|
Djiadjak Jaqeli
Jiajak Jaqeli ( ka, ჯიაჯაყ ჯაყელი) was the Empress consort of Alexios II of Trebizond. Family Jiajak was a daughter of Beka I, the Jaqeli atabeg of Samtskhe. The Jaqelis held the Georgian feudal office of Eristavi, which could be "governor of a region" or an "army-commander", roughly equivalent to the Byzantine ''strategos'' and normally translated into English as "duke". Marriage The marriage of Jiajak to Alexios II can be estimated to c. 1300. The Byzantine Emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos had been his guardian and wanted Alexios to marry a daughter of the high court official Nikephoros Choumnos, but, without asking for the permission, the young man instead married jiajak Jaqeli. Andronikos appealed to the Church to annul the marriage but the Patriarch refused to assist him, on the ground that Jiajak was reported to be already pregnant. Alexios' mother Eudokia Palaiologina, who returned to Trebizond on the pretext of inducing her son to dissolve the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexios II Of Trebizond
Alexios II Megas Komnenos ( el, Αλέξιος Μέγας Κομνηνός , translit=Alexios Megas Komnēnos; Sept./Dec. 1282 – 3 May 1330), was Emperor of Empire of Trebizond, Trebizond from 1297 to 1330. He was the elder son of John II of Trebizond, John II and Eudokia Palaiologina. Alexios proved to be a skillful and energetic ruler, under whose rule the Empire of Trebizond reached the climax of its prosperity. He rebuffed the inroads of the marauding Turkish people, Turks, and adequately handled the encroachment of Republic of Genoa, Genoa and Republic of Venice, Venice. He also cultivated the arts and sciences at his court serving as a patron to the Byzantine astronomer Gregory Chioniades and the scholar Constantine Loukites. Life He ascended the throne at the age of 14 after the death of his father. He came under the care of his uncle, the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos. The latter wanted to marry his young ward to a daughter of the high court official Nik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Of Demetrius II Of Georgia
The family of Demetrius II of Georgia was part of the Bagrationi dynasty of the Kingdom of Georgia. Demetrius II (Demetre, or Dimitri; ka, დემეტრე, დიმიტრი) was a king of Georgia, reigning from 1270 until his execution by the Mongol Ilkhans in 1289. He was a son of David VII of Georgia by his third wife Gvantsa Kakhaberidze. Demetrius, although a Christian, was polygamous, with three wives, and was survived by nine children, of whom three subsequently ruled as kings of Georgia. Parents and siblings Demetrius, born in 1259, was the second son and third child of King David VII. His mother was David's third wife Gvantsa née Kakhaberidze. He was only 3 or 4 years old when Gvantsa was put to death by the Mongols as a reaction to David's abortive rebellion against the Ilkhan hegemony. David himself died in 1270. Demetrius had an elder half-brother George, an heir apparent, who died before his father's death in 1268, and an elder half-sister Tamar, whom De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Births
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irene Palaiologina Of Trebizond
Irene Palaiologina (Greek: Ειρήνη Παλαιολογίνα, ''Eirēnē Palaiologina''), (c. 1315 – after 1341) was Empress regnant of Trebizond from April 6, 1340 to July 17, 1341. She was an illegitimate daughter of the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos, and she married Emperor Basil of Trebizond in 1335. Marriage Issues Soon after the marriage, however, Basil took a mistress, also named Irene, and in 1339 divorced Irene Palaiologina with the connivance of the local clergy. Irene Palaiologina's cause was backed by Patriarch John XIV of Constantinople and she probably still retained some position of influence in Trebizond. On April 6, 1340, she probably poisoned Basil and seized the throne for herself by what reads in the account of Nicephorus Gregoras as a palace coup. Her position was tenuous because of the means by which she gained the throne, and because she was not a member of the ruling Komnenian dynasty. To shore up her position, she sent off her dead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
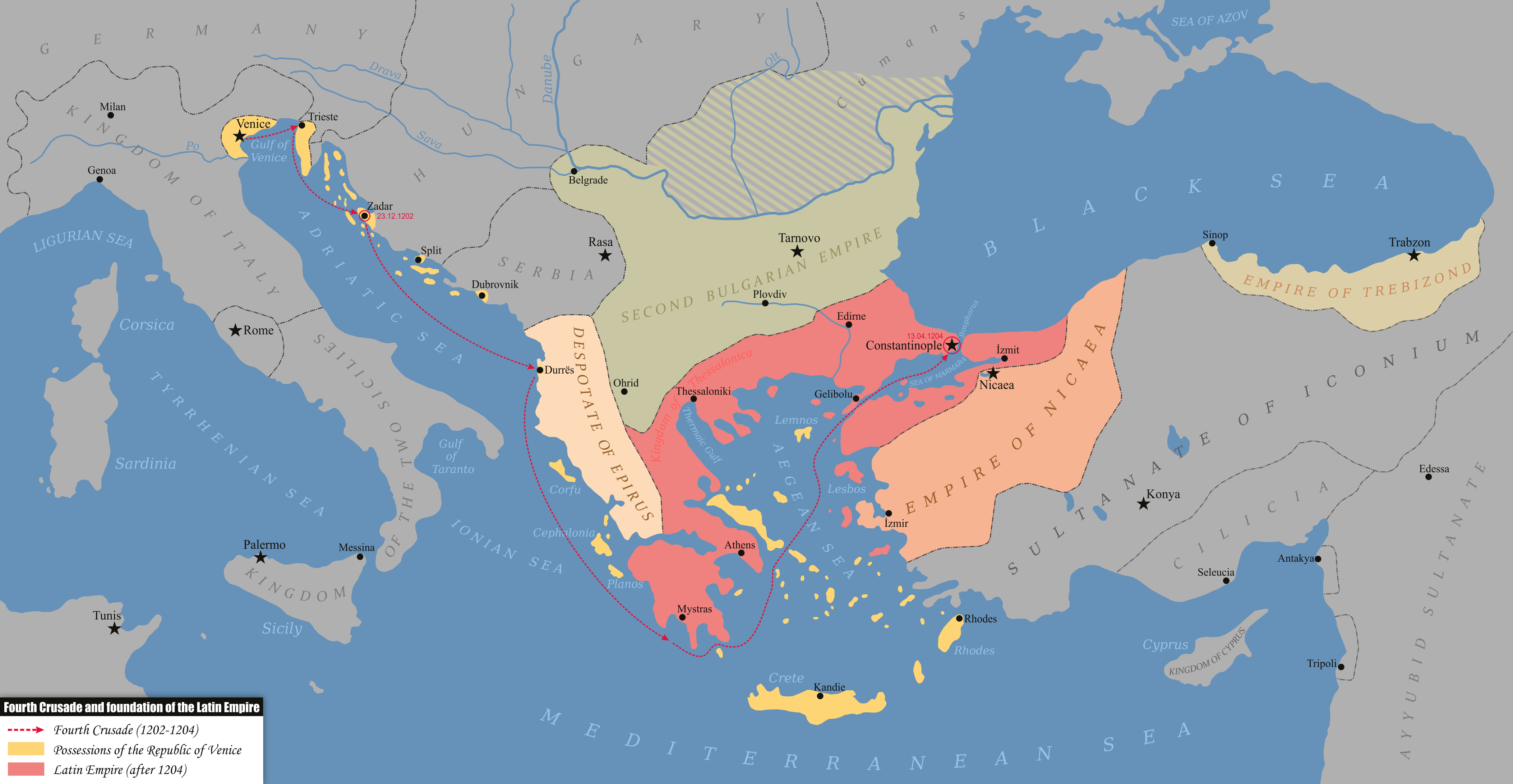
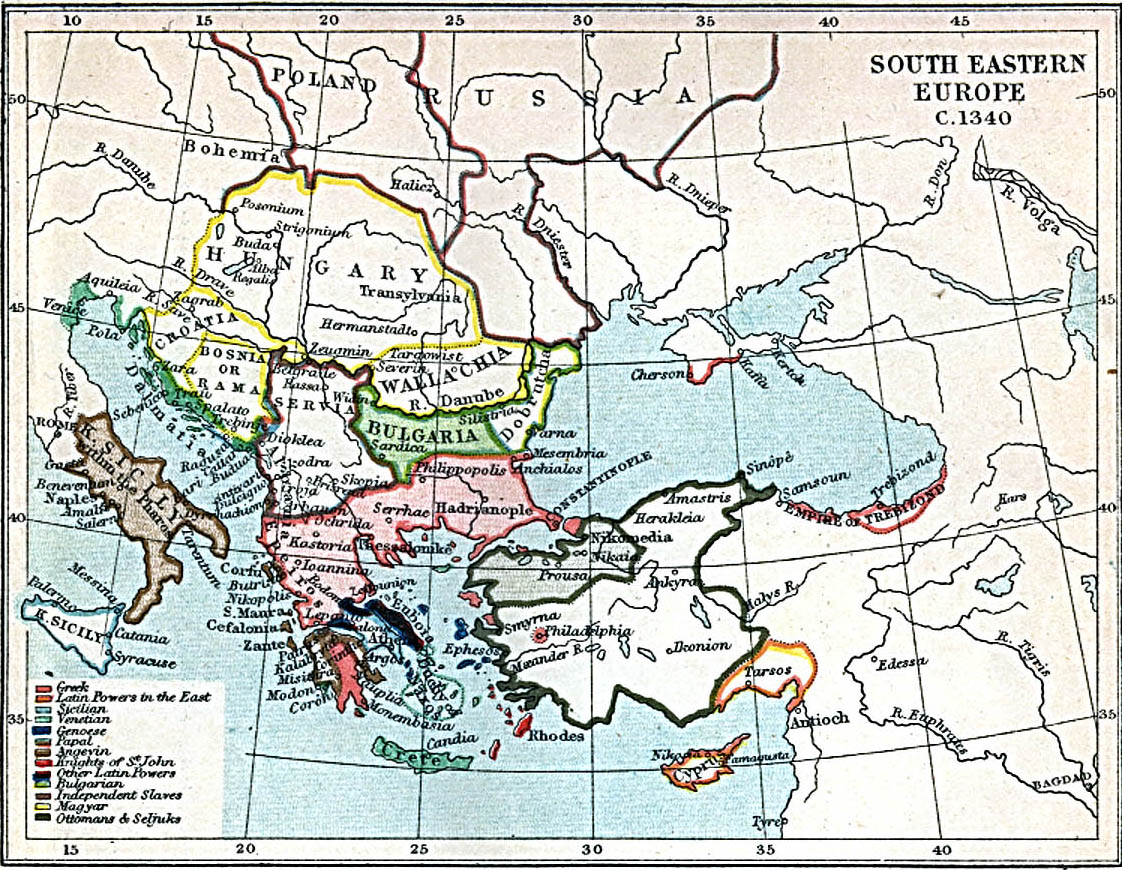
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to the 15th century, consisting of the far northeastern corner of Anatolia (the Pontus) and the southern Crimea. The empire was formed in 1204 with the help of the Georgian queen Tamar after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself Emperor and established himself in Trebizond (modern day Trabzon, Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of deposed Emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as "Roman emperors" against Byzantine Emperor Alexios V Doukas. The later Byzantine emperors, as well as Byzantine authors, such as George Pachymeres, Nicephorus Gregoras and to some extent Trapezun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinop, Turkey
Sinop, historically known as Sinope (; gr, Σινώπη, Sinōpē), is a city on the isthmus of İnce Burun (İnceburun, Cape Ince), near Cape Sinope (Sinop Burnu, Boztepe Cape, Boztepe Burnu) which is situated on the northernmost edge of the Turkish side of the Black Sea coast, in the ancient region of Paphlagonia, in modern-day northern Turkey. The city serves as the capital of Sinop Province. History Over a period of approximately 2,500 years, Sinope has at various times been settled by Colchians, Greeks (in the late 7th, late 5th, and 4th–3rd centuries BC), by Romans in the mid-1st century BC, and by Turkic people beginning in the 12th century. In the 19th and 20th centuries it was also settled by the '' muhacir'' who immigrated from the Balkans and Caucasus. Evidence for Hittite Kingdom settlement along the Black Sea's southern shore remains murky. Researchers in the 1940s and 50s debated whether the "Great Sea", mentioned on the Boghazkoy tablets describing war b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Of Trebizond
Anna Anachoutlou ( gr, Ἄννα Μεγάλη Κομνηνὴ Ἀναχουτλοῦ, Anna Megalē Komnēnē Anachoutloū; died 3 September 1342) ruled the Empire of Trebizond from 1341 to 1342. She was the eldest daughter of the List of Trapezuntine emperors, Trapezuntine emperor Alexios II of Trebizond, Alexios II Megas Komnenos () and had joined a convent as a nun during her father's reign. After the death of her father, Anna's brother Andronikos III of Trebizond, Andronikos III (), her nephew Manuel II of Trebizond, Manuel II (1332) and her other brother Basil of Trebizond, Basil () reigned in rapid succession. After Basil's death, his widow Irene Palaiologina of Trebizond, Irene Palaiologina, genealogically unconnected to the ruling Grand Komnenos dynasty of Trebizond, seized power as empress regnant. In June/July 1341, Anna escaped from her convent and rapidly began rallying support to fight against Irene. Despite being a woman and up until recently a nun, and there being s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basil Of Trebizond
Basil Megas Komnenos ( grc-x-medieval, Βασίλειος Μέγας Κομνηνός, Basileios Megas Komnēnos) (died 6 April 1340) was Emperor of Trebizond from August 1332 until his death in 1340. Although Basil's reign was a period of stability during the civil war that dominated the pocket empire during the second quarter of the 14th century, some of that conflict had its origins in his marital actions. Life Basil was a younger son of Emperor Alexios II of Trebizond and his wife Djiadjak Jaqeli. When his oldest brother Andronikos III assumed the throne in 1330 and killed his two brothers (Michael and George), Basil happened to be in Constantinople and escaped his brothers' fate. On the death of Andronikos III, his infant son Manuel II became emperor. However, Basil was invited from Constantinople to take the throne; Manuel was deposed in August 1332 and confined to a monastery. Basil purged the court of his brother and nephew's supporters (which included the '' megas d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos III Of Trebizond
Andronikos III Megas Komnenos, or Andronicus III ( el, Ανδρόνικος Μέγας Κομνηνός , translit=Andronikos Megas Komnēnos), (died 8 January 1332) was Emperor of Trebizond from 1330 to 1332. He was the eldest son of Emperor Alexios II of Trebizond and his Iberian wife, Djiadjak Jaqeli of Samckhe. According to Michael Panaretos, he reigned for 15 months, which suggests that there was an interregnum of five months — from the death of his father in May to October 1330. Rustam Shukurov suggested that Andronikos and his son Manuel were named for their distant ancestors, Andronikos I Komnenos and his son Manuel the Sebastokrator, arguing that their portraits appeared on the walls of the Imperial palace hall. One of his first actions when Andronikos became emperor was to put to death his two younger brothers, George Azachoutlou and Michael Achpougas. His other brother Basil managed to escape to Constantinople, where his uncle Michael Michael may refer to: P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Finlay
George Finlay (21 December 1799 – 26 January 1875) was a Scottish historian. Biography Finlay was born in Faversham, Kent, where his Scottish father, Captain John Finlay FRS, an officer in the Royal Engineers, was inspector of government powder mills. Finlay's father died in 1802, and his Scottish mother and uncle (Kirkman Finlay) took hand of his education. His love of history was attributed to his mother. Intended for the law, he was educated at the University of Glasgow, the University of Göttingen, and the University of Edinburgh The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 15 ..., but becoming an enthusiast in the cause of Greece, in 1823 he joined George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron, Byron in the Greek War of Independence, war of independence. Thereafter he bought a prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Georgian Chronicles
''The Georgian Chronicles'' is a conventional English name for the principal compendium of medieval Georgian historical texts, natively known as ''Kartlis Tskhovreba'' ( ka, ქართლის ცხოვრება), literally "Life of Kartli", Kartli being a core region of ancient and medieval Georgia, known to the Classical and Byzantine authors as Iberia. The chronicles are also known as ''The Georgian Royal Annals'', for they were essentially the official corpus of history of the Kingdom of Georgia.Rapp, Stephen H. (2003), Studies in Medieval Georgian Historiography: Early Texts And Eurasian Contexts', ''passim''. Peeters Publishers, . Retrieved on 26 April 2009.Toumanoff, Cyril (1963). ''Studies in Christian Caucasian History''. Washington, D.C.: Georgetown University Press, ''passim''. Chronicles The Chronicles consist of a series of distinct texts dating from the 9th to the 14th century. The dating of these works as well as the identification of their authors (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)