|
Dissacus Zengi
''Dissacus'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous jackal to coyote-sized mammals within the family Mesonychidae, an early group of hoofed mammals that evolved into hunters and omnivores. Their fossils are found in Paleocene to Early Eocene aged strata in France, Asia and southwest North America, from 66 to 50.3 mya, existing for approximately . Orientation patch analysis of the molar teeth of the North American ''D. praenuntius'' suggests it was an omnivore that ate a lot of meat, not an exclusive meat-eater like a cat or weasel. It shared its environment with more omnivorous mammals of a similar body size. Though they are not ancestral to Carnivora, ''Dissacus'' species may have had similar roles in Paleocene-early Eocene environments as the foxes and other small canids that evolved later: generalized hunters who also ate fruit or other foods, and caught small animals that lived on the ground. The bear-sized ''Ankalagon'' is closely related to ''Dissacus''. Some paleontologists c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Drinker Cope
Edward Drinker Cope (July 28, 1840 – April 12, 1897) was an American zoologist, paleontologist, comparative anatomist, herpetologist, and ichthyologist. Born to a wealthy Quaker family, Cope distinguished himself as a child prodigy interested in science; he published his first scientific paper at the age of 19. Though his father tried to raise Cope as a gentleman farmer, he eventually acquiesced to his son's scientific aspirations. Cope married his cousin and had one child; the family moved from Philadelphia to Haddonfield, New Jersey, although Cope would maintain a residence and museum in Philadelphia in his later years. Cope had little formal scientific training, and he eschewed a teaching position for field work. He made regular trips to the American West, prospecting in the 1870s and 1880s, often as a member of United States Geological Survey teams. A personal feud between Cope and paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh led to a period of intense fossil-finding competition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyly
In taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic group (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of synapomorphies and symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term was coined by Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia ( reptiles) which, as commonly named and traditionally defined, is paraphyletic with respect to mammals and birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles and all descendants of that ancestor, including all extant reptiles as well as the extinct synapsids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissacus Rotundus
''Dissacus'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous jackal to coyote-sized mammals within the family Mesonychidae, an early group of hoofed mammals that evolved into hunters and omnivores. Their fossils are found in Paleocene to Early Eocene aged strata in France, Asia and southwest North America, from 66 to 50.3 mya, existing for approximately . Orientation patch analysis of the molar teeth of the North American ''D. praenuntius'' suggests it was an omnivore that ate a lot of meat, not an exclusive meat-eater like a cat or weasel. It shared its environment with more omnivorous mammals of a similar body size. Though they are not ancestral to Carnivora, ''Dissacus'' species may have had similar roles in Paleocene-early Eocene environments as the foxes and other small canids that evolved later: generalized hunters who also ate fruit or other foods, and caught small animals that lived on the ground. The bear-sized ''Ankalagon'' is closely related to ''Dissacus''. Some paleontologists c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissacus Raslanloubatieri
''Dissacus'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous jackal to coyote-sized mammals within the family Mesonychidae, an early group of hoofed mammals that evolved into hunters and omnivores. Their fossils are found in Paleocene to Early Eocene aged strata in France, Asia and southwest North America, from 66 to 50.3 mya, existing for approximately . Orientation patch analysis of the molar teeth of the North American ''D. praenuntius'' suggests it was an omnivore that ate a lot of meat, not an exclusive meat-eater like a cat or weasel. It shared its environment with more omnivorous mammals of a similar body size. Though they are not ancestral to Carnivora, ''Dissacus'' species may have had similar roles in Paleocene-early Eocene environments as the foxes and other small canids that evolved later: generalized hunters who also ate fruit or other foods, and caught small animals that lived on the ground. The bear-sized ''Ankalagon'' is closely related to ''Dissacus''. Some paleontologists c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissacus Praenuntius
''Dissacus'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous jackal to coyote-sized mammals within the family Mesonychidae, an early group of hoofed mammals that evolved into hunters and omnivores. Their fossils are found in Paleocene to Early Eocene aged strata in France, Asia and southwest North America, from 66 to 50.3 mya, existing for approximately . Orientation patch analysis of the molar teeth of the North American ''D. praenuntius'' suggests it was an omnivore that ate a lot of meat, not an exclusive meat-eater like a cat or weasel. It shared its environment with more omnivorous mammals of a similar body size. Though they are not ancestral to Carnivora, ''Dissacus'' species may have had similar roles in Paleocene-early Eocene environments as the foxes and other small canids that evolved later: generalized hunters who also ate fruit or other foods, and caught small animals that lived on the ground. The bear-sized ''Ankalagon'' is closely related to ''Dissacus''. Some paleontologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissacus Navajovius
''Dissacus'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous jackal to coyote-sized mammals within the family Mesonychidae, an early group of hoofed mammals that evolved into hunters and omnivores. Their fossils are found in Paleocene to Early Eocene aged strata in France, Asia and southwest North America, from 66 to 50.3 mya, existing for approximately . Orientation patch analysis of the molar teeth of the North American ''D. praenuntius'' suggests it was an omnivore that ate a lot of meat, not an exclusive meat-eater like a cat or weasel. It shared its environment with more omnivorous mammals of a similar body size. Though they are not ancestral to Carnivora, ''Dissacus'' species may have had similar roles in Paleocene-early Eocene environments as the foxes and other small canids that evolved later: generalized hunters who also ate fruit or other foods, and caught small animals that lived on the ground. The bear-sized ''Ankalagon'' is closely related to ''Dissacus''. Some paleontologists c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissacus Magushanensis
''Dissacus'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous jackal to coyote-sized mammals within the family Mesonychidae, an early group of hoofed mammals that evolved into hunters and omnivores. Their fossils are found in Paleocene to Early Eocene aged strata in France, Asia and southwest North America, from 66 to 50.3 mya, existing for approximately . Orientation patch analysis of the molar teeth of the North American ''D. praenuntius'' suggests it was an omnivore that ate a lot of meat, not an exclusive meat-eater like a cat or weasel. It shared its environment with more omnivorous mammals of a similar body size. Though they are not ancestral to Carnivora, ''Dissacus'' species may have had similar roles in Paleocene-early Eocene environments as the foxes and other small canids that evolved later: generalized hunters who also ate fruit or other foods, and caught small animals that lived on the ground. The bear-sized ''Ankalagon'' is closely related to ''Dissacus''. Some paleontologists c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissacus Indigenus
''Dissacus'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous jackal to coyote-sized mammals within the family Mesonychidae, an early group of hoofed mammals that evolved into hunters and omnivores. Their fossils are found in Paleocene to Early Eocene aged strata in France, Asia and southwest North America, from 66 to 50.3 mya, existing for approximately . Orientation patch analysis of the molar teeth of the North American ''D. praenuntius'' suggests it was an omnivore that ate a lot of meat, not an exclusive meat-eater like a cat or weasel. It shared its environment with more omnivorous mammals of a similar body size. Though they are not ancestral to Carnivora, ''Dissacus'' species may have had similar roles in Paleocene-early Eocene environments as the foxes and other small canids that evolved later: generalized hunters who also ate fruit or other foods, and caught small animals that lived on the ground. The bear-sized ''Ankalagon'' is closely related to ''Dissacus''. Some paleontologists c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissacus Europaeus
''Dissacus'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous jackal to coyote-sized mammals within the family Mesonychidae, an early group of hoofed mammals that evolved into hunters and omnivores. Their fossils are found in Paleocene to Early Eocene aged strata in France, Asia and southwest North America, from 66 to 50.3 mya, existing for approximately . Orientation patch analysis of the molar teeth of the North American ''D. praenuntius'' suggests it was an omnivore that ate a lot of meat, not an exclusive meat-eater like a cat or weasel. It shared its environment with more omnivorous mammals of a similar body size. Though they are not ancestral to Carnivora, ''Dissacus'' species may have had similar roles in Paleocene-early Eocene environments as the foxes and other small canids that evolved later: generalized hunters who also ate fruit or other foods, and caught small animals that lived on the ground. The bear-sized ''Ankalagon'' is closely related to ''Dissacus''. Some paleontologists c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissacus Argenteus
''Dissacus'' is a genus of extinct carnivorous jackal to coyote-sized mammals within the family Mesonychidae, an early group of hoofed mammals that evolved into hunters and omnivores. Their fossils are found in Paleocene to Early Eocene aged strata in France, Asia and southwest North America, from 66 to 50.3 mya, existing for approximately . Orientation patch analysis of the molar teeth of the North American ''D. praenuntius'' suggests it was an omnivore that ate a lot of meat, not an exclusive meat-eater like a cat or weasel. It shared its environment with more omnivorous mammals of a similar body size. Though they are not ancestral to Carnivora, ''Dissacus'' species may have had similar roles in Paleocene-early Eocene environments as the foxes and other small canids that evolved later: generalized hunters who also ate fruit or other foods, and caught small animals that lived on the ground. The bear-sized ''Ankalagon'' is closely related to ''Dissacus''. Some paleontologists c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cursorial
A cursorial organism is one that is adapted specifically to run. An animal can be considered cursorial if it has the ability to run fast (e.g. cheetah) or if it can keep a constant speed for a long distance (high endurance). "Cursorial" is often used to categorize a certain locomotor mode, which is helpful for biologists who examine behaviors of different animals and the way they move in their environment. Cursorial adaptations can be identified by morphological characteristics (e.g. loss of lateral digits as in ungulate species), physiological characteristics, maximum speed, and how often running is used in life. There is much debate over how to define a cursorial animal specifically. The most accepted definitions include that a cursorial organism could be considered adapted to long-distance running at high speeds or has the ability to accelerate quickly over short distances. Among vertebrates, animals under 1 kg of mass are rarely considered cursorial, and cursorial behaviors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
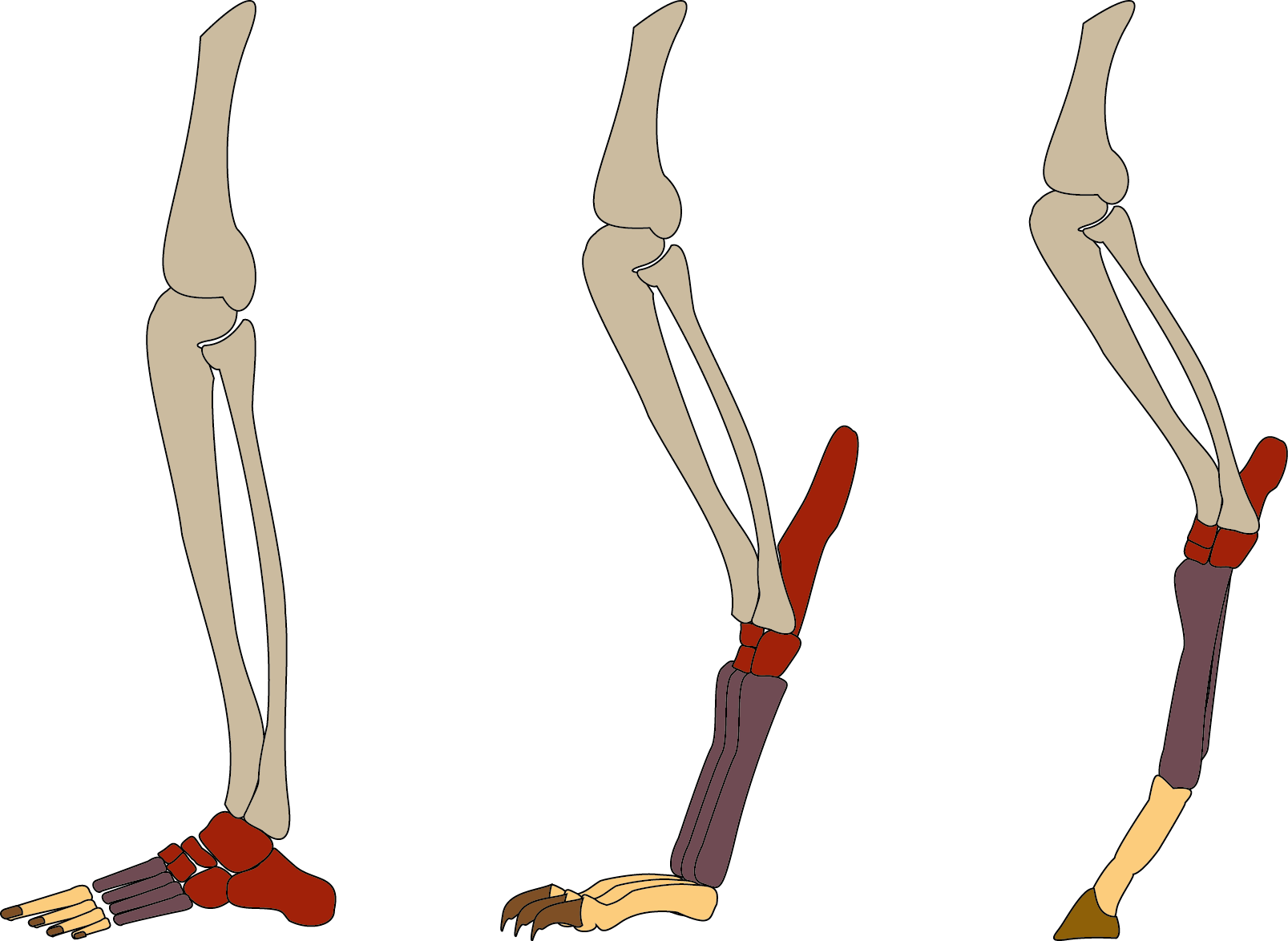
Digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the ground, and the rest of its foot lifted. Digitigrades include walking birds (what many assume to be bird knees are actually ankles), cats, dogs, and many other mammals, but not plantigrades or unguligrades. Digitigrades generally move more quickly and quietly than other animals. There are anatomical differences between the limbs of plantigrades, like humans, and both unguligrade and digitigrade limbs. Digitigrade and unguligrade animals have relatively long carpals and tarsals, and the bones which would correspond to the human ankle are thus set much higher in the limb than in a human. In a digitigrade animal, this effectively lengthens the foot, so much so that what are often thought of as a digitigrade animal's "hands" and "feet" correspon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |