|
Dunbeg Fort
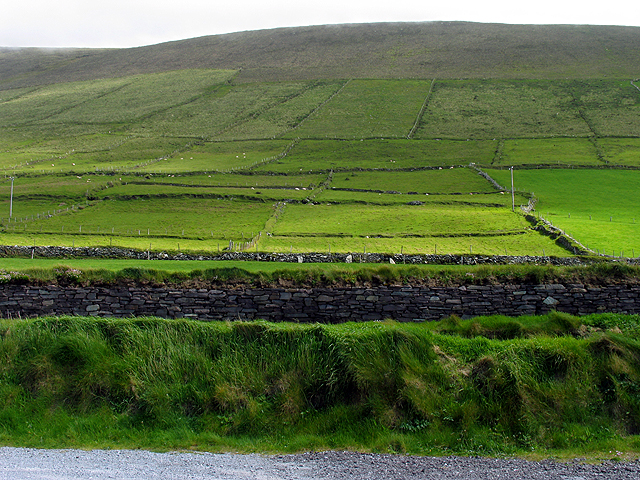
Dunbeg Fort ( ga, An Dún Beag) is a promontory fort built in the Iron Age near the modern village of Ventry in County Kerry, Ireland. Location Dunbeg Fort is located on a rocky promontory just south of Slea Head on the Dingle Peninsula, looking over Dingle Bay to the south and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The cliffs have eroded since it was built, and much of the fort has been lost to the sea. The fort's wall cut off access to the triangular promontory, which was later occupied by a single large "beehive" hut. Near to the fort there is a group of ''clocháns'', small stone structures also known as beehive huts that seem to have been built around 1000 BC. A visitor center at the site includes audiovisual displays, an information and craft room and a restaurant and café. In January 2014 the fort was closed when much of the western wall of the fort fell into the sea due to storm damage. The Office of Public Works and National Monuments Service sent personnel to inves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fahan, County Kerry
Fahan is an area on the Dingle Peninsula in County Kerry, Ireland, noted for a collection of clochán, or drystone beehive huts. Fahan lies below Mount Eagle on the southern coast of the Dingle peninsula, to the west of the fishing village of Ventry and to the east of the steep cliffs of Slea Head. Fahan has many antiquities, including cave dwellings, stone beehive huts, stone monuments and forts. Dunbeg Fort Dunbeg Fort is located on a rocky promontory looking over Dingle Bay to the south. The cliffs have eroded since it was built, and much of the fort has been lost to the sea. The fort's wall cut off access to the triangular promontory, which was later occupied by a single large "beehive" hut. A visitor center at the site includes audiovisual displays, an information and craft room and a restaurant and café. The date at which the Dunbeg fort was built is very uncertain, although its structure resembles other Western Stone Forts. It may have been built around the same tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In County Kerry
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huxter Fort
Huxter Fort is an Iron Age fortification on the island of Whalsay, in the Shetland islands of Scotland, dating to around 300 BC. It is on an islet in the Loch of Huxter, connected to the shore by a causeway. Origins The fort was probably built around 300 BC, the generally accepted date of most similar fortifications in the region. It resembles other fortifications such as the Crosskirk Broch, the blockhouse in front of the Broch of Clickimin and the Ness of Burgi fort at Scatness. Presumably these were built by culturally-related people. There are also similarities with stone forts in western Ireland, such as the Dunbeg Fort Dunbeg Fort ( ga, An Dún Beag) is a promontory fort built in the Iron Age near the modern village of Ventry in County Kerry, Ireland. Location Dunbeg Fort is located on a rocky promontory just south of Slea Head on the Dingle Peninsula, loo ... in County Kerry. This ring fort and blockhouse existed before the other two forts in Whalsay, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ness Of Burgi Fort
The Ness of Burgi fort is an iron-age promontory fort in the Old Scatness archaeological site on the Ness of Burgi, a narrow finger of land reaching south from the Scat Ness in the far south of the island of Mainland, Shetland in Scotland. Location The fort is about south from the village of Scatness, in the parish of Dunrossness, and may be reached by foot along a grass path that leads to the headland of the Ness of Burgi. The fort is on a rocky promontory on the east side of the Ness and is open to the public at all times. Structure The blockhouse, probably built about 100 BC seems to be excessively large for the area that it protects, and so was perhaps more designed to impress rather than to defend. The blockhouse structure seems to have been built as an integral part of the defensive wall. The walls do not reach the edges of the cliffs on either side. There is no evidence that they once reached further and since have been shortened through natural or human activity. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
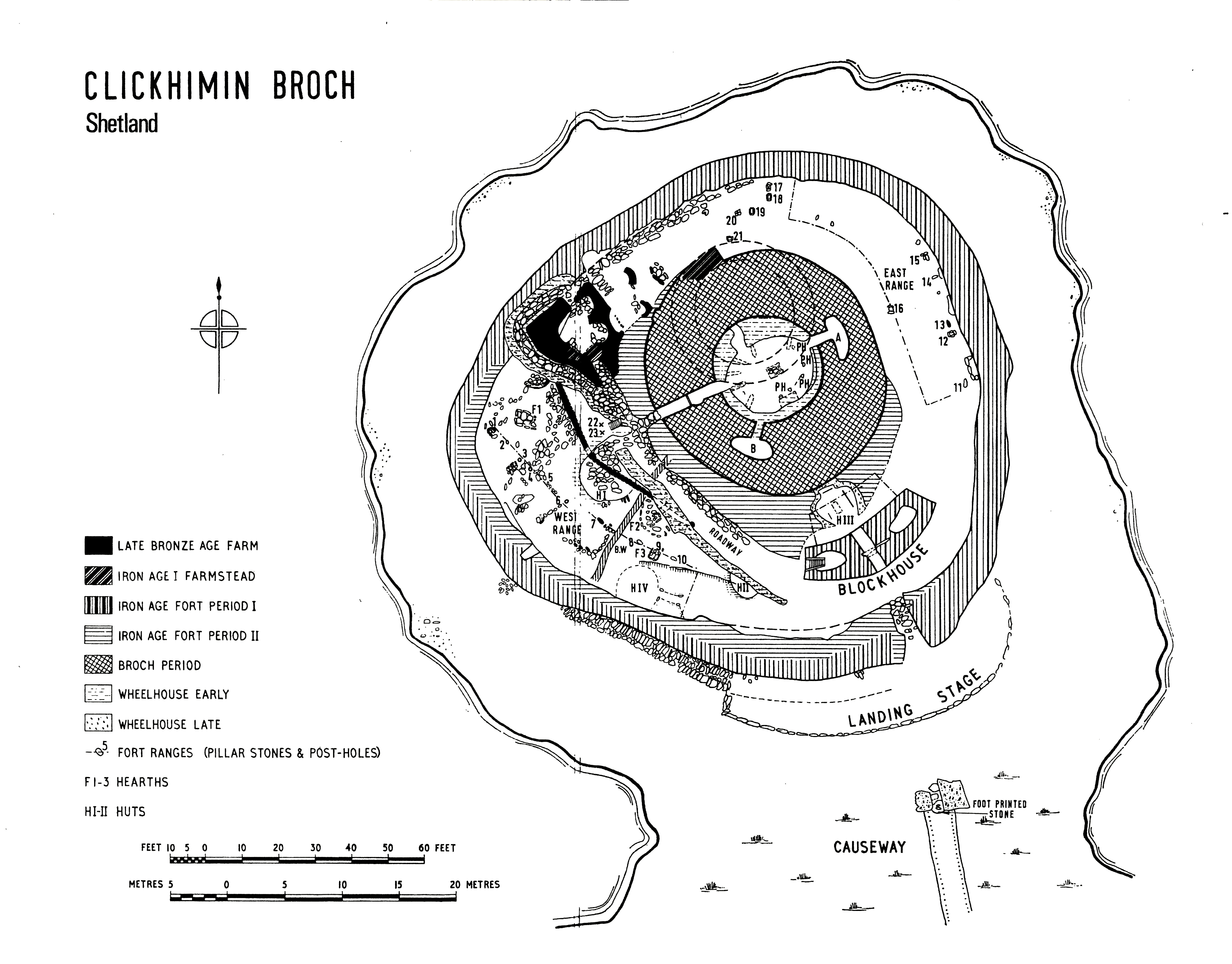
Clickimin Fort
The Broch of Clickimin (also Clickimin or Clickhimin Broch) is a large, well-preserved but restored broch in Lerwick in Shetland, Scotland (). Originally built on an island in Clickimin Loch, it was approached by a stone causeway. The broch is situated within a walled enclosure and, unusually for brochs, features a large "forework" or "blockhouse" between the opening in the enclosure and the broch itself. The site is maintained by Historic Scotland. According to its excavator, John R.C. Hamilton, there were several periods of occupation of the site: Late Bronze Age farmstead, Early Iron Age farmstead, Iron Age fort, broch period, and wheelhouse settlement. Location Clickimin Broch is situated on the south shore of the Clickimin Loch Clickimin Loch is a loch in Shetland, Scotland, west of Lerwick Lerwick (; non, Leirvik; nrn, Larvik) is the main town and port of the Shetland archipelago, Scotland. Shetland's only burgh, Lerwick had a population of about 7,000 reside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosskirk Fort
Crosskirk Broch was a fortification near the present day hamlet of Crosskirk near Thurso, Caithness, Scotland. After thorough archaeological exploration it was destroyed in 1972 since the site had become unsafe due to sea erosion. The site was unusual in having a broch, a large circular fortification, built within an older promontory fortification with a ring wall and blockhouse. History Crosskirk was occupied at the end of the Bronze Age. From the early Iron Age that followed there is carinated pottery that appears to be locally made but is similar to pottery of the same period in southern and eastern England. A few samples are black-burnished. Uncorrected radiocarbon dates for this pottery are in the 6th and 5th centuries BC. There seems to be a discontinuity in the middle Iron Age when the buildings were reconstructed and new types of pottery and artifacts were introduced, although variants of some of the older styles continued. This may be interpreted as being due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Eagle (Ireland)
Mount Eagle () is a mountain in County Kerry, Ireland. Geography The mountain is part of Mountains of the Central Dingle Peninsula and is the 419th highest in Ireland. Mount Eagle is located not faraway from Slea Head (Ceann Sléibhe), the most south-westerly point of the peninsula, and is connected with mount Brandon by a ridge of lower hills. On the mountain's top stands a trig point. History The mountain summit was the first European bit of land seen by Charles Lindbergh after his 1927 plane voyage across the Atlantic Ocean. Access to the summit Mount Eagle summit can be reached with a medium walk from Ventry Harbour. From the top of the mountain there is a good view of the neighbouring coast and the Blasket Islands. See also *List of mountains in Ireland In these lists of mountains in Ireland, those within Northern Ireland, or on the Republic of Ireland – United Kingdom border, are marked with an asterisk, while the rest are within the Republic of Ireland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Stone
Dry stone, sometimes called drystack or, in Scotland, drystane, is a building method by which structures are constructed from stones without any mortar to bind them together. Dry stone structures are stable because of their construction method, which is characterized by the presence of a load-bearing façade of carefully selected interlocking stones. Dry stone construction is best known in the context of stone walls, traditionally used for the boundaries of fields and churchyards, or as retaining walls for terracing, but dry stone sculptures, buildings, bridges, and other structures also exist. The term tends not to be used for the many historic styles which used precisely-shaped stone, but did not use mortar, for example the Greek temple and Inca architecture. The art of dry stone walling was inscribed in 2018 on the UNESCO representative list of the intangible cultural heritage of humanity, for dry stone walls in countries such as France, Greece, Italy, Slovenia, Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Victor Du Noyer
George Victor Du Noyer MRIA (1817 – 3 January 1869) was an Irish painter, geologist and antiquary of Huguenot descent. As an artist, his favourite medium was watercolour, but a large number of sketches by him in pencil and other mediums also survive. He was a gifted and extremely prolific artist. Most of his work relates exclusively to Ireland. Throughout his life, he was often commissioned to draw or paint realistic depictions of locations all over Ireland (making many of his works interesting from an Irish historical perspective). Much of this work took place during his time with the Irish Ordnance Survey and particularly the Geological Survey of Ireland. Personal life Born in 1817 and raised in Dublin, Ireland, George Victor Du Noyer, he was the son of Louis Victor Du Noyer (1782–1868) and Margaret Du Bédat (1794–1876), both of Huguenot descent. They had married in 1816. His father, Louis Victor, was a French teacher in Dublin. On 4 January 1858, George Victor Du No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Public Works
The Office of Public Works (OPW) ( ga, Oifig na nOibreacha Poiblí) (legally the Commissioners of Public Works in Ireland) is a major Irish Government agency, which manages most of the Irish State's property portfolio, including hundreds of owned and rented Government offices and police properties, oversees National Monuments and directly manages some heritage properties, and is the lead State engineering agency, with a special focus on flood risk management. It lies within the remit of the Minister for Public Expenditure and Reform, with functions largely delegated to a Minister of State at the Department of Public Expenditure and Reform with special responsibility for the Office. The OPW has a central role in driving the Government's property asset management reform process, both in respect of its own portfolio and that of the wider public service. The agency was initially known as Board of Works, a title inherited from a preceding body, and this term is still sometimes enco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

_position.jpeg/1200px-St_Mary's_Chapel_(Crosskirk)_position.jpeg)



