|
Dimercaprol
Dimercaprol, also called British anti-Lewisite (BAL), is a medication used to treat acute poisoning by arsenic, mercury, gold, and lead. It may also be used for antimony, thallium, or bismuth poisoning, although the evidence for those uses is not very strong. It is given by injection into a muscle. Common side effects include high blood pressure, pain at the site of the injection, vomiting, and fever. It is not recommended for people with peanut allergies as it is typically formulated as a suspension in peanut oil. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Dimercaprol is a chelator and works by binding with heavy metals. It has a very pungent odor. Dimercaprol was first made during World War II. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Dimercaprol has long been the mainstay of chelation therapy for lead or arsenic poisoning, and it is an essential drug. It is also used as an antidote to the chemical weapon Lewisit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Poisoning
Lead poisoning, also known as plumbism and saturnism, is a type of metal poisoning caused by lead in the body. The brain is the most sensitive. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, irritability, memory problems, infertility, and tingling in the hands and feet. It causes almost 10% of intellectual disability of otherwise unknown cause and can result in behavioral problems. Some of the effects are permanent. In severe cases, anemia, seizures, coma, or death may occur. Exposure to lead can occur by contaminated air, water, dust, food, or consumer products. Lead poisoning poses a significantly increased risk to children as they are far more likely to ingest lead indirectly by chewing on toys or other objects that are coated in lead paint. The amount of lead that can be absorbed by children is also higher than that of adults. Exposure at work is a common cause of lead poisoning in adults with certain occupations at particular risk. Diagnosis is typically by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewisite
Lewisite (L) (A-243) is an organoarsenic compound. It was once manufactured in the U.S., Japan, Germany and the Soviet Union for use as a chemical weapon, acting as a vesicant (blister agent) and lung irritant. Although the substance is colorless and odorless in its pure form, impure samples of lewisite are a yellow, brown, violet-black, green, or amber oily liquid with a distinctive odor that has been described as similar to geraniums. Chemical reactions The compound is prepared by the addition of arsenic trichloride to acetylene in the presence of a suitable catalyst: :AsCl3 + C2H2 → ClCHCHAsCl2 (Lewisite) Lewisite, like other arsenous chlorides, hydrolyses in water to form hydrochloric acid and chlorovinylarsenous oxide (a less-powerful blister agent): :ClCHCHAsCl2 + 2 H2O → ClCHCHAs(OH)2 + 2 HCl This reaction is accelerated in alkaline solutions, and forms acetylene and trisodium arsenate. Lewisite reacts with metals to form hydrogen gas. It is combustible, but diffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth Poisoning
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most diamagnetic element and one of the least thermally conductive metals known. Bismuth was long considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be extremely weakly radioactive. The metal's only primordial isotope, bismuth-209, experiences alpha decay at such a minut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson's Disease
Wilson's disease is a genetic disorder in which excess copper builds up in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, yellowish skin and itchiness. Brain-related symptoms include tremors, muscle stiffness, trouble in speaking, personality changes, anxiety, and psychosis. Wilson's disease is caused by a mutation in the Wilson disease protein (''ATP7B'') gene. This protein transports excess copper into bile, where it is excreted in waste products. The condition is autosomal recessive; for a person to be affected, they must inherit a mutated copy of the gene from both parents. Diagnosis may be difficult and often involves a combination of blood tests, urine tests and a liver biopsy. Genetic testing may be used to screen family members of those affected. Wilson's disease is typically treated with dietary changes and medication. Dietary changes involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic Poisoning
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III-V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds. A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in rats, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Poisoning
Mercury poisoning is a type of metal poisoning due to exposure to mercury. Symptoms depend upon the type, dose, method, and duration of exposure. They may include muscle weakness, poor coordination, numbness in the hands and feet, skin rashes, anxiety, memory problems, trouble speaking, trouble hearing, or trouble seeing. High-level exposure to methylmercury is known as Minamata disease. Methylmercury exposure in children may result in acrodynia (pink disease) in which the skin becomes pink and peels. Long-term complications may include kidney problems and decreased intelligence. The effects of long-term low-dose exposure to methylmercury are unclear. Forms of mercury exposure include metal, vapor, salt, and organic compound. Most exposure is from eating fish, amalgam-based dental fillings, or exposure at a workplace. In fish, those higher up in the food chain generally have higher levels of mercury, a process known as biomagnification. Less commonly, poisoning may occur a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Poisoning
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
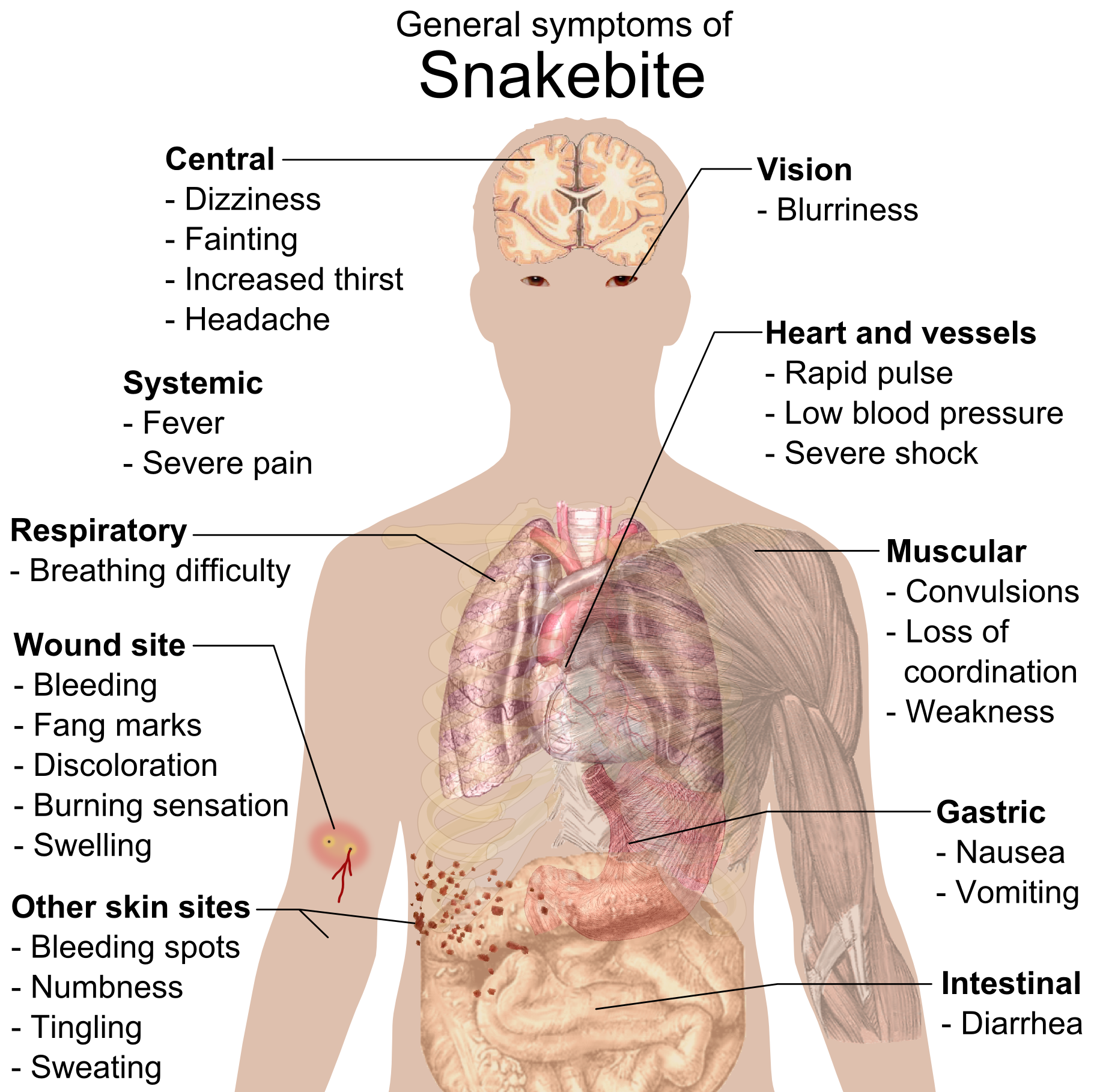
Snakebite
A snakebite is an injury caused by the bite of a snake, especially a venomous snake. A common sign of a bite from a venomous snake is the presence of two puncture wounds from the animal's fangs. Sometimes venom injection from the bite may occur. This may result in redness, swelling, and severe pain at the area, which may take up to an hour to appear. Vomiting, blurred vision, tingling of the limbs, and sweating may result. Most bites are on the hands, arms, or legs. Fear following a bite is common with symptoms of a racing heart and feeling faint. The venom may cause bleeding, kidney failure, a severe allergic reaction, tissue death around the bite, or breathing problems. Bites may result in the loss of a limb or other chronic problems or even death. The outcome depends on the type of snake, the area of the body bitten, the amount of snake venom injected, the general health of the person bitten and whether or not anti-venom serum has been administered by a doctor in a time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverse Effect
An adverse effect is an undesired harmful effect resulting from a medication or other intervention, such as surgery. An adverse effect may be termed a " side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. The term complication is similar to adverse effect, but the latter is typically used in pharmacological contexts, or when the negative effect is expected or common. If the negative effect results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or procedure, this is called a medical error and not an adverse effect. Adverse effects are sometimes referred to as " iatrogenic" because they are generated by a physician/treatment. Some adverse effects occur only when starting, increasing or discontinuing a treatment. Adverse effects can also be caused by placebo treatments (in which case the adverse effects are referred to as nocebo effects). Using a drug or other medical intervention which is contraindicated may increase the risk of adverse effects. Adverse effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succimer
Succimer, sold under the brand name Chemet among others, is a medication used to treat lead, mercury, and arsenic poisoning. When radiolabeled with technetium-99m, it is used in a number of types of diagnostic testing. A full course is 19 days of medications by mouth. More than two weeks should pass before a second course is given. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and low blood neutrophil levels. Liver problems and allergic reactions may also occur with use. Whether use during pregnancy is safe for the baby is unclear. Dimercaptosuccinic acid is in the chelating agent family of medications. It works by binding with lead and a number of other heavy metals, allowing them to leave the body in the urine. Dimercaptosuccinic acid has been used medically since the 1950s. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In the United States, no generic version was available as of 2015. Medical uses Dimercaptosuccinic acid is indicated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing and Shanghai, China and in Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)


.jpg)