|
Distal-less
Genes in the ''DLX'' family encode homeodomain transcription factors related to the ''Drosophila'' distal-less ''(Dll)'' gene. The family has been related to a number of developmental features such as jaws and limbs. The family seems to be well preserved across species. As ''DLX''/''Dll'' are involved in limb development in most of the major phyla, including vertebrates, it has been suggested that ''Dll'' was involved in appendage growth in an early bilaterial ancestor. Six members of the family are found in human and mice, numbered DLX1 to DLX6. They form two-gene clusters (bigene clusters) with each other. There are DLX1-DLX2, DLX3-DLX4, DLX5-DLX6 clusters in vertebrates, linked to Hox gene clusters HOXD, HOXB, and HOXA respectively. In higher fishes like the zebrafish, there are two additional ''DLX'' genes, ''dlx2b'' (''dlx5'') and ''dlx4a'' (''dlx8''). These additional genes are not linked with each other, or any other ''DLX'' gene. All six other genes remain in bigene cluste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DLX2
Homeobox protein DLX-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DLX2'' gene. Many vertebrate homeo box-containing genes have been identified on the basis of their sequence similarity with Drosophila developmental genes. Members of the Dlx gene family contain a homeobox that is related to that of Distal-less (Dll), a gene expressed in the head and limbs of the developing fruit fly. The Distal-less (Dlx) family of genes comprises at least 6 different members, DLX1-DLX6. The DLX proteins are postulated to play a role in forebrain and craniofacial development. This gene is located in a tail-to-tail configuration with another member of the gene family on the long arm of chromosome 2. Interactions DLX2 has been shown to interact with DLX5, MSX1 and Msh homeobox 2 Homeobox protein MSX-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MSX2'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the muscle segment homeobox gene family. The encoded protein is a transcriptional represso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DLX3
Homeobox protein DLX-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DLX3'' gene. Function Dlx3 is a crucial regulator of hair follicle differentiation and cycling. Dlx3 transcription is mediated through Wnt signaling pathway, Wnt, and colocalization of Dlx3 with phosphorylated, phospho-SMAD1/SMAD5, 5/SMAD8, 8 is involved in the regulation of transcription by Bone morphogenetic protein, BMP signaling. Dlx3 transcription is also induced by Bone morphogenetic protein 2, BMP-2 through transactivation with SMAD1 and SMAD4. Many vertebrate homeo box-containing genes have been identified on the basis of their sequence similarity with Drosophila developmental genes. Members of the Dlx gene family contain a homeobox that is related to that of Distal-less (Dll), a gene expressed in the head and limbs of the developing fruit fly. The Distal-less (Dlx) family of genes comprises at least 6 different members, DLX1-DLX6. This gene is located in a tail-to-tail configuration with another me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DLX4
Homeobox protein DLX-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DLX4'' gene. Function Many vertebrate homeobox-containing genes have been identified on the basis of their sequence similarity with ''Drosophila'' developmental genes. Members of the Dlx gene family contain a homeobox that is related to that of Distal-less (Dll), a gene expressed in the head and limbs of the developing fruit fly. The Distal-less (Dlx) family of genes comprises at least 6 different members, DLX1-DLX6. The DLX proteins are postulated to play a role in forebrain and craniofacial development. Three transcript variants have been described for this gene, however, the full length nature of one variant has not been described. Studies of the two splice variants revealed that one encoded isoform (BP1) functions as a repressor of the beta-globin Hemoglobin subunit beta (beta globin, β-globin, haemoglobin beta, hemoglobin beta) is a globin protein, coded for by the ''HBB'' gene, which along with al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hox Gene
Hox genes, a subset of homeobox genes, are a group of related genes that specify regions of the body plan of an embryo along the head-tail axis of animals. Hox proteins encode and specify the characteristics of 'position', ensuring that the correct structures form in the correct places of the body. For example, Hox genes in insects specify which appendages form on a segment (for example, legs, antennae, and wings in fruit flies), and Hox genes in vertebrates specify the types and shape of vertebrae that will form. In segmented animals, Hox proteins thus confer segmental or positional identity, but do not form the actual segments themselves. Studies on Hox genes in ciliated larvae have shown they are only expressed in future adult tissues. In larvae with gradual metamorphosis the Hox genes are activated in tissues of the larval body, generally in the trunk region, that will be maintained through metamorphosis. In larvae with complete metamorphosis the Hox genes are mainly express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallium (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, pallium refers to the layers of grey and white matter that cover the upper surface of the cerebrum in vertebrates. The non-pallial part of the telencephalon builds the subpallium. In basal vertebrates the pallium is a relatively simple three-layered structure, encompassing 3–4 histogenetically distinct domains, plus the olfactory bulb. It used to be thought that pallium equals cortex and subpallium equals telencephalic nuclei, but it has turned out, according to comparative evidence provided by molecular markers, that the pallium develops both cortical structures (allocortex and isocortex) and pallial nuclei ( claustroamygdaloid complex), whereas the subpallium develops striatal, pallidal, diagonal-innominate and preoptic nuclei, plus the corticoid structure of the olfactory tuberculum. In mammals, the cortical part of the pallium registers a definite evolutionary step-up in complexity, forming the cerebral cortex, most of which consists of a progressively e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
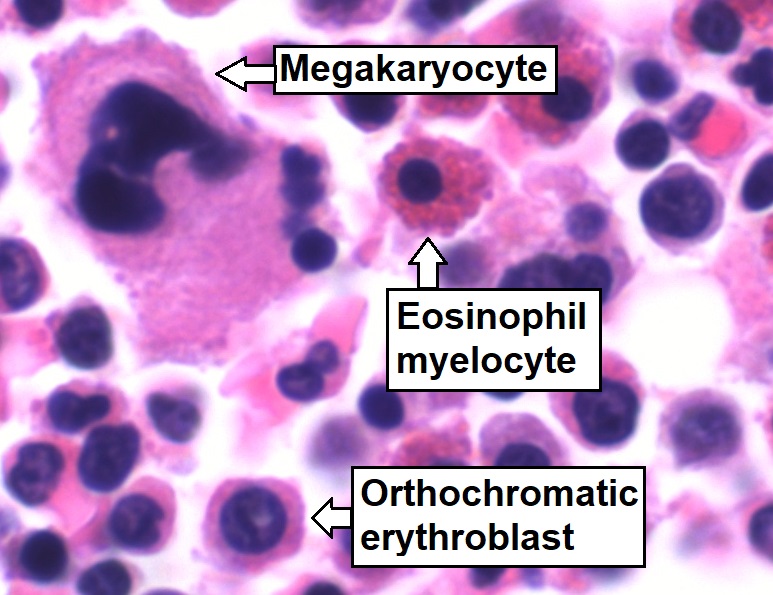
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prethalamus
The subthalamus or prethalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its most prominent structure is the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamus connects to the globus pallidus, a basal nucleus of the telencephalon. Structure The subthalamus is located ventral to the thalamus, medial to the internal capsule and lateral to the hypothalamus. It is a region formed by several grey matter nuclei and their associated white matter structures, namely: *The subthalamic nucleus, whose neurons contain glutamate and have excitatory effects over neurons of globus pallidus and substantia nigra *Zona incerta, located between fields of Forel H1 and H2. It is continuous with the thalamic reticular nucleus and receives input from the precentral cortex. *Subthalamic fasciculus, formed by fibers that connect the globus pallidus with the subthalamic nucleus *Fields of Forel *Ansa lenticularis During development the subthalamus is continuous with the hypothalamus, but is separated by white matter fibres mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zona Limitans Intrathalamica
The ''zona limitans intrathalamica'' (ZLI) is a lineage-restriction compartment and primary developmental boundary in the vertebrate forebrain (which is analogous to the human cerebrum) that serves as a signaling center and a restrictive border between the thalamus (also known as the dorsal thalamus) and the prethalamus (ventral thalamus). Sonic hedgehog (shh) signaling from the ZLI is crucial in the development of the '' diencephalon'', which develops into the thalamus, the pretectum, and the anterior tegmental structures. The ZLI together with the prethalamus and thalamus make up the mid-diencephalic territory (MDT). Discovery Cell lineage restriction boundaries, across which replicating cells cannot migrate, were first discovered in invertebrates, where the expression of various Hox genes in each compartment confer the differentiation of observable segments in the adult body of Drosophila melanogaster. Analogous structures were discovered in the developing vertebrate brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the alarming nature of their symptoms. The underlying mechanism of epileptic seizures is excessive and abnormal neuronal activity in the cortex of the brain which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG) of an individual. The reason this occurs in most cases of epilepsy is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three typesgroup A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrite
Dendrites (from Greek δένδρον ''déndron'', "tree"), also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimulation is transmitted onto dendrites by upstream neurons (usually via their axons) via synapses which are located at various points throughout the dendritic tree. Dendrites play a critical role in integrating these synaptic inputs and in determining the extent to which action potentials are produced by the neuron. Dendritic arborization, also known as dendritic branching, is a multi-step biological process by which neurons form new dendritic trees and branches to create new synapses. The morphology of dendrites such as branch density and grouping patterns are highly correlated to the function of the neuron. Malformation of dendrites is also tightly correlated to impaired nervous syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Development
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The field of neural development draws on both neuroscience and developmental biology to describe and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which complex nervous systems develop, from nematodes and Drosophila melanogaster, fruit flies to mammals. Defects in neural development can lead to malformations such as holoprosencephaly, and a wide variety of neurological disorders including paresis, limb paresis and paralysis, balance and vision disorders, and seizures, and in humans other disorders such as Rett syndrome, Down syndrome and intellectual disability. Overview of vertebrate brain development The vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) is derived from the ectoderm—the outermost germ layer of the embryo. A part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |