|
Dunantist
Dunantist is named after Henry Dunant (1828–1910), who inspired the creation of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement. It refers to the group of humanitarian practitioners, who follow the traditional or classic approach to humanitarianism, which comprises four fundamental principles: * Humanity – alleviate human suffering wherever it may be found * Neutrality – do not take sides in a conflict * Impartiality – aid should be based on needs alone, regardless of race, class, gender and sex * Independence – proactive disengagement from political and military actors to limit coercive control of the humanitarian actor's actions Aside from the strict subscription to the humanitarian principles that the Red Cross is based on, Dunantists also limit their action exclusively to humanitarian crises. History The term was coined by Abby Stoddard in the 2003 research article "Humanitarian NGOs: Challenges and Trends" published by the Humanitarian Policy Group of the Overs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Dunant
Henry Dunant (born Jean-Henri Dunant; 8 May 182830 October 1910), also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, and social activist. He was the visionary, promoter, and co-founder of the Red Cross. In 1901, he received the first Nobel Peace Prize together with Frédéric Passy. Dunant was the first Swiss Nobel laureate. In 1859, Dunant was witness to the aftermath of the Battle of Solferino in Italy. He recorded his memories and experiences in the book '' A Memory of Solferino'' which inspired the creation of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) in 1863. The 1864 Geneva Convention was based on Dunant's idea for an independent organization to care for wounded soldiers. Dunant was the founder of the Swiss branch of the YMCA. Early life and education Dunant was born in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1828 as the first son of businessman Jean-Jacques Dunant and Antoinette Dunant-Colladon. His family was devoutly Calvinist and had significant influenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Red Cross And Red Crescent Movement
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human suffering. Within it there are three distinct organisations that are legally independent from each other, but are united within the movement through common basic principles, objectives, symbols, statutes and governing organisations. History Foundation Until the middle of the nineteenth century, there were no organized or well-established army nursing systems for casualties, nor safe or protected institutions, to accommodate and treat those who were wounded on the battlefield. A devout Calvinist, the Swiss businessman Jean-Henri Dunant traveled to Italy to meet then-French emperor Napoleon III in June 1859 with the intention of discussing difficulties in conducting business in Algeria, which at that time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseas Development Institute
ODI (formerly the 'Overseas Development Institute') is a global affairs think tank, founded in 1960. Its mission is "to inspire people to act on injustice and inequality through collaborative research and ideas that matter for people and the planet." It does this through "research, convening and influencing, to lead new thinking and future agendas to deliver transformational change." Its Chair is Suma Chakrabarti. History In 1960 ODI began in small premises in Regent's Park, central London and operated a library devoted to international development issues as well as performing consultancy work and contracts with the Department for International Development (then known as the Overseas Development Agency) of the UK government. Since then it has moved several times and is on Blackfriars Road. Since 2004 it has had a Partnership Programme Arrangement with the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office. The institute also developed a strong focus on communications and 'bridging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
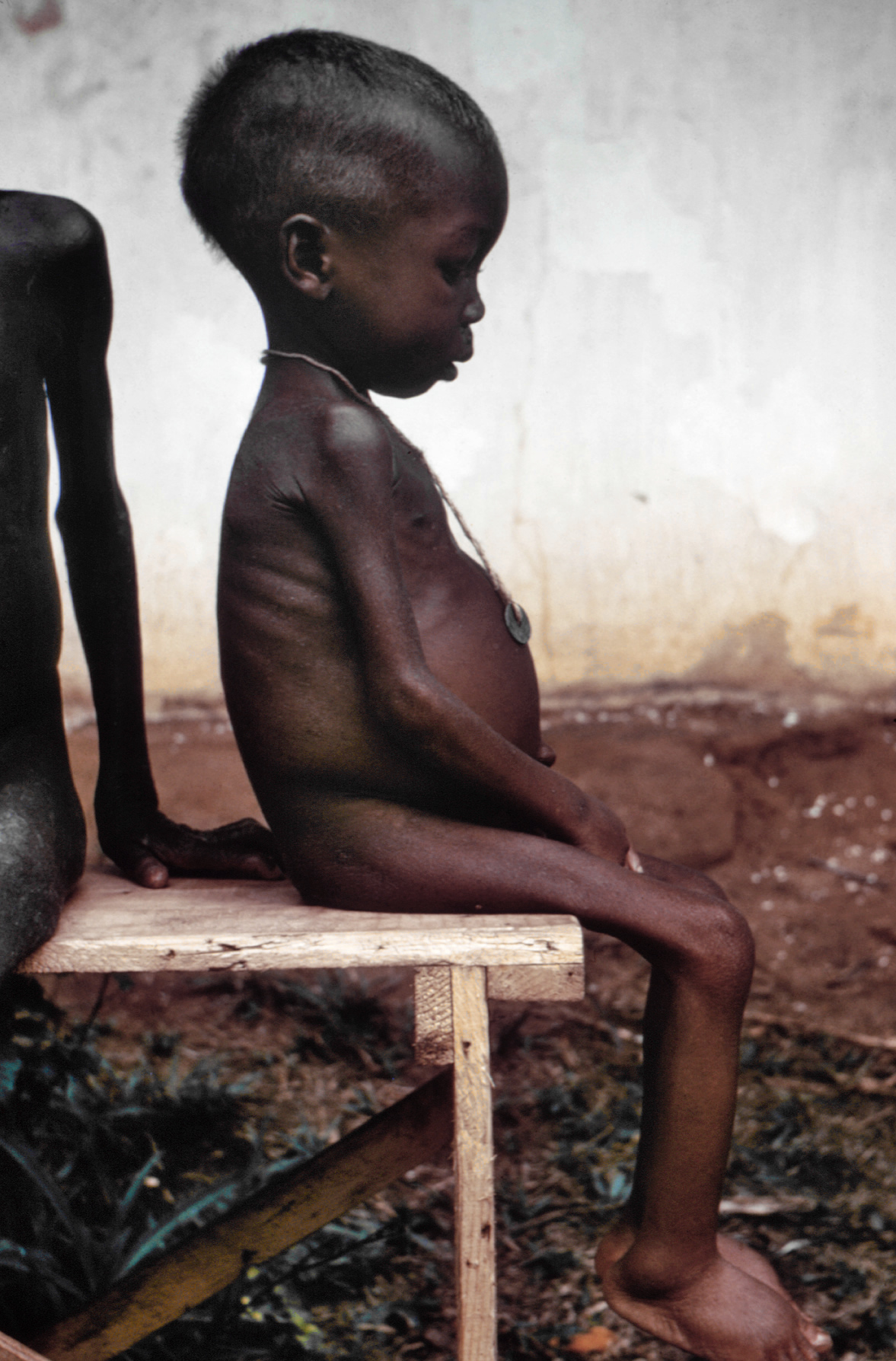
Médecins Sans Frontières
(MSF; pronounced ), also known as Doctors Without Borders, is a humanitarian medical non-governmental organisation (NGO) or charity of French origin known for its projects in conflict zones and in countries affected by endemic diseases. Main areas of work include diabetes, drug-resistant infections, HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C, tropical and neglected diseases, tuberculosis, vaccines and COVID-19. In 2019, the charity was active in 70 countries with over 35,000 personnel; mostly local doctors, nurses and other medical professionals, logistical experts, water and sanitation engineers, and administrators. Private donors provide about 90% of the organisation's funding, while corporate donations provide the rest, giving MSF an annual budget of approximately US$1.63 billion. MSF was founded in 1971, in the aftermath of the Biafran famine of the Nigerian Civil War, by a small group of French doctors and journalists who sought to expand accessibility to medical care across nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilsonianism
Wilsonianism, or Wilsonian idealism, is a certain type of foreign policy advice. The term comes from the ideas and proposals of President Woodrow Wilson. He issued his famous Fourteen Points in January 1918 as a basis for ending World War I and promoting world peace. He was a leading advocate of the League of Nations to enable the international community to avoid wars and end hostile aggression. Wilsonianism is a form of liberal internationalism. Principles Common principles that are often associated with Wilsonianism include: * Advocacy of the spread of democracy. Anne-Marie Slaughter writes that Wilson expected and hoped "that democracy would result from self-determination, but he never sought to spread democracy directly."Anne-Marie Slaughter, "Wilsonianism in the Twenty-first Century" in ''The Crisis of American Foreign Policy: Wilsonianism in the Twenty-first Century'' (eds. G. John Ikenberry, Thomas J. Knock, Anne Marie-Slaughter & Tony Smith: Princeton University Press, 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of Princeton University and as the governor of New Jersey before winning the 1912 presidential election. As president, Wilson changed the nation's economic policies and led the United States into World War I in 1917. He was the leading architect of the League of Nations, and his progressive stance on foreign policy came to be known as Wilsonianism. Wilson grew up in the American South, mainly in Augusta, Georgia, during the Civil War and Reconstruction. After earning a Ph.D. in political science from Johns Hopkins University, Wilson taught at various colleges before becoming the president of Princeton University and a spokesman for progressivism in higher education. As governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913, Wilson broke with party bosse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Rieff
David Rieff (; born September 28, 1952) is an American non-fiction writer and policy analyst. His books have focused on issues of immigration, international conflict, and humanitarianism. Biography Rieff is the only child of Susan Sontag, who was 19 years old when he was born. His father, whom Sontag divorced, was Philip Rieff, author of '' Freud: The Mind of the Moralist.'' Rieff was educated at the Lycée Français de New York and attended Amherst College as a member of the class of 1974, where he studied under Benjamin DeMott. He completed college at Princeton University, graduating with an A.B. in history in 1978. Career Rieff was a senior editor at Farrar, Straus and Giroux from 1978 to 1989. Rieff has at various times been a senior fellow at the World Policy Institute at the New School for Social Research, a fellow at the New York Institute for the Humanities at New York University, a board member of the Arms Division of Human Rights Watch, of the Central Eurasia Proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian People's Aid
Norwegian People's Aid ( no, Norsk Folkehjelp) was founded in 1939 to provide post-conflict reconstruction assistance and humanitarian relief during conflicts. NPA is now engaged in more than 33 countries in de-mining, humanitarian relief, promoting democratization; the rights of indigenous people, equality; and fair distribution of power and resources. NPA currently operates de-mineing activities in 16 countries and played a central role in the International Campaign to Ban Landmines and the Convention on Cluster Munitions which was signed in Oslo in 2008. NPA manages refugee reception centres, anti-racism campaigns, volunteer rescue teams, and a volunteer ambulance service. History 1930s Norwegian People's Aid (NPA) was founded on 7 December 1939 as a natural continuation of the work of several Norwegian organizations who had been working to alleviate human suffering during the Spanish Civil War and the Winter War in Finland. 1940s and 1950s During World War II, NPA m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Relief Services
Catholic Relief Services (CRS) is the international humanitarian agency of the Catholic community in the United States. Founded in 1943 by the Bishops of the United States, the agency provides assistance to 130 million people in more than 110 countries and territories in Africa, Asia, Latin America, the Middle East and Eastern Europe. A member of Caritas International, the worldwide network of Catholic humanitarian agencies, CRS provides relief in emergencies and helps people in the developing world break the cycle of poverty through community-based, sustainable development initiatives as well as Peacebuilding. Assistance is based solely on need, not race, creed or nationality. Catholic Relief Services is headquartered in the Posner Building in Baltimore, Maryland, while operating numerous field offices on five continents. CRS has approximately 5,000 employees around the world. The agency is governed by a Board of Directors consisting of 13 clergy (most of them bishops) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Vision
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of many parts. In ''scientific cosmology'' the world or universe is commonly defined as " e totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". '' Theories of modality'', on the other hand, talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. ''Phenomenology'', starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In ''philosophy of mind'', the world is commonly contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halliburton
Halliburton Company is an American multinational corporation responsible for most of the world's hydraulic fracturing operations. In 2009, it was the world's second largest oil field service company. It has operations in more than 70 countries. It owns hundreds of subsidiaries, affiliates, branches, brands, and divisions worldwide and employs approximately 55,000 people. The company has dual headquarters located in Houston and in Dubai, and remains incorporated in the United States.''"Halliburton to Move Headquarters to Dubai"'' – '''' – |
Hechtel
Hechtel-Eksel () is a municipality located in the Belgian province of Limburg. On 1 January 2018 it had a total population of 12,290 an area of 76.70 km² giving a population density of 150 inhabitants per km². The municipality was created in January 1977 as a merger of the two former municipalities Hechtel and Eksel. Events Hechtel was home to the "KBC Night of Athletics", a yearly international athletics meeting and the annual International Airshow at Sanicole Airport, taking place in September. Battle of Hechtel For seven days during World War II, from 6 to 12 September 1944, the town of Hechtel became the front line between German and British troops in what is known as the battle of Hechtel. German troops consisted of the 2nd Hermann Göring Tank Regiment. The 1st battalion was in Hechtel, with the 2nd placed 2km to the east in Wijchmaal. British forces were from the 1st and 2nd Battalion Welsh Guards, Scots Guards 'X'-Company, Grenadier Guards and other supporting u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |