|
Dream Of Fair To Middling Women
''Dream of Fair to Middling Women'' is Samuel Beckett’s first novel. Written in English "in a matter of weeks" in 1932 when Beckett was only 26 and living in Paris, the clearly autobiographical novel was rejected by publishers and shelved by the author. The novel was eventually published in 1992, three years after the author's death. Partial publication Three fragments from the book were published during Beckett's lifetime: "Text" and "Sedendo et Quiescendo" were actually published before he started working on the book and subsequently became part of it, whilst "Jem Higgins' Love-Letter to the Alba" was published in 1965. Beckett refused to allow the entire novel to be published during his lifetime, on the grounds that it was "immature and unworthy": his biographer Deirdre Bair believes that his reluctance to make it available to the reading public was to avoid offending lifelong friends whom Beckett satirised in the book. Setting and influences The novel is set in the town of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Beckett
Samuel Barclay Beckett (; 13 April 1906 – 22 December 1989) was an Irish novelist, dramatist, short story writer, theatre director, poet, and literary translator. His literary and theatrical work features bleak, impersonal and tragicomic experiences of life, often coupled with black comedy and nonsense. It became increasingly minimalist as his career progressed, involving more aesthetic and linguistic experimentation, with techniques of repetition and self-reference. He is considered one of the last modernist writers, and one of the key figures in what Martin Esslin called the Theatre of the Absurd. A resident of Paris for most of his adult life, Beckett wrote in both French and English. During the Second World War, Beckett was a member of the French Resistance group Gloria SMH (Réseau Gloria). Beckett was awarded the 1969 Nobel Prize in Literature "for his writing, which—in new forms for the novel and drama—in the destitution of modern man acquires its elevation". He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Williamson
Henry William Williamson (1 December 1895 – 13 August 1977) was an English writer who wrote novels concerned with wildlife, English social history and ruralism. He was awarded the Hawthornden Prize for literature in 1928 for his book ''Tarka the Otter''. He was born in London, and brought up in a semi-rural area where he developed his love of nature, and nature writing. He fought in World War I and, having witnessed the Christmas truce and the devastation of trench warfare, he developed first a pacifist ideology, then fascist sympathies. He moved to Devon after World War II and took up farming and writing; he wrote many other novels. He married twice. He died in a hospice in Ealing in 1977, and was buried in North Devon. Early years Henry Williamson was born in Brockley in south-east London to bank clerk William Leopold Williamson (1865-1946) and Gertrude Eliza (1867-1936; née Leaver). In early childhood his family moved to Ladywell, and he received a grammar school educati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novels By Samuel Beckett
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itself from the la, novella, a singular noun use of the neuter plural of ''novellus'', diminutive of ''novus'', meaning "new". Some novelists, including Nathaniel Hawthorne, Herman Melville, Ann Radcliffe, John Cowper Powys, preferred the term Romance (literary fiction), "romance" to describe their novels. According to Margaret Doody, the novel has "a continuous and comprehensive history of about two thousand years", with its origins in the Ancient Greek novel, Ancient Greek and Roman novel, in Chivalric romance, and in the tradition of the Italian renaissance novella.Margaret Anne Doody''The True Story of the Novel'' New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 1996, rept. 1997, p. 1. Retrieved 25 April 2014. The ancient romance form was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1992 Novels
Year 199 ( CXCIX) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was sometimes known as year 952 ''Ab urbe condita''. The denomination 199 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Mesopotamia is partitioned into two Roman provinces divided by the Euphrates, Mesopotamia and Osroene. * Emperor Septimius Severus lays siege to the city-state Hatra in Central-Mesopotamia, but fails to capture the city despite breaching the walls. * Two new legions, I Parthica and III Parthica, are formed as a permanent garrison. China * Battle of Yijing: Chinese warlord Yuan Shao defeats Gongsun Zan. Korea * Geodeung succeeds Suro of Geumgwan Gaya, as king of the Korean kingdom of Gaya confederacy, Gaya (traditional date). By topic Religion * Pope Zephyrinus succeeds Pope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1932 Novels
Year 193 ( CXCIII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sosius and Ericius (or, less frequently, year 946 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 193 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * January 1 – Year of the Five Emperors: The Roman Senate chooses Publius Helvius Pertinax, against his will, to succeed the late Commodus as Emperor. Pertinax is forced to reorganize the handling of finances, which were wrecked under Commodus, to reestablish discipline in the Roman army, and to suspend the food programs established by Trajan, provoking the ire of the Praetorian Guard. * March 28 – Pertinax is assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard, who storm the imperial palace. The Empire is auctioned off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proust (Beckett Essay)
Samuel Beckett's essay ''Proust'', published in 1930, is a study of Marcel Proust. History Beckett wrote ''Proust'' in the summer of 1930, in response to a commission precipitated by Thomas MacGreevy, Charles Prentice, and Richard Aldington, during his stay at the École Normale in Paris. By the end of September, he delivered it by hand to Charles Prentice at Chatto and Windus. The book sold 2,600 copies by 1937, and the remaining 400 copies were remaindered by 1941. In retrospect, Beckett dismissed it as having been written in “cheap flashy philosophical jargon.” Interpretation The essay serves double duty as its author’s aesthetic and epistemological manifesto, proclaiming on behalf of its ostensible subject: “We cannot know and we cannot be known.” In dense and allusive language, Beckett credits his current influences, notably Schopenhauer and Calderón, and forecasts his future preoccupations, reading them into the prose of Marcel Proust: The laws of memory are su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
More Pricks Than Kicks
''More Pricks Than Kicks'' is a collection of short prose by Samuel Beckett, first published in 1934. It contains extracts from his earlier novel, ''Dream of Fair to Middling Women'' (for which he was unable to find a publisher), as well as other short stories. The stories chart the life of the book's main character, Belacqua Shuah, from his days as a student to his accidental death. Beckett takes the name Belacqua from a figure in Dante's ''Purgatorio'', a Florentine lute-maker famed for his laziness, who has given up on ever reaching heaven. The opening story, "Dante and the Lobster," features Belacqua's horrified reaction to the discovery that the lobster he has bought for dinner must be boiled alive. "It's a quick death, God help us all," Belacqua tells himself, before the narrator's stern interjection to the contrary: "It is not." "The Smeraldina's Billet Doux" is a love letter to Belacqua in fractured English by the German-speaking Smeraldina Rima, a character based on B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
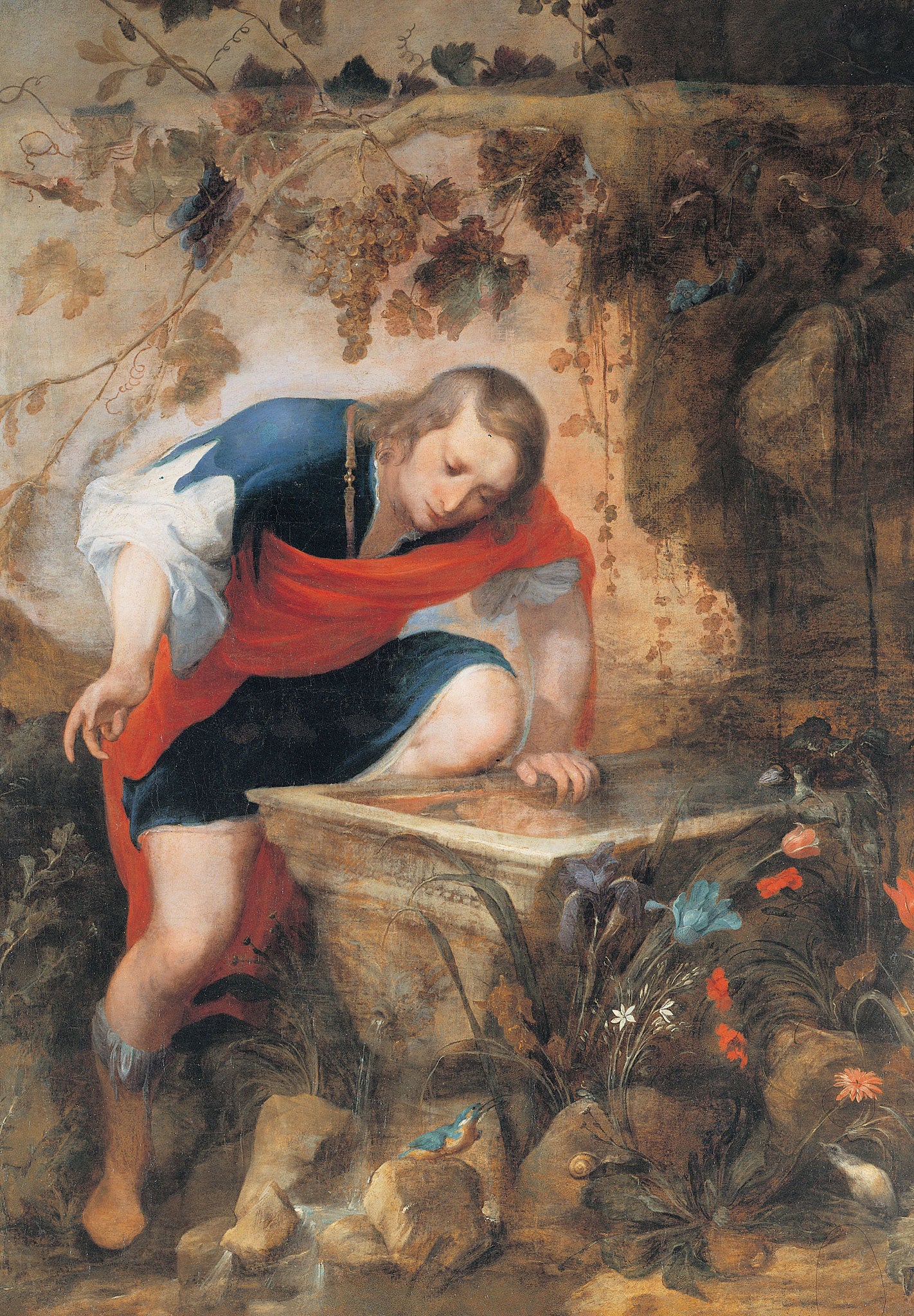
Narcissus (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Narcissus (; Ancient Greek: Νάρκισσος ''Nárkissos'') was a hunter from Thespiae in Boeotia (alternatively Mimas or modern day Karaburun, Izmir) who was known for his beauty. According to Tzetzes, he rejected all romantic advances, eventually falling in love with his own reflection in a pool of water, staring at it for the remainder of his life. After he died, in his place sprouted a flower bearing his name. The character of Narcissus is the origin of the term narcissism, a fixation with oneself. This quality, in turn, contributes to the definition of narcissistic personality disorder, a psychiatric condition marked by grandiosity, excessive need for attention and admiration, and an inability to empathize. Like the myth of Laius and Chrysippus, the myth of Narcissus is a Boeotian pederastic cautionary tale, a story meant to teach by counter-example. Etymology The name is of Greek etymology. According to R. S. P. Beekes, " e suffixes ισ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label=genitive, , ; , is one of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. The national divinity of the Greeks, Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. Seen as the most beautiful god and the ideal of the ''kouros'' (ephebe, or a beardless, athletic youth), Apollo is considered to be the most Greek of all the gods. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as ''Apulu''. As the patron deity of Delphi (''Apollo Pythios''), Apollo is an oracul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proust
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust (; ; 10 July 1871 – 18 November 1922) was a French novelist, critic, and essayist who wrote the monumental novel ''In Search of Lost Time'' (''À la recherche du temps perdu''; with the previous English title translation of ''Remembrance of Things Past''), originally published in French in seven volumes between 1913 and 1927. He is considered by critics and writers to be one of the most influential authors of the 20th century. Background Proust was born on 10 July 1871 at the home of his great-uncle in the Paris Borough of Auteuil (the south-western sector of the then-rustic 16th arrondissement), two months after the Treaty of Frankfurt formally ended the Franco-Prussian War. His birth took place at the very beginning of the Third Republic, during the violence that surrounded the suppression of the Paris Commune, and his childhood corresponded with the consolidation of the Republic. Much of ''In Search of Lost Time'' concerns the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jane Austen
Jane Austen (; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for her six major novels, which interpret, critique, and comment upon the British landed gentry at the end of the 18th century. Austen's plots often explore the dependence of women on marriage in the pursuit of favourable social standing and economic security. Her works critique the novels of sensibility of the second half of the 18th century and are part of the transition to 19th-century literary realism. Her use of biting irony, along with her realism and social commentary, have earned her acclaim among critics, scholars and readers alike. With the publication of ''Sense and Sensibility'' (1811), '' Pride and Prejudice'' (1813), ''Mansfield Park'' (1814), and '' Emma'' (1816), she achieved modest success but only little fame in her lifetime since the books were published anonymously. She wrote two other novels—''Northanger Abbey'' and '' Persuasion'', both published posthumou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |