|
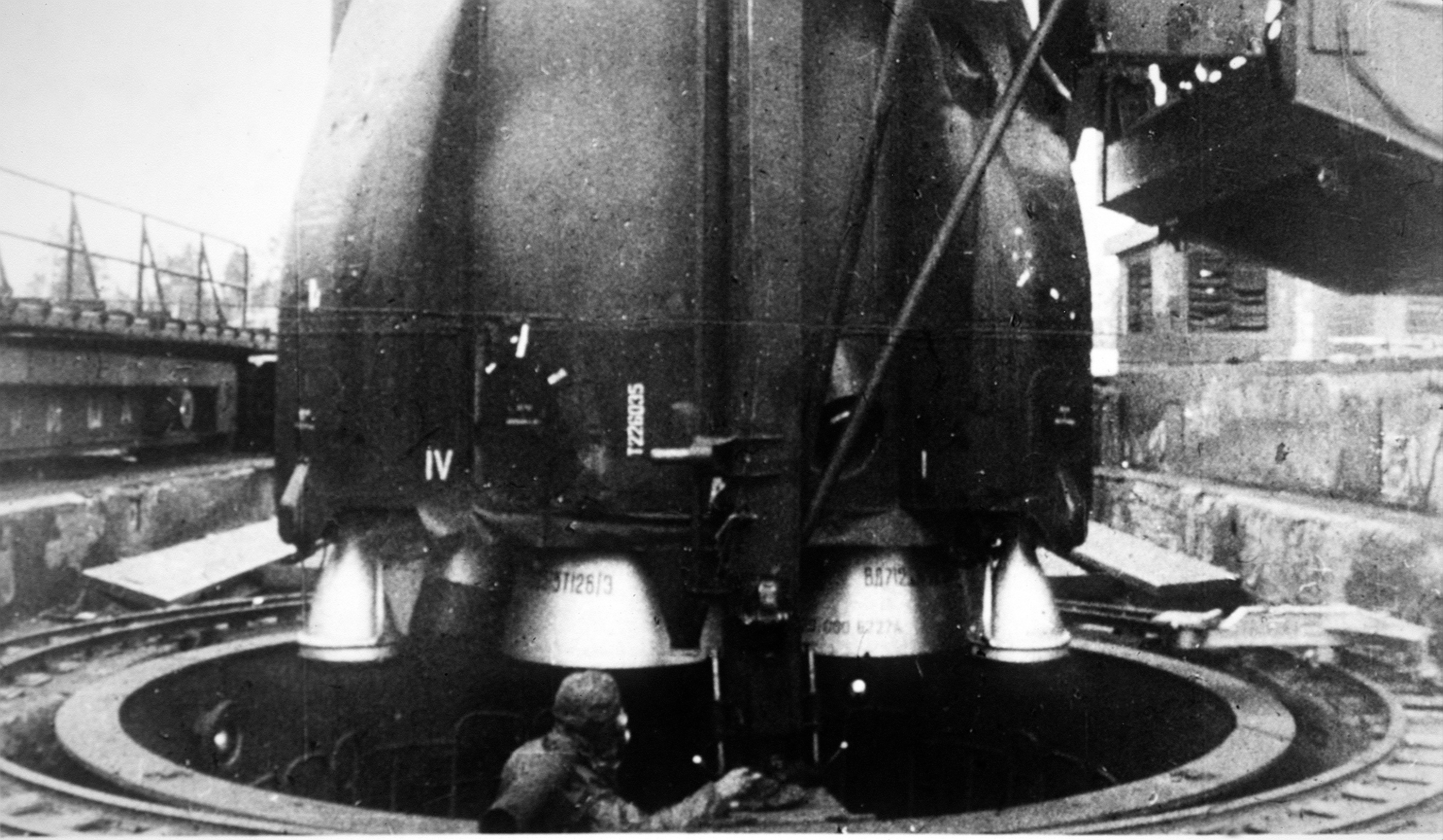
Dnepr Rocket
The Dnepr rocket (russian: Днепр, translit=Dnepr; uk, Дніпро, translit=Dnipró) was a space launch vehicle named after the Dnieper River. It was a converted ICBM used for launching artificial satellites into orbit, operated by launch service provider ISC Kosmotras. The first launch, on April 21, 1999, successfully placed UoSAT-12, a 350 kg demonstration mini-satellite, into a 650 km circular Low Earth orbit. History The Dnepr was based on the R-36MUTTH Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM)called the ''SS-18 Satan'' by NATOdesigned in the 1970s by the Yuzhnoe Design Bureau in Dnepropetrovsk, Ukrainian SSR. The Dnepr control system was developed and produced by the JSC "Khartron", Kharkiv. The Dnepr was a three-stage rocket using storable hypergolic liquid propellants. The launch vehicles used for satellite launches have been withdrawn from ballistic missile service with the Russian Strategic Rocket Forces and stored for commercial use. A group o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Rocket
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch control center, launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to large operating costs. An orbital spaceflight, orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital spaceflight, Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles are multistage rockets which use chemical propellants such as Solid-propellant rocket, solid fuel, liquid hydrogen, kerosene, liquid oxygen, or Hypergolic propellants. Launch vehicles are cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RD-0255
The RD-0255 is a propulsion module composed of an RD-0256 main engine and a RD-0257 vernier engine. Both are liquid rocket engine, burning UDMH in N2O4. The RD-0256 main engine operates in the oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle, while the vernier RD-0257 uses the simpler gas generator cycle. It was used on the R-36MUTTKh (GRAU:15A18) and R-36M2 (GRAU:15A18M). Subsequently, it has been in the Dnepr second stage and as of 2016 it is still in active service. The RD-0256 is an improved version of the RD-0228 (GRAU: 15D84), itself composed of an RD-0229 (GRAU: 15D84) main engine and a RD-0230 (GRAU: 15D79) vernier engine. The RD-0228 was developed between 1967 and 1974 for the first generation of R-36M (GRAU: 15D83) ICBM second stage, but was replaced on subsequent iterations by the RD-0256. The RD-0228 debut was on January 21, 1973. With the START I and START II the RD-0228 was retired and its successor, the RD-0256, only continued as the Dnepr. See also * R-36M – A Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-36 (missile)
The R-36 (russian: Р-36) is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles (Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-9 Scarp. It was able to carry three warheads and was the first Soviet MRV (multiple re-entry vehicle) missile. The later version, the R-36M was produced under the GRAU designations 15A14 and 15A18 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-18 Satan. This missile was viewed by certain United States analysts as giving the Soviet Union first strike advantage over the U.S., particularly because of its rapid silo-reload ability, very heavy throw weight and extremely large number of re-entry vehicles. Some versions of the R-36M were deployed with 10 warheads and up to 40 penetration aids and the missile's high throw-weight made it theoretically capable of carrying more warheads or penetration aids. Contemporary U.S. miss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnepr 2013
Dnepr may refer to: *Dnieper, a river flowing through Russia, Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea *Dnepr (motorcycle), a Ukraininan motocycle brand *Dnepr (rocket), a 1999 space launch vehicle *Dnepr radar, Soviet space surveillance and early warning radar See also *Dnieper (other) Dnieper is a major river, rising in Russia and flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Dnieper may also refer to: * Dnieper Ukraine, usually referring territory on either side of the middle course of the Dnieper River * Battle of t ... * Dnipro (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd
Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd, or SSTL, is a company involved in the manufacture and operation of small satellites. A spin-off company of the University of Surrey, it is presently wholly owned by Airbus Defence and Space. The company began out of research efforts centred upon amateur radio satellites, known by the UoSAT (University of Surrey Satellite) name or by an OSCAR (Orbital Satellite Carrying Amateur Radio) designation. SSTL was founded in 1985, following successful trials on the use of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components on satellites, cumulating in the ''UoSat-1'' test satellite. It funds research projects with the university's Surrey Space Centre, which does research into satellite and space topics. In April 2008, the University of Surrey agreed to sell its majority share in the company to European multinational conglomerate EADS Astrium. In August 2008, SSTL opened a US subsidiary, which included both offices and a production site in Denver, Colorado; [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UoSAT-12
UoSAT-12 is a British satellite in Low Earth Orbit. It is the twelfth satellite in the University of Surrey series and was designed and built by Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd. (SSTL). It was launched into orbit in April 1999 on board a Dnepr rocket from Yasny Russia.M. Fouquet and M. SweetingUoSAT-12 minisatellite for high performance Earth observation at low cost proceedings of IAF '96. Mission UoSAT-12 was an experimental mission used to demonstrate and test a number of new technologies. Imaging cameras and a high-speed 1 Mbit/s S-band downlink (the MERLION experiment) were tested. An Internet Protocol stack was uploaded to the satellite, allowing experiments in extending the Internet to space to be made by NASA Goddard as part of its Operating Missions as Nodes on the Internet (OMNI) effort.K. Hogie, ''et al.''Using standard Internet Protocols and applications in space Computer Networks, special issue on Interplanetary Internet, vol. 47 no. 5, pp. 603-650, April 2005.K. Hogi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISC Kosmotras
The International Space Company Kosmotras or ISC Kosmotras (russian: ЗАО Международная космическая компания “Космотрас”) is a joint project, between Russia, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan, established in 1997. It developed and now operates a commercial expendable launch system using the Dnepr rocket. The Dnepr is a converted decommissioned SS-18 ICBM. ISC Kosmotras conducts Dnepr launches from Baikonur Cosmodrome and Yasny launch base in Dombarovskiy, Russia. In February 2015, following a year of strained relations as a result of a Russian military intervention into Ukraine, Russia announced that it would sever its "joint program with Ukraine to launch Dnepr rockets". ISC Kosmotras said it would honor its remaining launch contracts. Of the three launches planned for 2015, only one took place. As of 2016, it appears ISC Kosmotras no longer has customers, and thus whether the company is operational or not is uncertain. In May 2017, ISC Ko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Satellites
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called Transponder (satellite communications), transponders. Many satellites use a Satellite bus, standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which is small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as a group, forming Satellite constellation, constellations. Because of the high launch cost to space, satellites are designed to be as lightweight and robust as possible. Most communication satellites are radio Broadcast relay station, relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz. Satellites are placed from the surface to orbit by launch vehicles, high enough to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICBM
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper River
} The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth-longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. It is approximately long, with a drainage basin of . In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat, immediately above that tributary's confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and is connected by the Dnieper–Bug Canal to other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch control center, launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to large operating costs. An orbital spaceflight, orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital spaceflight, Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles are multistage rockets which use chemical propellants such as Solid-propellant rocket, solid fuel, liquid hydrogen, kerosene, liquid oxygen, or Hypergolic propellants. Launch vehicles are cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RD-864
The RD-864 (GRAU: 15D177) is a Soviet liquid propellant rocket engine burning UDMH and nitrogen tetroxide in a gas generator combustion cycle. It has a four combustion chambers that provide thrust vector control by gimbaling each nozzle in a single axis ±55°. It is used on the third stage of the R-36M UTTKh (GRAU: 15A18) and Dnepr. For the R-36M2 (GRAU: 15A18M), an improved version, the RD-869 (GRAU: 15D300) was developed. History When the Soviet military developed an improved version of the R-36M ICBM, Yangel's OKB-586 developed a new engine for the third stage, the RD-864. Developed between 1976 and 1978 it flew for the first time on October 31, 1977. With the START I and START II the some 150 R-36M and R-36M UTTKh were retired and to be destroyed by 2007. So, a civilian application was looked for and during the 1990s, Yuzhnoe Design Bureau (the R-36M designer) successfully developed the Dnepr launch vehicle. It flew for the first time on April 21, 1999 and as of June 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |