|
Don Sanche
''Don Sanche, ou Le château de l'amour'' ( en, Don Sanche, or The Castle of Love), S.1, is an opera in one act composed in 1824–25 by Franz Liszt in his early teen years, with French libretto by Théaulon and de Rancé, based on a story by Jean-Pierre Claris de Florian. For 30 years it was believed to be lost until it was rediscovered in 1903. The first modern performance took place in 1977, 74 years after its rediscovery. History Composition The opera appears to have been ready as early as September 1824. It is known that on 20 June 1825, Liszt presented an overture in his second Birmingham concert. This is probably the one from ''Don Sanche'' since no other overture exists from this period. The manuscript contains many passages that are reminiscent of the style of his compositions teacher Ferdinando Paer, who admittedly helped Liszt with orchestration. Liszt received a mere 170 francs for his opera (approximately 2100 dollars in 2016 USD). Later in the 1840s, Liszt tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Liszt
Franz Liszt, in modern usage ''Liszt Ferenc'' . Liszt's Hungarian passport spelled his given name as "Ferencz". An orthographic reform of the Hungarian language in 1922 (which was 36 years after Liszt's death) changed the letter "cz" to simply "c" in all words except surnames; this has led to Liszt's given name being rendered in modern Hungarian usage as "Ferenc". From 1859 to 1867 he was officially Franz Ritter von Liszt; he was created a ''Ritter'' (knight) by Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria, Francis Joseph I in 1859, but never used this title of nobility in public. The title was necessary to marry the Princess Carolyne zu Sayn-Wittgenstein without her losing her privileges, but after the marriage fell through, Liszt transferred the title to his uncle Eduard in 1867. Eduard's son was Franz von Liszt., group=n (22 October 1811 – 31 July 1886) was a Hungarian composer, pianist and teacher of the Romantic music, Romantic period. With a diverse List of compositions by Franz L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Czerny
Carl Czerny (; 21 February 1791 – 15 July 1857) was an Austrian composer, teacher, and pianist of Czech origin whose music spanned the late Classical and early Romantic eras. His vast musical production amounted to over a thousand works and his books of studies for the piano are still widely used in piano teaching. He was one of Ludwig van Beethoven's best-known pupils. Early life Infancy Carl Czerny was born in Vienna (Leopoldstadt) and was baptized in St. Leopold parish. His parents were of Czech origin; his mother was Moravian. His parents spoke Czech with him. Czerny came from a musical family: his grandfather was a violinist at Nymburk, near Prague, and his father, Wenzel, was an oboist, organist and pianist. When Czerny was six months old, his father took a job as a piano teacher at a Polish manor and the family moved to Poland, where they lived until the third partition of Poland prompted the family to return to Vienna in 1795. As a child prodigy, Czerny began playin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One-act Operas
A one-act play is a play that has only one act, as distinct from plays that occur over several acts. One-act plays may consist of one or more scenes. The 20-40 minute play has emerged as a popular subgenre of the one-act play, especially in writing competitions. One act plays make up the overwhelming majority of Fringe Festival shows including at the Edinburgh Fringe Festival. The origin of the one-act play may be traced to the very beginning of recorded Western drama: in ancient Greece, ''Cyclops'', a satyr play by Euripides, is an early example. The satyr play was a farcical short work that came after a trilogy of multi-act serious drama plays. A few notable examples of one act plays emerged before the 19th century including various versions of the Everyman play and works by Moliere and Calderon.Francis M. Dunn. ''Tragedy's End: Closure and Innovation in Euripidean Drama''. Oxford University Press (1996). One act plays became more common in the 19th century and are now a standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French-language Operas
French opera is one of Europe's most important operatic traditions, containing works by composers of the stature of Rameau, Berlioz, Gounod, Bizet, Massenet, Debussy, Ravel, Poulenc and Messiaen. Many foreign-born composers have played a part in the French tradition as well, including Lully, Gluck, Salieri, Cherubini, Spontini, Meyerbeer, Rossini, Donizetti, Verdi and Offenbach. French opera began at the court of Louis XIV of France with Jean-Baptiste Lully's ''Cadmus et Hermione'' (1673), although there had been various experiments with the form before that, most notably '' Pomone'' by Robert Cambert. Lully and his librettist Quinault created ''tragédie en musique'', a form in which dance music and choral writing were particularly prominent. Lully's most important successor was Rameau. After Rameau's death, the German Gluck was persuaded to produce six operas for the Paris, Parisian stage in the 1770s. They show the influence of Rameau, but simplified and with greater foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operas By Franz Liszt
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by Singing, singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a libretto, librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, Theatrical scenery, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conducting, conductor. Although musical theatre is closely related to opera, the two are considered to be distinct from one another. Opera is a key part of the Western culture#Music, Western classical music tradition. Originally understood as an entirely sung piece, in contrast to a play with songs, opera has come to include :Opera genres, numerous genres, including some that include spoken dialogue such as ''Singspiel'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungaroton
Hungaroton is the oldest record and music publisher company in Hungary. Hungaroton was founded in 1951, when its only competitors in the Hungarian music market were record labels like Melodiya, Supraphon and from other socialist countries. Previously called Qualiton, its name was changed to Hungaroton in the mid-1960s, though the Qualiton brand remained as a label for operetta and gypsy music releases. Also new popular music, rock and jazz labels (Pepita, Bravó, and Krém) were founded. In the early 1990s the massive import of foreign records caused a serious decrease in Hungaroton's sales. Although the original company went into liquidation, new and smaller companies arose on the ruins of Hungaroton. The Hungaroton Gong and Hungaroton Classic companies went private in 1995, and were reunited in 1998 under the name Hungaroton Records Publisher Ltd. Nowadays it publishes approximately 150 new records per year, half of it classical and half of it popular music. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julia Hamari
Julia Hamari (born 21 November 1942) is a Hungarian mezzo-soprano and alto singer in opera and concert, appearing internationally. She is an academic voice teacher in Stuttgart. Professional career Julia Hamari was born in Budapest where she received her vocal training with Fatime Martins and Jenö Sipos. She studied at the Franz Liszt Academy of Music and received her diploma for both singer and singing teacher. In 1964 she won the Erkel International Singing Competition in Budapest. She then continued her studies at the Staatliche Hochschule für Musik Stuttgart until 1966. In 1966, she made her debut as a soloist in Bach's ''St Matthew Passion'' with Karl Richter in Vienna, together with Teresa Stich-Randall, Peter Schreier, Hermann Prey and Ernst Gerold Schramm. Opera Her opera debut was the part of Mercedes in Bizet's ''Carmen'' at the Salzburg Festival of 1967 (with Grace Bumbry, Jon Vickers and Mirella Freni, Herbert von Karajan conducting). Shortly thereafter she appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baritone
A baritone is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the bass and the tenor voice-types. The term originates from the Greek (), meaning "heavy sounding". Composers typically write music for this voice in the range from the second F below middle C to the F above middle C (i.e. F2–F4) in choral music, and from the second A below middle C to the A above middle C (A2 to A4) in operatic music, but the range can extend at either end. Subtypes of baritone include the baryton-Martin baritone (light baritone), lyric baritone, ''Kavalierbariton'', Verdi baritone, dramatic baritone, ''baryton-noble'' baritone, and the bass-baritone. History The first use of the term "baritone" emerged as ''baritonans'', late in the 15th century, usually in French sacred polyphonic music. At this early stage it was frequently used as the lowest of the voices (including the bass), but in 17th-century Italy the term was all-encompassing and used to describe the averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
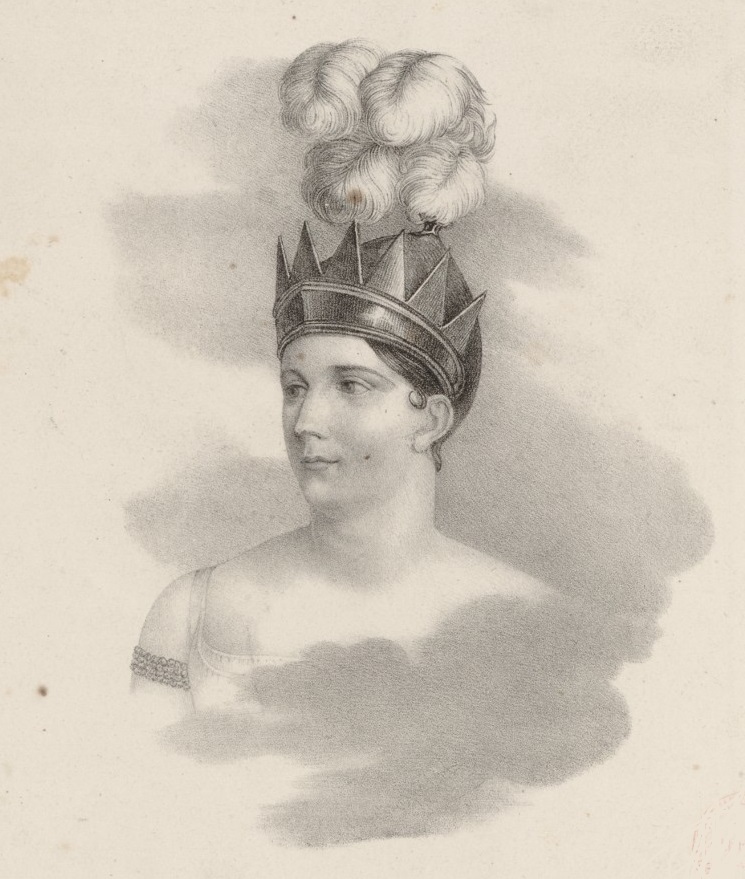
Caroline Grassari
Caroline Grassari, born Marie-Caroline-Josephine Gérard (baptised 15 June 1795 – after 1832) was a French opera singer active at the Paris Opéra from 1816 to 1828 where she sang leading soprano roles. Amongst the many roles she created were Almazie in Isouard's ''Aladin ou La lampe merveilleuse'' and Aurora in Carafa's ''La belle au bois dormant''. Life and career Grassari was born Marie-Caroline-Josephine Gérard in Tongeren, Belgium, where she was baptised on 15 June 1795. Her father was , a highly decorated French general. Her mother, Anne-Christine Tournay, was the daughter of Tongeren's Burgomaster. Her parents divorced in her childhood and she initially lived with her mother in Belgium, where she began her musical studies. In 1814, she was sent to Paris under the care of her father and finished her studies at the Conservatoire de Paris. She made her stage debut under the name "Mademoiselle Grassari" at the Paris Opéra on 13 February 1816 singing Antigone in Sacchini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mezzo-soprano
A mezzo-soprano or mezzo (; ; meaning "half soprano") is a type of classical female singing voice whose vocal range lies between the soprano and the contralto voice types. The mezzo-soprano's vocal range usually extends from the A below middle C to the A two octaves above (i.e. A3–A5 in scientific pitch notation, where middle C = C4; 220–880 Hz). In the lower and upper extremes, some mezzo-sopranos may extend down to the F below middle C (F3, 175 Hz) and as high as "high C" (C6, 1047 Hz). The mezzo-soprano voice type is generally divided into the coloratura, lyric, and dramatic mezzo-soprano. History While mezzo-sopranos typically sing secondary roles in operas, notable exceptions include the title role in Bizet's '' Carmen'', Angelina (Cinderella) in Rossini's ''La Cenerentola'', and Rosina in Rossini's ''Barber of Seville'' (all of which are also sung by sopranos and contraltos). Many 19th-century French-language operas give the leading female role to mezzos, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soprano
A soprano () is a type of classical female singing voice and has the highest vocal range of all voice types. The soprano's vocal range (using scientific pitch notation) is from approximately middle C (C4) = 261 Hz to "high A" (A5) = 880 Hz in choral music, or to "soprano C" (C6, two octaves above middle C) = 1046 Hz or higher in operatic music. In four-part chorale style harmony, the soprano takes the highest part, which often encompasses the melody. The soprano voice type is generally divided into the coloratura, soubrette, lyric, spinto, and dramatic soprano. Etymology The word "soprano" comes from the Italian word '' sopra'' (above, over, on top of),"Soprano" '' |
Adolphe Nourrit
Adolphe Nourrit (3 March 1802 – 8 March 1839) was a French operatic tenor, librettist, and composer. One of the most esteemed opera singers of the 1820s and 1830s, he was particularly associated with the works of Gioachino Rossini and Giacomo Meyerbeer. Early life Nourrit was born on 3 March 1802 and raised in Montpellier, Hérault. His father, Louis Nourrit, was a well-known operatic tenor and diamond merchant. Louis' example deeply influenced Adolphe (and Adolphe's brother Auguste, who would also become a tenor). Adolphe studied singing and musical theory with his father and then, despite his father's objections, took lessons with Manuel del Pópulo Vicente García. He began his performing career shortly after finishing his studies with García, which lasted for 18 months. Career Not yet 20 years of age, Adolphe Nourrit made his professional operatic debut in 1821 as Pylades in Gluck's '' Iphigénie en Tauride'', being welcomed by his father performing the tiny role of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |