|
Direct Torque Control
Direct torque control (DTC) is one method used in variable-frequency drives to control the torque (and thus finally the speed) of three-phase electric motor, AC electric motors. This involves Calculation, calculating an estimate of the motor's magnetic flux and torque based on the measured voltage and Electric current, current of the motor. DTC control platform Stator flux linkage is estimated by Integral, integrating the stator voltages. Torque is estimated as a cross product of estimated stator flux linkage vector (geometric), vector and measured motor Electric current, current vector (geometric), vector. The estimated flux magnitude and torque are then compared with their reference values. If either the estimated flux or torque Allowance (engineering), deviates too far from the reference Engineering tolerance, tolerance, the transistors of the variable frequency drive are turned off and on in such a way that the flux and torque errors will return in their tolerant bands as fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable-frequency Drive
A variable-frequency drive (VFD) is a type of motor drive used in electro-mechanical drive systems to control AC motor speed and torque by varying motor input frequency and, depending on topology, to control associated voltage or current variation., quote is per definition on p. 4 of NEMA Standards Publication ICS 7.2-2021. VFDs may also be known as 'AFDs' (adjustable-frequency drives), 'ASDs' (adjustable-speed drives), 'VSDs' (variable-speed drives), 'AC drives', 'micro drives', 'inverter drives' or, simply, 'drives'. VFDs are used in applications ranging from small appliances to large compressors. An increasing number of end users are showing greater interest in electric drive systems due to more stringent emission standards and demand for increased reliability and better availability. Systems using VFDs can be more efficient than those using throttling control of fluid flow, such as in systems with pumps and damper control for fans. However, the global market penetratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allowance (engineering)
In engineering and machining, an allowance is a planned deviation between an exact dimension and a nominal or theoretical dimension, or between an intermediate-stage dimension and an intended final dimension. The unifying abstract concept is that a certain amount of difference ''allows for'' some known factor of compensation or interference. For example, an area of excess metal may be left because it is needed to complete subsequent machining. Common cases are listed below. An ''allowance,'' which is a ''planned'' deviation from an ideal, is contrasted with a '' tolerance,'' which accounts for expected but unplanned deviations. Allowance is basically the size difference between components that work together. Allowance between parts that are assembled is very important. For example, the axle of a car has to be supported in a bearing otherwise it will fall to the ground. If there was no gap between the axle and the bearing then there would be a lot of friction and it would be difficu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Spectrum
The power spectrum S_(f) of a time series x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into a number of discrete frequencies, or a spectrum of frequencies over a continuous range. The statistical average of a certain signal or sort of signal (including noise) as analyzed in terms of its frequency content, is called its spectrum. When the energy of the signal is concentrated around a finite time interval, especially if its total energy is finite, one may compute the energy spectral density. More commonly used is the power spectral density (or simply power spectrum), which applies to signals existing over ''all'' time, or over a time period large enough (especially in relation to the duration of a measurement) that it could as well have been over an infinite time interval. The power spectral density (PSD) then refers to the spectral energy distribution that would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque Ripple
Torque ripple is an effect seen in many electric motor designs, referring to a periodic increase or decrease in output torque as the motor shaft rotates. It is measured as the difference in maximum and minimum torque over one complete revolution, generally expressed as a percentage. Examples A common example is "cogging torque" due to slight asymmetries in the magnetic field A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ... generated by the motor windings, which causes variations in the reluctance depending on the rotor position. This effect can be reduced by careful selection of the winding layout of the motor, or through the use of realtime controls to the power delivery. References"Torque ripple" Emetor Electric motors Torsional vibration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PI Controller
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an ''error value'' e(t) as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted ''P'', ''I'', and ''D'' respectively), hence the name. In practical terms, PID automatically applies an accurate and responsive correction to a control function. An everyday example is the cruise control on a car, where ascending a hill would lower speed if constant engine power were applied. The controller's PID algorithm restores the measured speed to the desired speed with minimal delay and overshoot by increasing the power output of the engine in a controlled manner. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast rate. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of reducing the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching, because their inertia causes them to react slowly. The PWM switching frequency has to be high enough not to affect the load, which is to say that the resultant waveform perceived by the load must be as smooth as possible. The rate (or frequency) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation (mathematics)
Rotation in mathematics is a concept originating in geometry. Any rotation is a motion of a certain space that preserves at least one point. It can describe, for example, the motion of a rigid body around a fixed point. Rotation can have sign (as in the sign of an angle): a clockwise rotation is a negative magnitude so a counterclockwise turn has a positive magnitude. A rotation is different from other types of motions: translations, which have no fixed points, and (hyperplane) reflections, each of them having an entire -dimensional flat of fixed points in a -dimensional space. Mathematically, a rotation is a map. All rotations about a fixed point form a group under composition called the rotation group (of a particular space). But in mechanics and, more generally, in physics, this concept is frequently understood as a coordinate transformation (importantly, a transformation of an orthonormal basis), because for any motion of a body there is an inverse transformation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
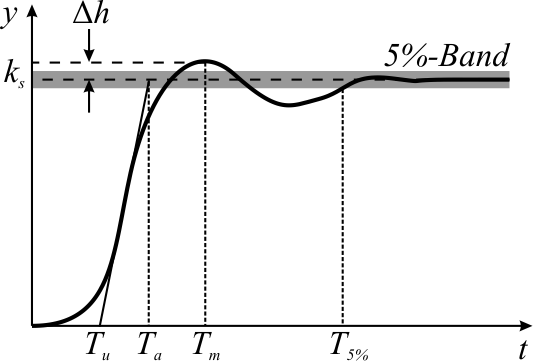
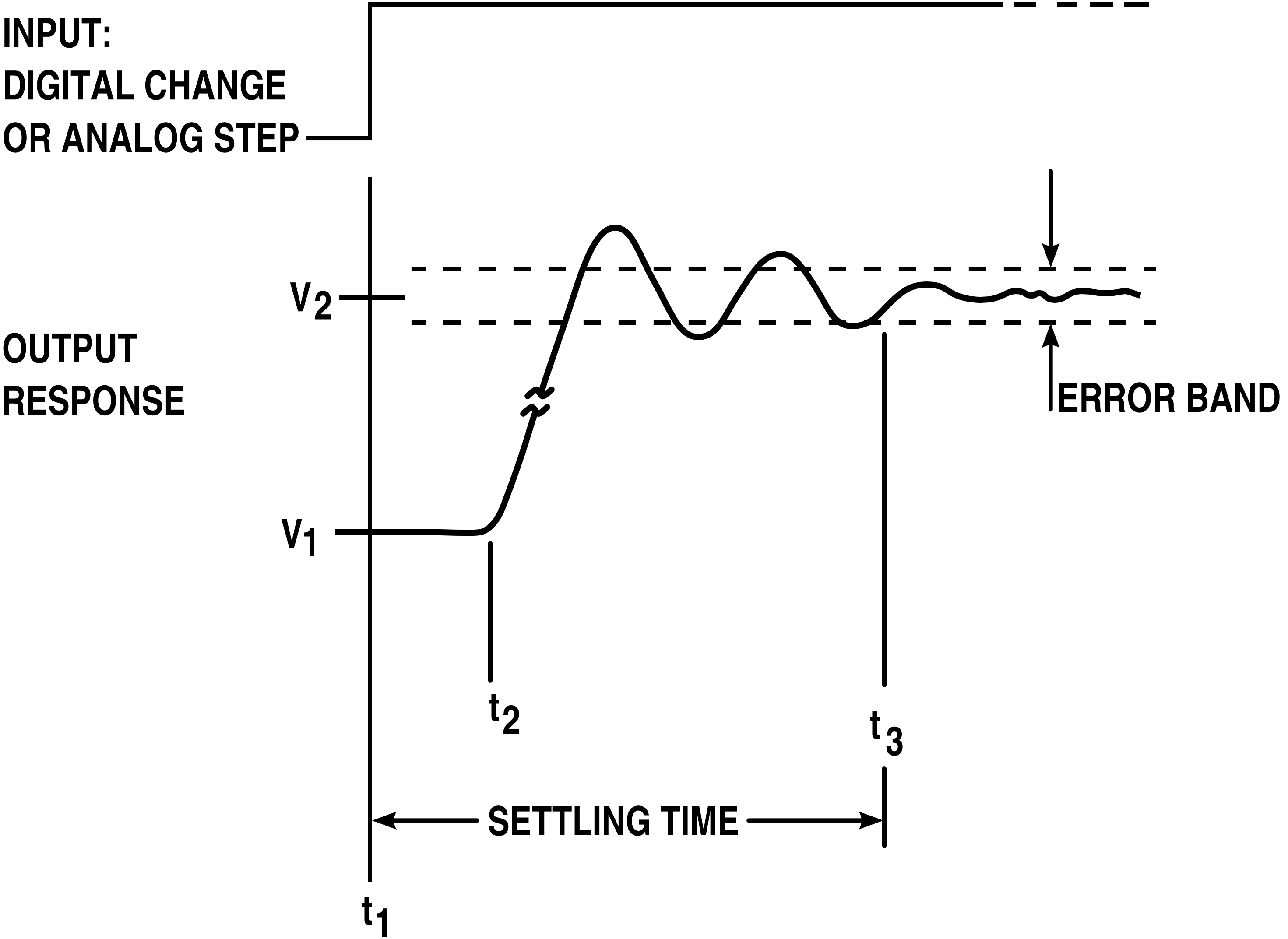
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is the occurrence of a signal or function exceeding its target. Undershoot is the same phenomenon in the opposite direction. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters. It is often followed by ringing, and at times conflated with the latter. Definition Maximum overshoot is defined in Katsuhiko Ogata's ''Discrete-time control systems'' as "the maximum peak value of the response curve measured from the desired response of the system." Control theory In control theory, overshoot refers to an output exceeding its final, steady-state value. For a step input, the ''percentage overshoot'' (PO) is the maximum value minus the step value divided by the step value. In the case of the unit step, the ''overshoot'' is just the maximum value of the step response minus one. Also see the definition of ''overshoot'' in an electronics context. For second-order sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Step Response
The step response of a system in a given initial state consists of the time evolution of its outputs when its control inputs are Heaviside step functions. In electronic engineering and control theory, step response is the time behaviour of the outputs of a general system when its inputs change from zero to one in a very short time. The concept can be extended to the abstract mathematical notion of a dynamical system using an evolution parameter. From a practical standpoint, knowing how the system responds to a sudden input is important because large and possibly fast deviations from the long term steady state may have extreme effects on the component itself and on other portions of the overall system dependent on this component. In addition, the overall system cannot act until the component's output settles down to some vicinity of its final state, delaying the overall system response. Formally, knowing the step response of a dynamical system gives information on the stability of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Control (motor)
Vector control, also called field-oriented control (FOC), is a variable-frequency drive (VFD) control method in which the stator currents of a three-phase AC or brushless DC electric motor are identified as two orthogonal components that can be visualized with a vector. One component defines the magnetic flux of the motor, the other the torque. The control system of the drive calculates the corresponding current component references from the flux and torque references given by the drive's speed control. Typically proportional-integral (PI) controllers are used to keep the measured current components at their reference values. The pulse-width modulation of the variable-frequency drive defines the transistor switching according to the stator voltage references that are the output of the PI current controllers. FOC is used to control AC synchronous and induction motors. It was originally developed for high-performance motor applications that are required to operate smoothly over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DTC Block Diagram
The DTC may refer to: Places *Desert Training Center, a World War II training area located mostly in southwestern California and western Arizona * Downtown Transit Center (TC), San Joaquin Regional Transit District *Denver Technological Center, a business park in Denver and Greenwood Village, Colorado People *Dominic Treadwell-Collins (born 1977), British television producer Companies and organizations * Defence Technology Centres, British military research facilities *Delhi Transport Corporation, the bus transport provider in Delhi *Depository Trust Company, American securities depository, subsidiary of Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation (DTCC) * Diamond Trading Company, rough diamonds sales and distribution arm of De Beers * Digital Trust Center, Dutch organisation and platform with the aim to help businesses with digital matters *Doctoral Training Centres, British centres for managing PhD studies *Discount Tire Company, an American tire and wheel retailer Software * Dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bang-bang Control
Bang Bang or Bang Bang Bang or similar may refer to: Food *Bang bang chicken, a Chinese dish *Bang bang shrimp, a Chinese dish People * Abdul Razzaq (cricketer) (born 1979), nicknamed Bang Bang Razzaq * Bang Bang (Dubliner) (1906–1981), eccentric elderly gentleman in Dublin known for playing cowboy in the streets * Bang-Bang Club, four photographers active in South Africa during the Apartheid period * Keith "Bang Bang" McCurdy (born 1985), a celebrity tattoo artist Technology * Bang–bang control, a controller that switches abruptly between two states * Bang-bang robot, or pick and place robot * Bang bang, Australian slang for a coffee knockbox Film, TV and entertainment * Bang Bang (TV channel), Albanian TV channel * "Bang-Bang" (''CSI''), 2006 episode of ''CSI: Crime Scene Investigation'' * ''Bang Bang'' (telenovela), 2005 Brazilian TV series * ''Bang Bang'' (2011 film), independent film by Byron Q *''Bang Bang!'', 2014 Bollywood film * ''Bang Bang!'' (play) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |