|
Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drug
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) comprise a category of otherwise unrelated disease-modifying drugs defined by their use in rheumatoid arthritis to slow down disease progression. The term is often used in contrast to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (which refers to agents that treat the inflammation, but not the underlying cause) and steroids (which blunt the immune response but are insufficient to slow down the progression of the disease). The term "antirheumatic" can be used in similar contexts, but without making a claim about an effect on the disease course. Other terms that have historically been used to refer to the same group of drugs are "remission-inducing drugs" (RIDs) and "slow-acting antirheumatic drugs" (SAARDs). Terminology Although the use of the term DMARDs was first propagated in rheumatoid arthritis (hence their name), the term has come to pertain to many other diseases, such as Crohn's disease, lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methotrexate Skeletal
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, gestational trophoblastic disease, and osteosarcoma. Types of autoimmune diseases it is used for include psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It can be given by mouth or by injection. Common side effects include nausea, feeling tired, fever, increased risk of infection, low white blood cell counts, and breakdown of the skin inside the mouth. Other side effects may include liver disease, lung disease, lymphoma, and severe skin rashes. People on long-term treatment should be regularly checked for side effects. It is not safe during breastfeeding. In those with kidney problems, lower doses may be needed. It acts by blocking the body's use of folic acid. Methotrexate was first made in 1947 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-reactive Protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin-6 secretion by macrophages and T cells. Its physiological role is to bind to lysophosphatidylcholine expressed on the surface of dead or dying cells (and some types of bacteria) in order to activate the complement system via C1q. CRP is synthesized by the liver in response to factors released by macrophages and fat cells (adipocytes). It is a member of the pentraxin family of proteins. It is not related to C-peptide (insulin) or protein C (blood coagulation). C-reactive protein was the first pattern recognition receptor (PRR) to be identified. History Discovered by Tillett and Francis in 1930, it was initially thought that CRP might be a pathogenic secretion since it was elevated in a variety of illnesses, including cancer. The later d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purine Synthesis Inhibitor
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms. Biosynthesis Purines are biologically synthesized as nucleotides and in particular as ribotides, i.e. bases attached to ribose 5-phosphate. Both adenine and guanine are derived from the nucleotide inosine monophosphate (IMP), which is the first compound in the pathway to have a completely formed purine ring system. IMP Inosine monophosphate is synthesized on a pre-existing ribose-phosphate through a complex pathway (as shown in the figure on the right). The source of the carbon and nitrogen atoms of the purine ring, 5 and 4 respectively, come from multiple sources. The amino acid glycine contributes all its carbon (2) and nitrogen (1) atoms, with additional nitrogen atoms from glutamine (2) and aspartic acid (1), and additional carbon atoms from formyl groups (2), which are transferred from the coenzyme tetrahydrofolate as 10-formyltetrahydrofolate, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azathioprine
Azathioprine (AZA), sold under the brand name Imuran, among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used in rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus erythematosus, and in kidney transplants to prevent rejection. It is listed by the International Agency for Research on Cancer as a group 1 carcinogen (carcinogenic to humans). It is taken by mouth or injected into a vein. Common side effects include bone-marrow suppression and vomiting. Bone-marrow suppression is especially common in people with a genetic deficiency of the enzyme thiopurine S-methyltransferase. Other serious risk factors include an increased risk of certain cancers. Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. Azathioprine is in the purine analogue and antimetabolite family of medications. It works via 6-thioguanine to disrupt the making of RNA and DNA by cells. Azathioprine was first made in 1957. It is on the World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphodiesterase 4
At least four types of the enzyme phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) are known: * PDE4A * PDE4B * PDE4C * PDE4D See also * 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase * Phosphodiesterase A phosphodiesterase (PDE) is an enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond. Usually, ''phosphodiesterase'' refers to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance and are described below. However, there are many ot ... (PDE) * PDE4 inhibitor {{chemistry index Molecular biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apremilast
Apremilast, sold under the brand name Otezla among others, is a medication for the treatment of certain types of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. It may also be useful for other immune system-related inflammatory diseases. The drug acts as a selective inhibitor of the enzyme phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) and inhibits spontaneous production of TNF-alpha from human rheumatoid synovial cells. It is taken by mouth. Medical uses Apremilast is indicated in the United States for the treatment of adults with active psoriatic arthritis, adult patients with plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, and adults with oral ulcers associated with Behçet's disease. In the European Union, apremilast alone or in combination with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), is indicated for the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in adults who have had an inadequate response or who have been intolerant to a prior DMARD therapy. It is also indicated for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anakinra
Anakinra, sold under the brand name Kineret, is a biopharmaceutical medication used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes, familial Mediterranean fever, and Still's disease. It is a recombinant and slightly modified version of the human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist protein. It is marketed by Swedish Orphan Biovitrum. Anakinra is administered by subcutaneous injection. Medical uses It is used as a second line treatment to manage symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis after treatment with a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) has failed. It can be used in combination with some DMARDs. It is used to people with a cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome, including neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease. It is used to treat Schnitzler's syndrome (off label in the US). Its response rate is such that it has been suggested that "Treatment failures should lead to reconsider the diagnosis." Off label, it is used to treat systemic juv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNF Inhibitor
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa and refractory asthma, so TNF inhibitors may be used in their treatment. The important side effects of TNF inhibitors include lymphomas, infections (especially reactivation of latent tuberculosis), congestive heart failure, demyelinating disease, a lupus-like syndrome, induction of auto-antibodies, injection site reactions, and systemic side effects. The global market for TNF inhibitors in 2008 was $13.5 billion and $22 billion in 2009. Examples Inhibition of TNF effects can be achieved with a monoclonal antibody such as infliximab, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, and golimumab, or with a circulating receptor fusion protein such as etanercept. Tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adalimumab
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, among others, is a monoclonal antibody used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, uveitis, and juvenile idiopathic arthritis. It is administered by injection under the skin. Common side effects include upper respiratory tract infections, pain at the site of injection, rash, and headache. Other side effects may include serious infections, cancer, anaphylaxis, reactivation of hepatitis B, multiple sclerosis, heart failure, liver failure, and aplastic anemia. Use during pregnancy is not recommended, but some sources show use during breastfeeding may be safe. Adalimumab is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) and monoclonal antibody that works by inactivating tumor necrosis factor-alpha ( TNFα). Adalimumab was approved for medical use in the United States in 2002. It is on the World Health Organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Co-stimulation
Co-stimulation is a secondary signal which immune cells rely on to activate an immune response in the presence of an antigen-presenting cell. In the case of T cells, two stimuli are required to fully activate their immune response. During the activation of lymphocytes, co-stimulation is often crucial to the development of an effective immune response. Co-stimulation is required in addition to the antigen-specific signal from their antigen receptors. T cell co-stimulation T cells require two signals to become fully activated. A first signal, which is antigen-specific, is provided through the T cell receptor (TCR) which interacts with peptide- MHC molecules on the membrane of antigen presenting cells (APC). A second signal, the co-stimulatory signal, is antigen nonspecific and is provided by the interaction between co-stimulatory molecules expressed on the membrane of APC and the T cell. One of the best characterized co-stimulatory molecules expressed by T cells is CD28, which inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abatacept
Abatacept, sold under the brand name Orencia, is a medication used to treat autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, by interfering with the immune activity of T cells. It is a modified antibody. Abatacept is a fusion protein composed of the Fc region of the immunoglobulin IgG1 fused to the extracellular domain of CTLA-4. In order for a T cell to be activated and produce an immune response, an antigen-presenting cell must present two signals to the T cell. One of those signals is the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), combined with the antigen, and the other signal is the CD80 or CD86 molecule (also known as B7-1 and B7-2). Abatacept binds to the CD80 and CD86 molecule, and prevents the second signal. Without the second signal, the T cell can't be activated. Abatacept was developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb and is licensed in the United States for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in the case of inadequate response to anti- TNFα therapy. Abatacept received app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
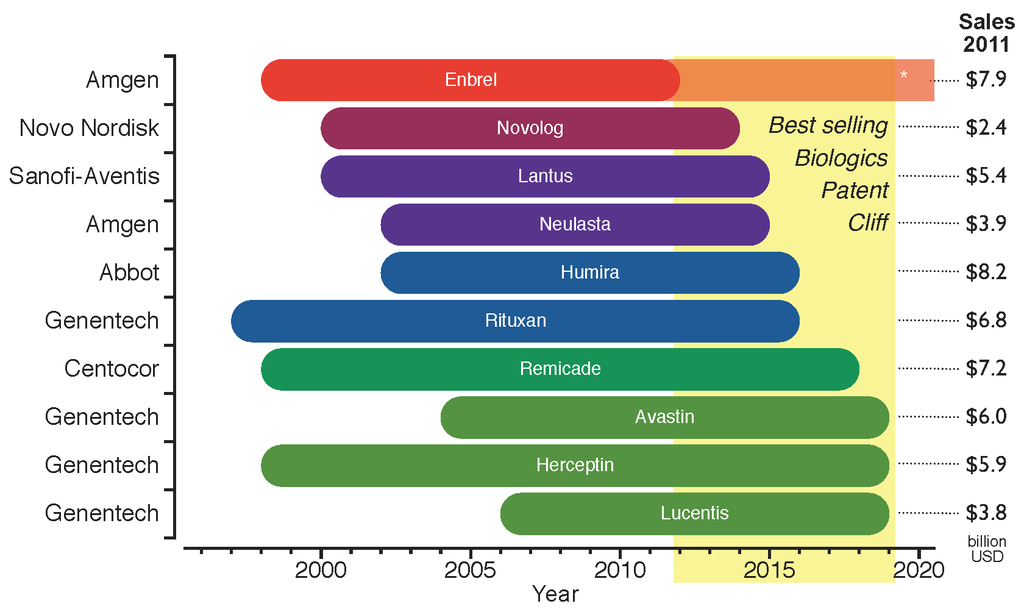
Biosimilar
A biosimilar (also known as follow-on biologic or subsequent entry biologic) is a biologic medical product that is almost an identical copy of an original product that is manufactured by a different company. Biosimilars are officially approved versions of original "innovator" products and can be manufactured when the original product's patent expires. Reference to the innovator product is an integral component of the approval. Unlike with generic drugs of the more common small-molecule type, biologics generally exhibit high molecular complexity and may be quite sensitive to changes in manufacturing processes. Despite that heterogeneity, all biopharmaceuticals, including biosimilars, must maintain consistent quality and clinical performance throughout their lifecycle. Drug-related authorities such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) of the European Union, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the Health Products and Food Branch of Health Canada hold the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |