|
Dorrigo Steam Railway And Museum
The Dorrigo Steam Railway & Museum in Dorrigo, New South Wales, Australia is a large, privately owned collection of railway vehicles and equipment from the railways of New South Wales, covering both Government and private railways. The collection dates from 1878 until 1985. Status The museum was opened very briefly in 1986, but has been described as "not yet open to the public" ever since. History The museum's origins stem from the formation of the Hunter Valley Steam Railway & Museum in 1973 which was formed following the closure of the Glenreagh to Dorrigo branch line the previous year with the aim of restoring the 69 kilometres as a tourist railway. Much of the rolling stock was stored at the former Rhondda Colliery, three kilometres from Cockle Creek while the line was repaired. It was renamed the Dorrigo Steam Railway & Museum in 1982. On 20 December 1984, the section from Glenreagh to Lowanna was reopened with 5069 hauling the first train. On 5 April 1986 the line w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorrigo, New South Wales
Dorrigo, a small town on the Waterfall Way, is located on the Northern Tablelands, in northern New South Wales, Australia. The town is part of Bellingen local government area. It is approximately north of the state capital, Sydney via the Pacific Highway, and west from the coastal city of Coffs Harbour. The town is situated on the Dorrigo Plateau near the New England Escarpment, which is part of the Great Dividing Range. Dorrigo is above sea level. At the 2016 census, Dorrigo had a population of 1,042 people. History The area now known as Dorrigo lies on the traditional land of the Gumbainggir people. European settlement of the area followed on from the early timber cutters in the 1860s. The first official European in the district was Land Commissioner Oakes who sighted the mouth of the Bellinger River. Dorrigo is derived from the Aboriginal word, ''dondorrigo'' or Dandarrga, meaning "stringy-bark". For many decades it was believed that explorer and settler Major Edward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North British Locomotive Company
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park Works) and Dübs and Company (Queens Park Works), creating the largest locomotive manufacturing company in Europe and the British Empire. Its main factories were located at the neighbouring Atlas and Hyde Park Works in central Springburn, as well as the Queens Park Works in Polmadie. A new central Administration and Drawing Office for the combined company was completed across the road from the Hyde Park Works on Flemington Street by James Miller in 1909, later sold to Glasgow Corporation in 1961 to become the main campus of North Glasgow College (now Glasgow Kelvin College). The two other Railway works in Springburn were St. Rollox railway works, owned by the Caledonian Railway and Cowlairs railway works, owned by the North British Railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ROD 2-8-0
The Railway Operating Division (ROD) ROD 2-8-0 is a type of 2-8-0 steam locomotive which was the standard heavy freight locomotive operated in Europe by the ROD during the First World War. ROD need for a standard locomotive During the First World War the Railway Operating Division of the Royal Engineers requisitioned about 600 locomotives of various types from thirteen United Kingdom railway companies; the first arrived in France in late 1916. As the war became prolonged it became clear that the ROD needed its own standard locomotive, so the ROD adopted the Great Central Railway Class 8K 2-8-0 designed by John G. Robinson in 1911. Procurement of RODs There were three batches of orders. The first batch of orders were placed between February and June 1917 for 223 locomotives. The second batch of orders was for 100 locomotives, placed between February and August 1918; onwards, followed by an order for 188 more in Autumn 1918 to sustain the UK's locomotive manufacturing industry af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
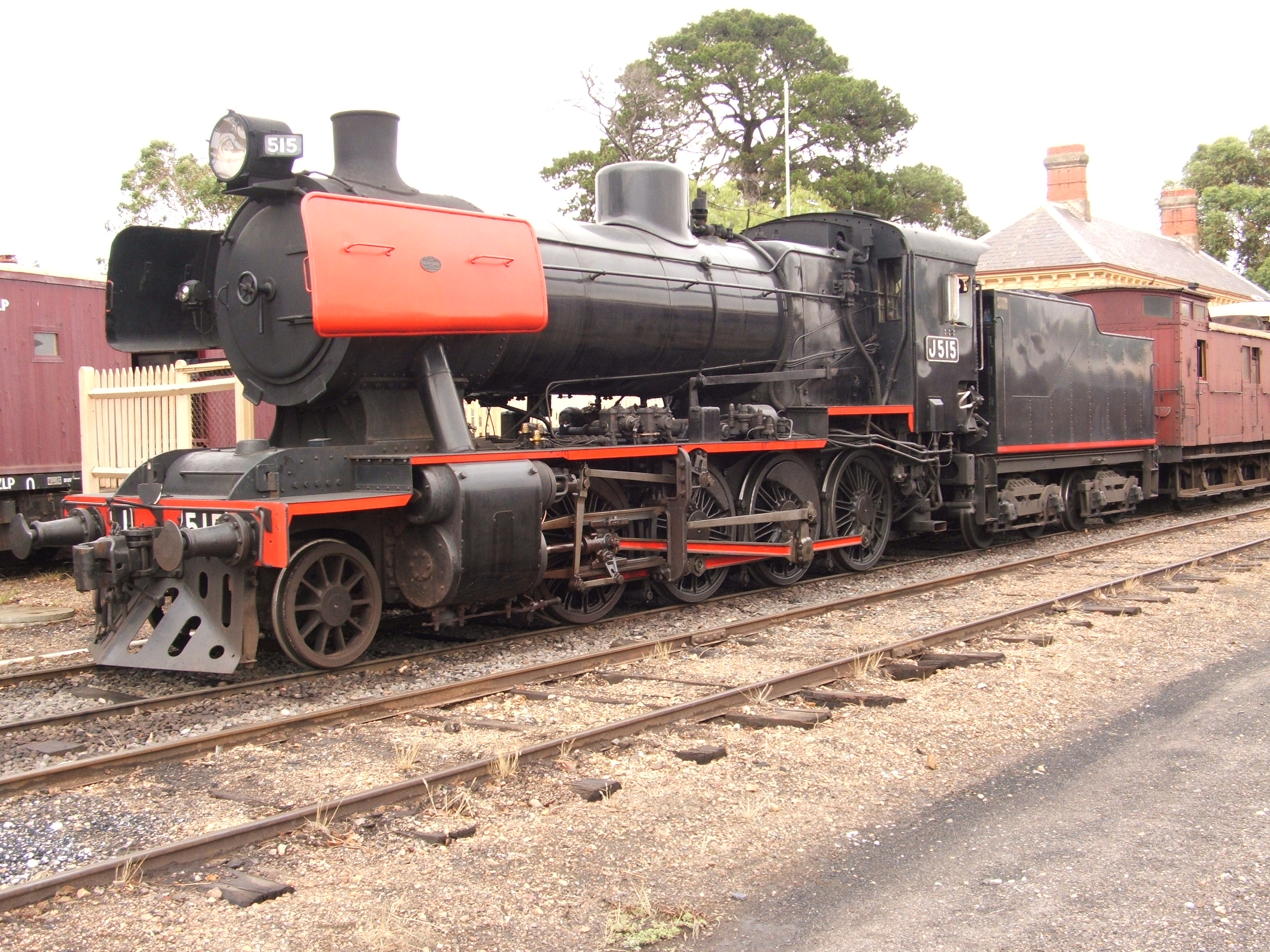
New South Wales D53 Class Locomotive
The D53 class was a class of 2-8-0 steam locomotives built for the New South Wales Government Railways of Australia. History This class of locomotive was designed by the New South Wales Government Railways as an improved version of the T class. All the coupled wheels had flanges and a certain amount of side movement was given to the middle pairs with a laterally operating knuckle joint being provided in the middle section of the coupling rods. Clyde Engineering delivered the first locomotive in April 1912 and by November 1917, a total of 190 were in service. Most were fitted with superheaters when built and some fitted at a later date. There was a problem with the locomotives being unbalanced, causing speed restrictions to be imposed to avoid rough riding and track damage. Following further investigations, 24 of the class received balanced coupled wheels and these were permitted to operate at higher speed on mail and fruit trains. When introduced, most of the class were fitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clyde Engineering
Clyde Engineering was an Australian manufacturer of locomotives, rolling stock, and other industrial products. It was founded in September 1898 by a syndicate of Sydney businessmen buying the Granville factory of timber merchants Hudson Brothers. The company won contracts for railway rolling stock, a sewerage system, trams and agricultural machinery. In 1907 it won its first contract for steam locomotives for the New South Wales Government Railways. By 1923 it had 2,200 employees. After contracting during the depression it became a major supplier of munitions during World War II. In 1950 it was awarded the first of many contracts for diesel locomotives by the Commonwealth Railways after it was appointed the Australian licensee for Electro-Motive Diesel products. Apart from building locomotives and rolling stock, Clyde Engineering diversified into telephone and industrial electronic equipment, machine tools, domestic aluminium ware, road making and earth making equipmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. In the United States and elsewhere, this wheel arrangement is commonly known as a Consolidation, after the Lehigh and Mahanoy Railroad’s ''Consolidation'', the name of the first 2-8-0.White, John H. Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, p. 65. The notation 2-8-0T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in side-tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. The Consolidation represented a notable advance in locomotive power. After 1875, it became "the most popular type of freight locomotive in the United States and was built in greater quantities than any other si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiff Locomotive Workshops
The Cardiff Locomotive Workshops (now known as the Cardiff Maintenance Centre) is a rail yard and rolling stock facility located between Cockle Creek and Cardiff stations near Newcastle, on the Main North railway line in New South Wales, Australia. The site is currently occupied by Downer Rail, where rolling stock is assembled, maintained and stored. Early northern workshops The Hunter River Railway Company established meagre maintenance facilities adjacent to its line at its eastern terminus, near the current day Civic station. Civic Station is no longer in use. (All stations from Wickham to Newcastle are now served by the Newcastle Light Rail which terminates at Newcastle Beach. Opened 17 February 2019) These formed the basis of the Honeysuckle Point Workshops the old buildings of which now lie within the area redeveloped by the Honeysuckle Development Corporation."Cardiff Farewell" Ron Preston ''Railway Digest'' February 1994 page 18 The workshops grew in size as the isol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The locomotive became almost globally known as a Pacific type. Overview The introduction of the design in 1901 has been described as "a veritable milestone in locomotive progress". On many railways worldwide, Pacific steam locomotives provided the motive power for express passenger trains throughout much of the early to mid-20th century, before either being superseded by larger types in the late 1940s and 1950s, or replaced by electric locomotive, electric or diesel locomotive, diesel-electric locomotives during the 1950s and 1960s. Nevertheless, new Pacific designs continued to be built until the mid-1950s. The type is generally considered to be an enlargement of the 4-4-2 (locomotive), Atlantic type, although its NZR Q class (1901), prototype had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
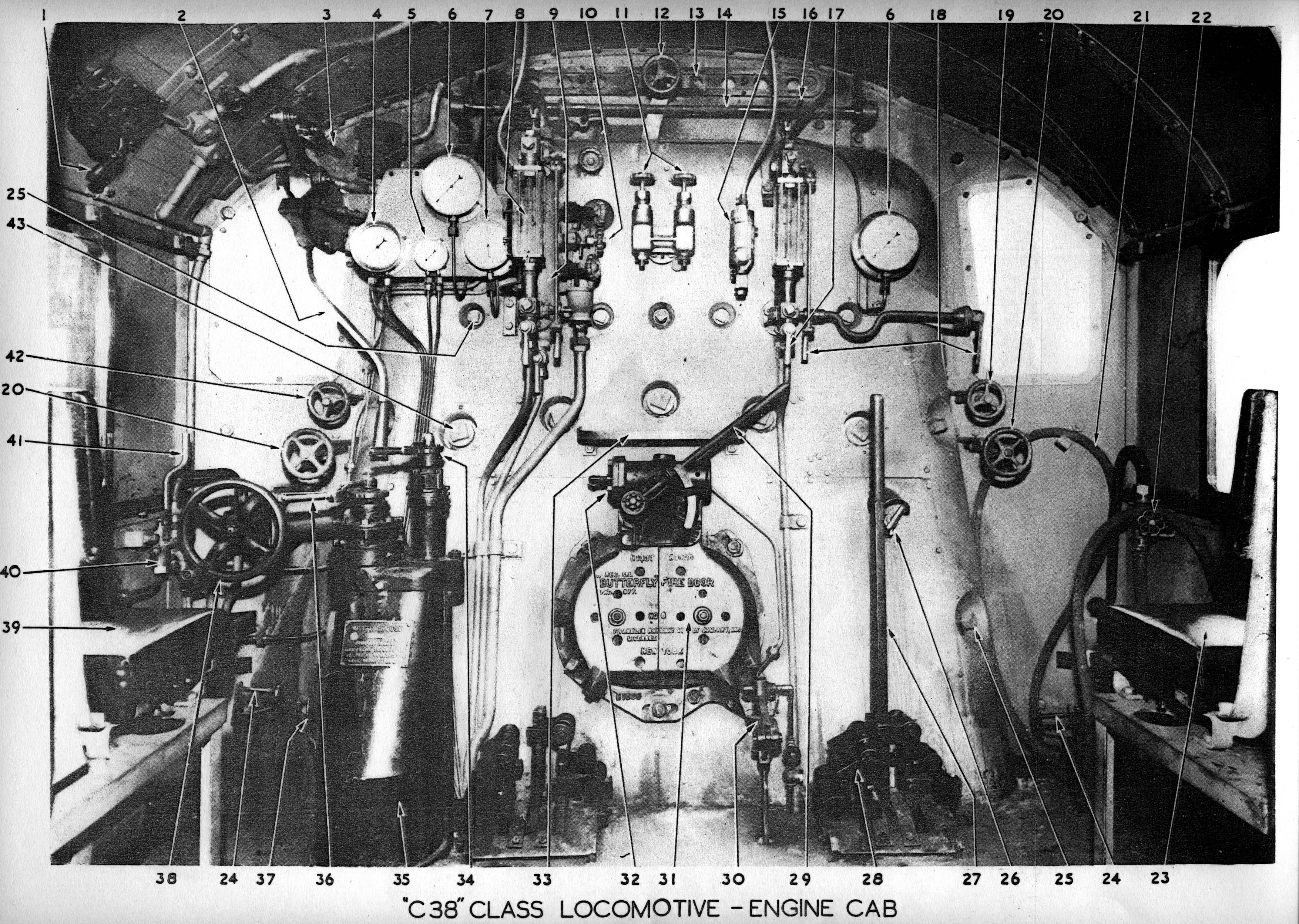
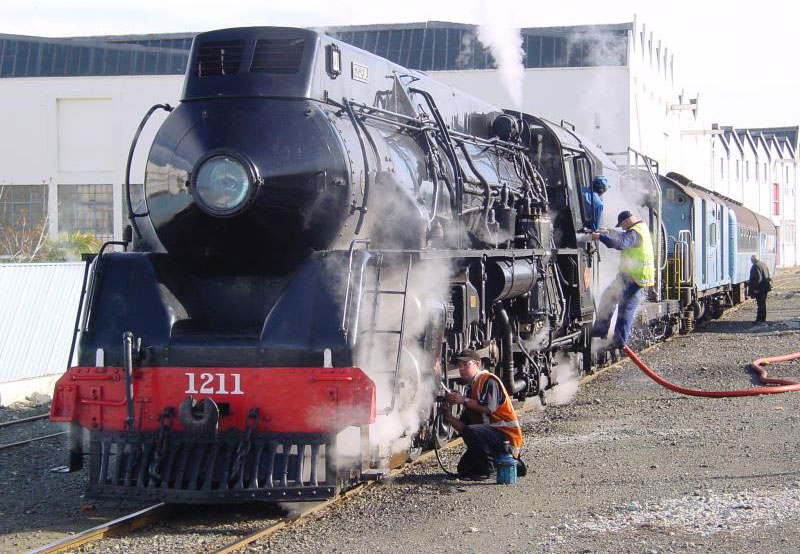
New South Wales C38 Class Locomotive
The C38 class (occasionally known as the 38 class and nicknamed "Pacifics" by some railwaymen) was a class of steam locomotive built for the New South Wales Government Railways in Australia. Constructed between January 1943 and November 1949, the 30 locomotives in the class were designed to haul express passenger services throughout New South Wales. They were the only New South Wales locomotives to use the popular Pacific 4-6-2 wheel arrangement and were the last steam locomotives in the state to be built for passenger train operation, all subsequent deliveries being specifically for freight haulage. Design The 38 class were first conceived in the 1930s when the NSWGR established there was a need for a locomotive to eliminate the complications of double heading on a number of fast intrastate passenger trains. The design was influenced by the fashion for streamlining at the time, including elements of the class J locomotives of the Norfolk and Western Railway and of some of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-6-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels and four trailing wheels. In France where the type was first used, it is known as the Baltic while it became known as the Hudson in most of North America. Overview Tender locomotives The 4-6-4 tender locomotive was first introduced in 1911 and throughout the 1920s to 1940s, the wheel arrangement was widely used in North America and to a lesser extent in the rest of the world. The type combined the basic design principles of the 4-6-2 type with an improved boiler and larger firebox that necessitated additional support at the rear of the locomotive. In general, the available tractive effort differed little from that of the 4-6-2, but the steam-raising ability was increased, giving more power at speed. The 4-6-4 was best suited to high-speed running across flat terrain. Since the type had fewer driving wheels than carryin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)