|
Domain (biology)
In biological taxonomy, a domain ( or ) (Latin: ''regio''), also dominion, superkingdom, realm, or empire, is the highest taxonomic rank of all organisms taken together. It was introduced in the three-domain system of taxonomy devised by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler and Mark Wheelis in 1990. According to the domain system, the tree of life consists of either three domains such as Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya, or two domains consisting of Archaea and Bacteria, with Eukarya included in Archaea. The first two are all prokaryotes, single-celled microorganisms without a membrane-bound nucleus. All organisms that have a cell nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles are included in Eukarya. Non-cellular life is not included in this system. Alternatives to the three-domain system include the earlier two-empire system (with the empires Prokaryota and Eukaryota), and the eocyte hypothesis (with two domains of Bacteria and Archaea, with Eukarya included as a branch of Arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations.Based on definition from: Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicellular Organism
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. All prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular such as protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early protocells possibly emerging 3.8–4.0 billion years ago. Although some prokaryotes live in colonies, they are not specialised cells with differing functions. These organisms live together, and each cell must carry out all life processes to survive. In contrast, even the simplest multicellular organisms have cells that depend on each other to survive. Most multicellular organisms have a unicellular life-cycle stage. Gametes, for example, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1977
Events January * January 8 – Three bombs explode in Moscow within 37 minutes, killing seven. The bombings are attributed to an Armenian separatist group. * January 10 – Mount Nyiragongo erupts in eastern Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo). * January 17 ** 49 marines from the and are killed as a result of a collision in Barcelona harbour, Spain. * January 18 ** Scientists identify a previously unknown bacterium as the cause of the mysterious Legionnaires' disease. ** Australia's worst railway disaster at Granville, a suburb of Sydney, leaves 83 people dead. ** SFR Yugoslavia Prime minister Džemal Bijedić, his wife and 6 others are killed in a plane crash in Bosnia and Herzegovina. * January 19 – An Ejército del Aire CASA C-207C Azor (registration T.7-15) plane crashes into the side of a mountain near Chiva, on approach to Valencia Airport in Spain, killing all 11 people on board. * January 20 – Jimmy Carter is sworn in as the 39th P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history and was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey. Darwin's early interest in nature led him to neglect his medical education at the University of Edinburgh; instead, he helped to investigate marine invertebrates. His studies at the University of Cambridge's Christ's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Century
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. Among other things, a taxonomy can be used to organize and index knowledge (stored as documents, articles, videos, etc.), such as in the form of a library classification system, or a search engine taxonomy, so that users can more easily find the information they are searching for. Many taxonomies are hierarchies (and thus, have an intrinsic tree structure), but not all are. Originally, taxonomy referred only to the categorisation of organisms or a particular categorisation of organisms. In a wider, more general sense, it may refer to a categorisation of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such a categorisation. Taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon")." Taxonomy is different from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his Nobility#Ennoblement, ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royall T
Royall may refer to: ;Surname * Isaac Royall, Jr. (1719–1781), American landowner, gave land for Harvard Law School * Anne Royall (1769–1854), travel writer and newspaper editor * William B. Royall (1825–1895), US Army general * J. Powell Royall (1874–1945), politician in Virginia, USA * Kenneth Claiborne Royall (1894–1971), US Army general, Secretary of the Army * Joe Royall (1912–1975), baseball player * Kenneth Claiborne Royall, Jr. (1918–1999), politician in North Carolina, USA * Robert V. Royall (born 1934), former US ambassador to Tanzania * Janet Royall, Baroness Royall of Blaisdon (born 1955), British politician, principal of Somerville College, Oxford * Paul Royall, BBC journalist ;Given name * Royall Tyler (1757–1826), American jurist and playwright * Royall T. Wheeler (1810–1864), judge in Texas, USA * Royall Tyler (historian) (1884–1953), American historian * Royall T. Moore (1930–2014), American mycologist * Royall Tyler (academic) (bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
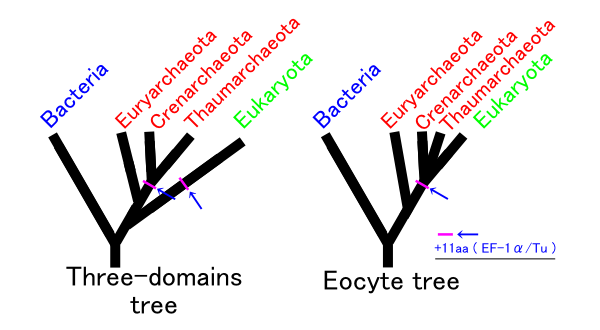
Eocyte Hypothesis
The eocyte hypothesis in evolutionary biology proposes the origin of eukaryotes from a group of prokaryotes called eocytes (later classified as Thermoproteota, a group of archaea). After his team at the University of California, Los Angeles discovered eocytes in 1984, James A. Lake formulated the hypothesis as "eocyte tree" that proposed eukaryotes as part of archaea. Lake hypothesised the tree of life as having only two primary branches: Parkaryoates that include Bacteria and Archaea, and karyotes that comprise Eukaryotes and eocytes. Parts of this early hypothesis were revived in a newer two-domain system of biological classification which named the primary domains as Archaea and Bacteria. Lake's hypothesis was based on an analysis of the structural components of ribosomes. It was largely ignored, being overshadowed by the three-domain system which relied on more precise genetic analysis. In 1990, Carl Woese and his colleagues proposed that cellular life consists of three dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-empire System
The two-empire system (two-superkingdom system) was the top-level biological classification system in general use before the establishment of the three-domain system. It classified cellular life into Prokaryota and Eukaryota as either "empires" or "superkingdoms". When the three-domain system was introduced, some biologists preferred the two-superkingdom system, claiming that the three-domain system overemphasized the division between Archaea and Bacteria. However, given the current state of knowledge and the rapid progress in biological scientific advancement, especially due to genetic analyses, that view has all but vanished. Some prominent scientists, such as the late Thomas Cavalier-Smith, still hold and held to the two-empire system. The late Ernst Mayr, one of the 20th century's leading evolutionary biologists, wrote dismissively of the three-domain system, "I cannot see any merit at all in a three empire cladification." Additionally, the scientist Radhey Gupta argues for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-cellular Life
Non-cellular life, or acellular life is life that exists without a cellular structure for at least part of its life cycle. Historically, most (descriptive) definitions of life postulated that an organism must be composed of one or more cells, but this is no longer considered necessary, and modern criteria allow for forms of life based on other structural arrangements. The primary candidates for non-cellular life are viruses. Some biologists consider viruses to be organisms, but others do not. Their primary objection is that no known viruses are capable of autonomous reproduction: they must rely on cells to copy them. Engineers sometimes use the term " artificial life" to refer to software and robots inspired by biological processes, but these do not satisfy any biological definition of life. Viruses as non-cellular life The nature of viruses was unclear for many years following their discovery as pathogens. They were described as poisons or toxins at first, then as "infe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane-bound Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the suffix ''-elle'' being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bound organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bound organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some function units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst. Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organelles, particularly in eukaryotic cells. They include structures that make up the endomembrane system (such as the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, and G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |