|
Dogs Trust
Dogs Trust, known until 2003 as the National Canine Defence League, is a British animal welfare charity and humane society which specialises in the well-being of dogs. It is the largest dog welfare charity in the United Kingdom, caring for over 15,000 animals each year. Dogs Trust's primary objective is to protect all dogs in the UK and elsewhere from maltreatment, cruelty and suffering. It focuses on the rehabilitation and rehoming of dogs which have been either abandoned or given up by their owners through rehoming services. Dogs Trust has 22 rehoming centres across the UK and Ireland. Its first international rehoming centre opened in November 2009 in Dublin, Ireland. Its charity guidelines ensure that no mentally or physically healthy dog taken into the protection of its rehoming centres are euthanised. Dogs Trust also manages microchipping and neutering schemes in the United Kingdom and abroad, in order to reduce the number of unwanted litters of puppies and stray dogs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivisection
Vivisection () is surgery conducted for experimental purposes on a living organism, typically animals with a central nervous system, to view living internal structure. The word is, more broadly, used as a pejorative catch-all term for Animal testing#Definitions, experimentation on live animalsTansey, E.MReview of ''Vivisection in Historical Perspective by Nicholaas A. Rupke, book reviews, National Center for Biotechnology Information, p. 226. by organizations opposed to animal experimentation,Yarri, Donna''The Ethics of Animal Experimentation: A Critical Analysis and Constructive Christian Proposal, Oxford University Press, 2005, p. 163. but the term is rarely used by practising scientists. Human vivisection, such as live organ harvesting, has been perpetrated as a form of torture. Animal vivisection Research requiring vivisection techniques that cannot be met through other means is often subject to an external ethics review in conception and implementation, and in many jurisdict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Executive
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a central executive officer (CEO), chief administrator officer (CAO) or just chief executive (CE), is one of a number of corporate executives charged with the management of an organization especially an independent legal entity such as a company or nonprofit institution. CEOs find roles in a range of organizations, including public and private corporations, non-profit organizations and even some government organizations (notably state-owned enterprises). The CEO of a corporation or company typically reports to the board of directors and is charged with maximizing the value of the business, which may include maximizing the share price, market share, revenues or another element. In the non-profit and government sector, CEOs typically aim at achieving outcomes related to the organization's mission, usually provided by legislation. CEOs are also frequently assigned the role of main manager of the organization and the highest-ranking offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosnia And Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and Herzegovina borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest. In the south it has a narrow coast on the Adriatic Sea within the Mediterranean, which is about long and surrounds the town of Neum. Bosnia, which is the inland region of the country, has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. In the central and eastern regions of the country, the geography is mountainous, in the northwest it is moderately hilly, and in the northeast it is predominantly flat. Herzegovina, which is the smaller, southern region of the country, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous. Sarajevo is the capital and the largest city of the country followed by Banja Luka, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Media Age
''New Media Age'' (''NMA'') was a weekly news magazine, covering business is use of interactive media in the UK is now ''Econsultancy''. New Media Age is owned by Centaur Media, Centaur Media plc. It was launched as a newsletter in May 1995 under editor Phil Dwyer with reporters Nick Jones and Catherine Stewart. They worked together in Centaur's newsletter's division and conceived the idea in 1994 Once considered title for the publication was InfoBahn. They were joined by freelancer Julianna Koranteng. They were joined by Mike Butcher in 1996, who subsequently became Deputy Editor under Dwyer. In 1998, Mike Butcher took over as editor, when Dwyer, Jones and Stewart left to start the European operation of Jupiter Research. Later that year, the title moved to a magazine format. Butcher resigned in 2000 to join The Industry Standard Europe. He was replaced by Michael Nutley in 2000. In 2007, Nutley became editor-in-chief, and Justin Pearse was promoted from deputy editor to editor. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
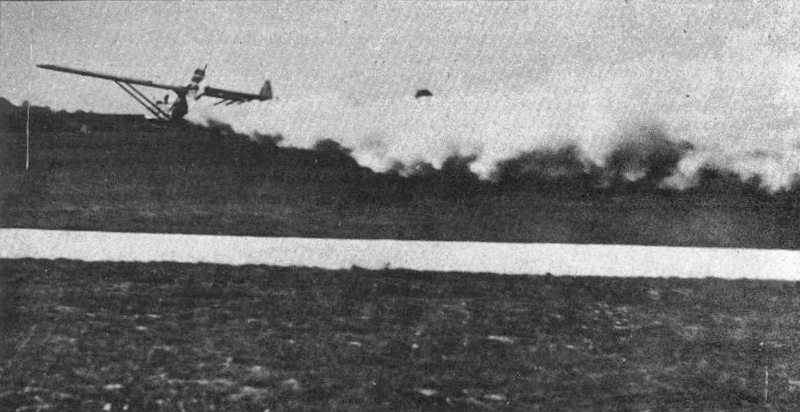
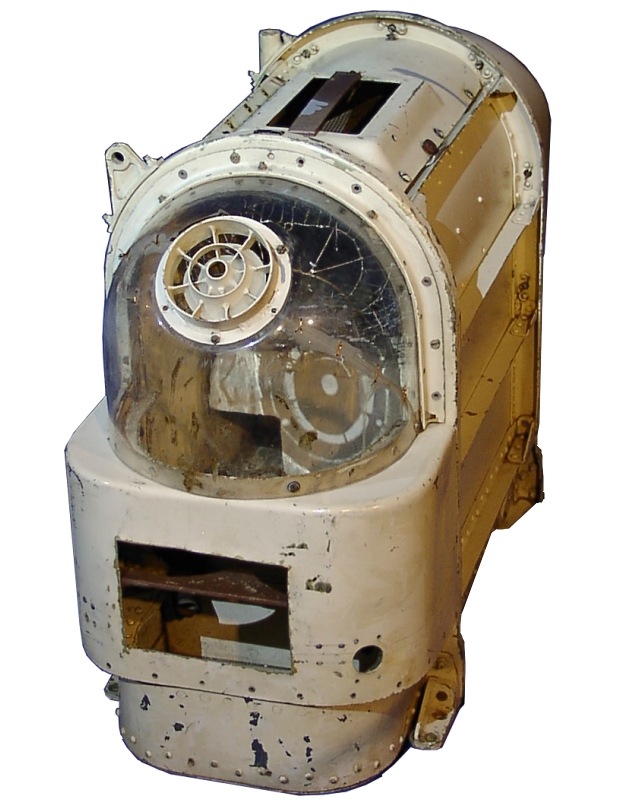
Laika
Laika (russian: link=no, Лайка; – 3 November 1957) was a Soviet space dog who was one of the first animals in space and the first to orbit the Earth. A stray mongrel from the streets of Moscow, she flew aboard the Sputnik 2 spacecraft, launched into low orbit on 3 November 1957. As the technology to de-orbit had not yet been developed, Laika's survival was never expected. She died of overheating hours into the flight, on the craft's fourth orbit. Little was known about the impact of spaceflight on living creatures at the time of Laika's mission, and animal flights were viewed by engineers as a necessary precursor to human missions. The experiment, which monitored Laika's vital signs, aimed to prove that a living organism could survive being launched into orbit and continue to function under conditions of weakened gravity and increased radiation, providing scientists with some of the first data on the biological effects of spaceflight. Laika died within hours f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Flight
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly spacecraft into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in orbit around Earth, but also includes space probes for flights beyond Earth orbit. Such spaceflight operates either by telerobotic or autonomous control. The more complex human spaceflight has been pursued soon after the first orbital satellites and has reached the Moon and permanent human presence in space around Earth, particularly with the use of space stations. Human spaceflight programs include the Soyuz, Shenzhou, the past Apollo Moon landing and the Space Shuttle programs, with currently the International Space Station as the main destination of human spaceflight missions while China's Tiangong Space Station is under construction. Spaceflight is used for placing in Earth's orbit communications satellites, reconnaissance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Space Dogs
During the 1950s and 1960s the Soviet space program used dogs for sub-orbital and orbital space flights to determine whether human spaceflight was feasible. In this period, the Soviet Union launched missions with passenger slots for at least 57 dogs. The number of dogs in space is smaller, as some dogs flew more than once. Most survived; the few that died were lost mostly through technical failures, according to the parameters of the test. A notable exception is Laika, the first animal to be sent into orbit, whose death during the 3 November 1957 Sputnik 2 mission was expected from its outset. Training Dogs were the preferred animal for the experiments because scientists felt dogs were well suited to endure long periods of inactivity. As part of their training, they were confined in small boxes for 15–20 days at a time. Stray dogs, rather than animals accustomed to living in a house, were chosen because the scientists felt they would be able to tolerate the rigorous and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Pet Massacre
The British pet massacre was an event in 1939 in the United Kingdom where over 750,000 pets were killed in preparation for food shortages during World War II."What happened to Britain's pets during the second World War" ''Express'', Clare Campbell, Oct 31, 2013 Background  In 1939, the British government formed the National Air Raid Precautions Animals Committee (NARPAC) to decide what to do ...
In 1939, the British government formed the National Air Raid Precautions Animals Committee (NARPAC) to decide what to do ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Euthanasia
Animal euthanasia ( euthanasia from el, εὐθανασία; "good death") is the act of killing an animal or allowing it to die by withholding extreme medical measures. Reasons for euthanasia include incurable (and especially painful) conditions or diseases, lack of resources to continue supporting the animal, or laboratory test procedures. Euthanasia methods are designed to cause minimal pain and distress. Euthanasia is distinct from animal slaughter and pest control although in some cases the procedure is the same. In domesticated animals, this process is commonly referred to by euphemisms such as "put down" or "put to sleep". Methods The methods of euthanasia can be divided into pharmacological and physical methods. Acceptable pharmacological methods include injected drugs and gases that first depress the central nervous system and then cardiovascular activity. Acceptable physical methods must first cause rapid loss of consciousness by disrupting the central nervous sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handgun
A handgun is a short-barrelled gun, typically a firearm, that is designed to be usable with only one hand. It is distinguished from a long gun (i.e. rifle, shotgun or machine gun, etc.), which needs to be held by both hands and also braced against the shoulder to be used properly. The two most common types of handguns in modern times are revolvers and semi-automatic pistols, although other types such as derringers and machine pistols also see infrequent usage. Before commercial mass production, handguns were often considered a badge of office, comparable to a ceremonial sword. As they had limited utility and were more expensive than the long guns of the era, the few who could only afford to purchase them carried these handguns. However, in 1836, Samuel Colt patented the Colt Paterson, the first practical mass-produced revolver, which was capable of firing five shots in rapid succession and very quickly became a popular defensive weapon, giving rise to the saying, "God crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |