi (彬芷 ''Bīn Zhǐ''), one of the most celebrated 20th-century Chinese women authors. She is known for her feminist and socialist realist literature. Ding was active in leftist literary circles connected to the Chinese Communist Party and was imprisoned by the Chinese Nationalist Party for her politics. She later became a leader in the literary community in the Communist base of Yan'an, and held high literature and culture positions in the early government of the People's Republic of China. She was awarded the Soviet Union's Stalin second prize for Literature in 1951 for her socialist-realist work ''The Sun Shines Over Sanggan River''. After the Anti-Rightist Campaign in 1958, Ding was denounced and purged and was sent to exile in Manchuria, to be rehabilitated only in 1979. She passed away in Beijing in 1986. Early life Ding Ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of Left-Wing Writers
__NOTOC__ The League of Left-Wing Writers (), commonly abbreviated as the Zuolian in Chinese, was an organization of writers formed in Shanghai, China, on 2 March 1930, at the instigation of the Chinese Communist Party and the influence of the celebrated author Lu Xun. Other prominent members included Ding Ling, Hu Feng, and Mei Zhi. The purpose of the League was to promote socialist realism in support of the Communist Revolution, and it eventually became very influential in Chinese cultural circles. Lu Xun delivered the opening address to the organizational meeting, but he became disillusioned when it quickly became clear that he would have little influence.Leo Oufan Lee, "Literary Trends: The Road to Revolution 1927-1949," Ch 9 in Other members included leaders of the Sun Society and the Creation Society, and Zhou Yang, who became Mao Zedong's favorite literary figure and after 1949 zealously enforced political orthodoxy. The League articulated theories on the political role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Zaoshi
Wang Zaoshi (, September 2, 1903 – August 5, 1971) was a Chinese lawyer and activist for human rights and constitutional government under both the Nationalist Government in Republican China and the People's Republic of China. He was educated at Tsinghua University then went to the United States for a doctorate at University of Wisconsin, Madison and post-doctoral work at University of London. In the years leading up to the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937-1945) he was prominent in the () that agitated for resistance to Japan and criticized the Nationalist government for its weak policies. He was one of the so-called , liberal scholars and activists arrested in 1936 for advocating a United Front between the Nationalist Party and the Communist Party of China in order to fight Japanese expansionism. He was active in the China Democratic League during and after the war. After the foundation of the People's Republic of China, he continued to advocate constitutional government, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ye Shengtao
Ye Shengtao (28 October 1894 – 16 February 1988) was a Chinese writer, journalist, educator, publisher and politician. He was a founder of the Association for Literary Studies (), the first literature association during the May Fourth Movement in China. He served as the Vice-Minister of Culture of the People's Republic of China. Throughout his life, he was dedicated to publishing and language education. He subscribed to the philosophy that "Literature is for Life" (). Biography Early life Ye was born on 28 October 1894 in Wu County, Jiangsu province. His name at birth was Ye Shaojun (), and his courtesy name was Bingchen (). His father worked as a bookkeeper for a landlord and they lived a very modest life. When he was six years old, he entered a mediocre school for primary study. He often followed his father to work. He travelled around the city and experienced the lives of the poor. In 1907, Ye entered Caoqiao Secondary School (). After his graduation, he worked as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |