|
Dollosuchus
''Dollosuchus'' (meaning "Louis Dollo's crocodile") is an extinct monospecific genus of tomistomine crocodilian originally named as a species of ''Gavialis''. It is a basal form possibly related to ''Kentisuchus'', according to several phylogenetic analyses that have been conducted in recent years, and is the oldest known tomistomine to date. Fossils have been found from Belgium and the United Kingdom.Swinton, W. E. (1937)The Crocodile of Maransart (Dollosuchus dixoni [Owen]).''Mémoire'' 80: 3-46 It had large supratemporal fenestrae in relation to its orbits, similar to ''Kentisuchus'' and ''Thecachampsa''. ''Dollosuchus'' was originally described on the basis of numerous mandibular fragments found from the Early to Middle Eocene Bracklesham Beds Formation in the United Kingdom. The material cannot be distinguished from other related longirostrine, or long-snouted, crocodilians. A nearly complete skeleton from Belgium (IRScNB 482) discovered in 1915 and described by Swi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomistomine
Tomistominae is a subfamily of crocodylians that includes one living species, the false gharial. Many more extinct species are known, extending the range of the subfamily back to the Eocene epoch. In contrast to the false gharial, which is a freshwater species that lives only in southeast Asia, extinct tomistomines had a global distribution and lived in estuaries and along coastlines. The classification of tomistomines among Crocodylia has been in flux; while traditionally thought to be within Crocodyloidea, molecular evidence indicates that they are more closely related to true gharials as members of Gavialoidea. Description Tomistomines have narrow or longirostrine snouts like gharials. The living false gharial lives in fresh water and uses its long snout and sharp teeth to catch fish, although true gharials are more adapted toward piscivory, or fish-eating. Despite the similarity with gharials, the shapes of bones in tomistomine skulls link them with crocodiles. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
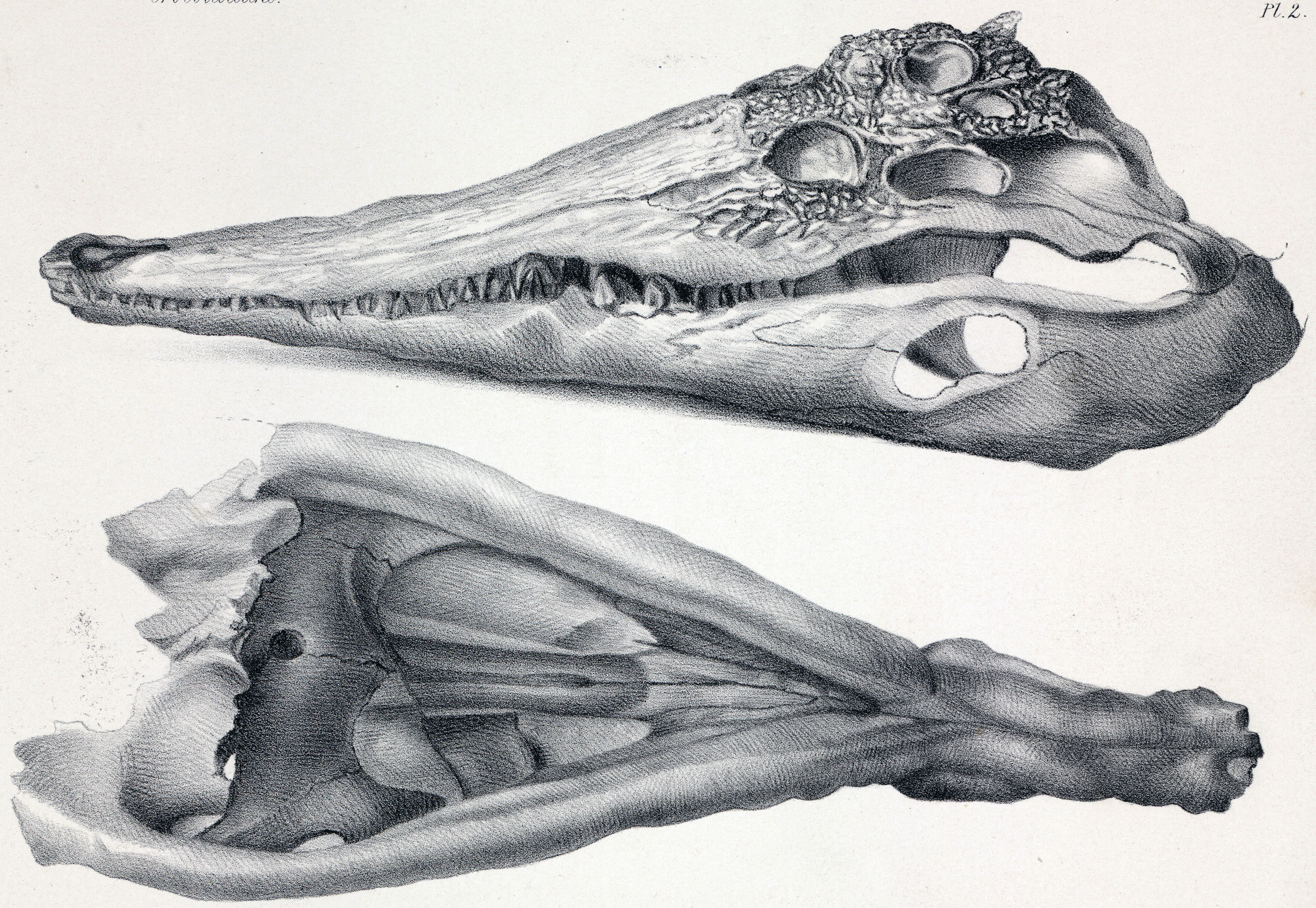
Dollosuchoides Densmorei
''Dollosuchoides'', colloquially known as the Crocodile of Maransart, is an extinct monospecific genus of gavialoid crocodilian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found in the Brussel Formation of Maransart, Belgium and date back to the middle Eocene. The holotype, IRScNB 482, was discovered in 1915 and it was prepared during 1926–1927 by M. Hubert, J. Mehschaert and M. Jean de Kleermaeker, and also in 1927, Louis Dollo had the holotype put on display in the Museum of Natural Sciences and he intended to describe the specimen but he died in 1931 before he was able to describe it and the specimen was eventually referred to '' Dollosuchus'' by Swinton (1937)Swinton, W. E. (1937)The Crocodile of Maransart (Dollosuchus dixoni [Owen]).''Mémoire'' 80: 3–46 until it was moved to its own genus by Brochu (2007). It is currently housed in the Gand Museum in Belgium. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram based morphological studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavialis
''Gavialis'' is a genus of crocodylians that includes the living gharial ''Gavialis gangeticus'' and one known extinct species, '' Gavialis bengawanicus.'' ''G. gangeticus'' comes from the Indian Subcontinent, while ''G. bengawanicus'' is known from Java. ''Gavialis'' likely first appeared in the Indian Subcontinent in the Pliocene and dispersed into the Malay Archipelago through a path called the Siva–Malayan route in the Quaternary. Remains attributed to ''Gavialis'' have also been found on Sulawesi and Woodlark Island east of the Wallace Line, suggesting a prehistoric lineage of ''Gavialis'' was able to traverse marine environments and reach places possibly as far as western Oceania. The genus ''Gavialis'' was reevaluated in 2018 based on specimens in the Natural History Museum, London that were collected in the Sivalik Hills. The author concluded that ''G. gangeticus'' and '' G. bengawanicus'' are the only two species in the genus ''Gavialis'', with '' G. hysudricus'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charactosuchus
''Charactosuchus'' is an extinct genus of crocodilian. It was assigned to the family Crocodylidae in 1988. Specimens have been found in Colombia, Brazil, Jamaica, and possibly Florida and South Carolina. It was gharial-like in appearance with its long narrow snout but bore no relation to them, being more closely related to modern crocodiles than to gharials. Species South America The type species, ''C. fieldsi'', has been found from the Villavieja Formation at the Konzentrat-Lagerstätte La Venta in Colombia and dates back to the Middle Miocene (Laventan). It has also been found in the Mayoan to Montehermosan Urumaco Formation at Urumaco in Venezuela,''Charactosuchus'' at Fossilworks.org and in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in size only by Brussels and Antwerp. It is a port and university city. The city originally started as a settlement at the confluence of the Rivers Scheldt and Leie and in the Late Middle Ages became one of the largest and richest cities of northern Europe, with some 50,000 people in 1300. The municipality comprises the city of Ghent proper and the surrounding suburbs of Afsnee, Desteldonk, Drongen, Gentbrugge, Ledeberg, Mariakerke, Mendonk, Oostakker, Sint-Amandsberg, Sint-Denijs-Westrem, Sint-Kruis-Winkel, Wondelgem and Zwijnaarde. With 262,219 inhabitants at the beginning of 2019, Ghent is Belgium's second largest municipality by number of inhabitants. The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers an area of and had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these items available for public viewing through exhibits that may be permanent or temporary. The largest museums are located in major cities throughout the world, while thousands of local museums exist in smaller cities, towns, and rural areas. Museums have varying aims, ranging from the conservation and documentation of their collection, serving researchers and specialists, to catering to the general public. The goal of serving researchers is not only scientific, but intended to serve the general public. There are many types of museums, including art museums, natural history museums, science museums, war museums, and children's museums. According to the International Council of Museums (ICOM), there are more than 55,000 museums in 202 countrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(2).jpg)
