|
Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used together with other chemotherapy agents. Doxorubicin is given by injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, vomiting, rash, and inflammation of the mouth. Other serious side effects may include allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis, heart damage, tissue damage at the site of injection, radiation recall, and treatment-related leukemia. People often experience red discoloration of the urine for a few days. Doxorubicin is in the anthracycline and antitumor antibiotic family of medications. It works in part by interfering with the function of DNA. Doxorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1974. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Versions th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracycline
Anthracyclines are a class of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy that are extracted from ''Streptomyces'' bacterium. These compounds are used to treat many cancers, including leukemias, lymphomas, breast, stomach, uterine, ovarian, bladder cancer, and lung cancers. The first anthracycline discovered was daunorubicin (trade name Daunomycin), which is produced naturally by ''Streptomyces peucetius'', a species of Actinomycetota. Clinically the most important anthracyclines are doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin and idarubicin. The anthracyclines are among the most effective anticancer treatments ever developed and are effective against more types of cancer than any other class of chemotherapeutic agents. Their main adverse effect is cardiotoxicity, which considerably limits their usefulness. Use of anthracyclines has also been shown to be significantly associated with cycle 1 severe or febrile neutropenia. Other adverse effects include vomiting. The drugs act mainly by interc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy Medication
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms (palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
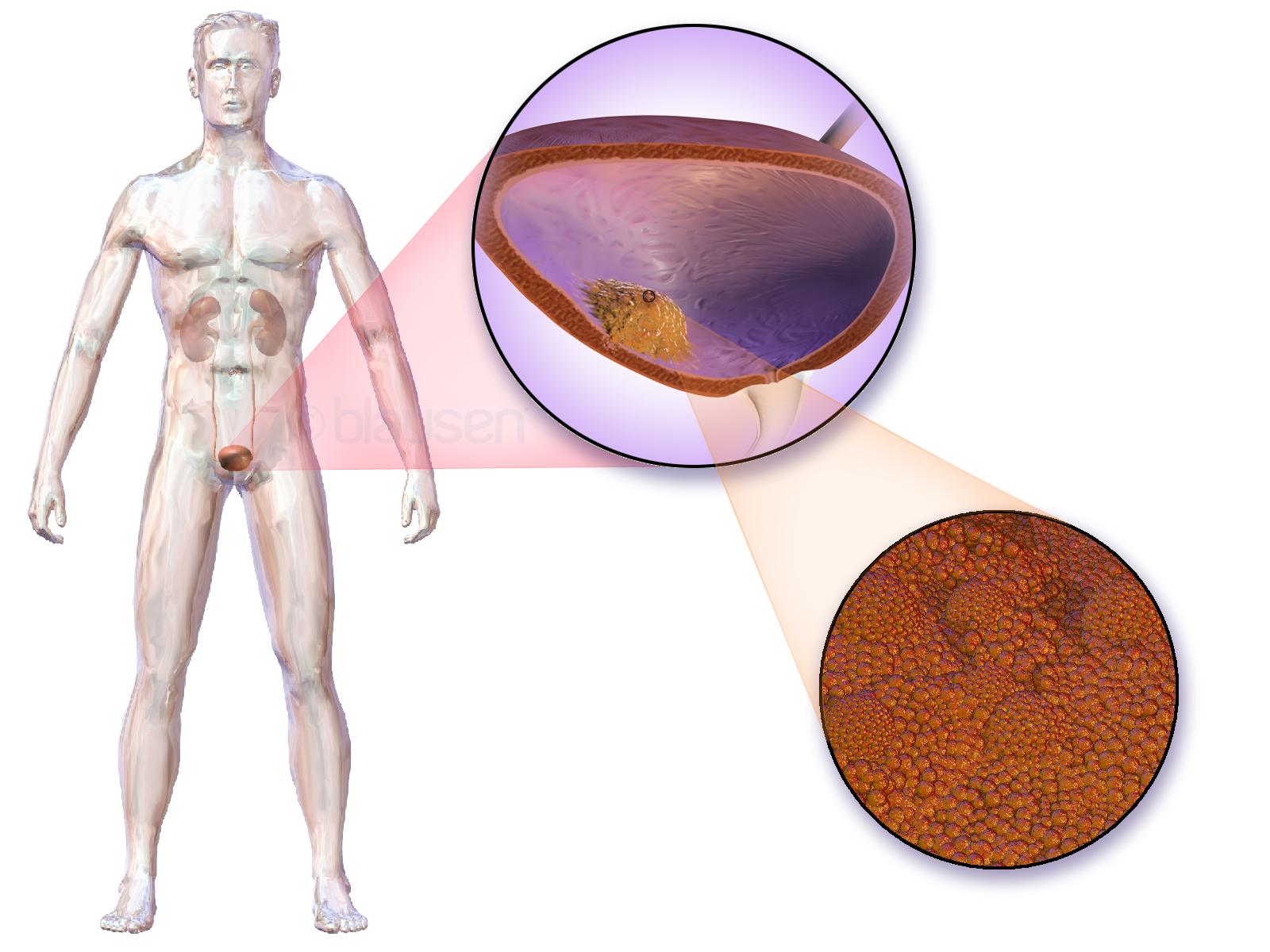
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become malignant. Risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, family history, prior radiation therapy, frequent bladder infections, and exposure to certain chemicals. The most common type is transitional cell carcinoma. Other types include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Diagnosis is typically by cystoscopy with tissue biopsies. Staging of the cancer is determined by transurethral resection and medical imaging. Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer. It may include some combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. Surgical options may include transurethral resection, partial or complete removal of the bladder, or urinary diversion. The typical five-year survival rates in the United States i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pegylated
PEGylation (or pegylation) is the process of both covalent and non-covalent attachment or amalgamation of polyethylene glycol (PEG, in pharmacy called macrogol) polymer chains to molecules and macrostructures, such as a drug, therapeutic protein or vesicle, which is then described as PEGylated. PEGylation affects the resulting derivatives or aggregates interactions, which typically slows down their coalescence and degradation as well as elimination in vivo. PEGylation is routinely achieved by the incubation of a reactive derivative of PEG with the target molecule. The covalent attachment of PEG to a drug or therapeutic protein can "mask" the agent from the host's immune system (reducing immunogenicity and antigenicity), and increase its hydrodynamic size (size in solution), which prolongs its circulatory time by reducing renal clearance. PEGylation can also provide water solubility to hydrophobic drugs and proteins. Having proven its pharmacological advantages and acceptability, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ''leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia— acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myeloi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combination Chemotherapy
The era of cancer chemotherapy began in the 1940s with the first use of nitrogen mustards and folic acid antagonist drugs. The targeted therapy revolution has arrived, but many of the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply. Beginnings The beginnings of the modern era of cancer chemotherapy can be traced directly to the German introduction of chemical warfare during World War I. Among the chemical agents used, mustard gas was particularly devastating. Although banned by the Geneva Protocol in 1925, the advent of World War II caused concerns over the possible re-introduction of chemical warfare. Such concerns led to the discovery of nitrogen mustard, a chemical warfare agent, as an effective treatment for cancer. Two pharmacologists from the Yale School of Medicine, Louis S. Goodman and Alfred Gilman, were recruited by the US Department of Defense to investigate potential therapeutic applications of chemical warfare agents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Peucetius
''Streptomyces peucetius'' is a bacterium species in the genus ''Streptomyces''. ''S. peucetius'' produces the anthracycline antitumor antibiotics daunorubicin and doxorubicin Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used togeth ... (also known as adriamycin).Adriamycin, 14-hydroxydaimomycin, a new antitumor antibiotic from S. Peucetius var. caesius. F. Arcamone, G. Cassinelli, G. Fantini, A. Grein, P. Orezzi, C. Pol and C. Spalla, Biotechnology and Bioengineering, November 1969, Volume 11, Issue 6, pages 1101–1110, References External links ''Streptomyces peucetius'' on www.uniprot.orgType strain of ''Streptomyces peucetius'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase peucetius Bacteria described in 1963 {{Streptomyces-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bortezomib
Bortezomib, sold under the brand name Velcade among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma. This includes multiple myeloma in those who have and have not previously received treatment. It is generally used together with other medications. It is given by injection. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, tiredness, low platelets, fever, numbness, low white blood cells, shortness of breath, rash and abdominal pain. Other severe side effects include low blood pressure, tumour lysis syndrome, heart failure, and reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. It is in the class of medications known as proteasome inhibitor. It works by inhibiting proteasomes, cellular complexes that break down proteins. Bortezomib was approved for medical use in the United States in 2003 and in the European Union in 2004. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaposi's Sarcoma
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a type of cancer that can form masses in the skin, in lymph nodes, in the mouth, or in other organs. The skin lesions are usually painless, purple and may be flat or raised. Lesions can occur singly, multiply in a limited area, or may be widespread. Depending on the sub-type of disease and level of immune suppression, KS may worsen either gradually or quickly. Except for Classical KS where there is generally no immune suppression, KS is caused by a combination of immune suppression (such as due to HIV/AIDS) and infection by Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8 – also called KS-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)). Four sub-types are described: classic, endemic, immunosuppression therapy-related (also called iatrogenic), and epidemic (also called AIDS-related). Classic KS tends to affect older men in regions where KSHV is highly prevalent (Mediterranean, Eastern Europe, Middle East), is usually slow-growing, and most often affects only the legs. Endemic KS is most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liposomes
A liposome is a small artificial Vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicle, spherical in shape, having at least one lipid bilayer. Due to their hydrophobicity and/or hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, particle size and many other properties, liposomes can be used as drug delivery vehicles for route of administration, administration of pharmaceutical drugs and nutrients, such as solid lipid nanoparticles, lipid nanoparticles in mRNA vaccines, and DNA vaccination, DNA vaccines. Liposomes can be prepared by disrupting biological membranes (such as by sonication). Liposomes are most often composed of phospholipids, especially phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol, but may also include other lipids, such as Egg (food), egg, phosphatidylethanolamine, as long as they are compatible with lipid bilayer structure. A liposome design may employ surface ligands for attaching to unhealthy tissue. The major types of liposomes are the multilamellar vesicle (MLV, with several lamellar phase lipid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |