|
Dihydropyridine Receptor
Cav1.1 also known as the calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1S subunit, (CACNA1S), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CACNA1S'' gene. It is also known as CACNL1A3 and the dihydropyridine receptor (DHPR, so named due to the blocking action DHP has on it). Function This gene encodes one of the five subunits of the slowly inactivating L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel in skeletal muscle cells. Mutations in this gene have been associated with hypokalemic periodic paralysis, thyrotoxic periodic paralysis and malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Cav1.1 is a voltage-dependent calcium channel found in the transverse tubule of muscles. In skeletal muscle it associates with the ryanodine receptor RyR1 of the sarcoplasmic reticulum via a mechanical linkage. It senses the voltage change caused by the end-plate potential from nervous stimulation and propagated by sodium channels as action potentials to the T-tubules. It was previously thought that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells that is similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in other Cell (biology), cells. The main function of the SR is to store calcium ions (Ca2+). Calcium in biology, Calcium ion levels are kept relatively constant, with the concentration of calcium ions within a cell being 10,000 times smaller than the concentration of calcium ions outside the cell. This means that small increases in calcium ions within the cell are easily detected and can bring about important cellular changes (the calcium is said to be a second messenger). Calcium is used to make calcium carbonate (found in chalk) and calcium phosphate, two compounds that the body uses to make teeth and bones. This means that too much calcium within the cells can lead to hardening (calcification) of certain intracellular structures, including the mitochondrion, mitochondria, leading to cell death. Therefore, it is vital that calcium ion levels a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Blocker
A channel blocker is the biological mechanism in which a particular molecule is used to prevent the opening of ion channels in order to produce a physiological response in a cell. Channel blocking is conducted by different types of molecules, such as cations, anions, amino acids, and other chemicals. These blockers act as ion channel antagonists, preventing the response that is normally provided by the opening of the channel. Ion channels permit the selective passage of ions through cell membranes by utilizing proteins that function as pores, which allow for the passage of electrical charge in and out of the cell. These ion channels are most often gated, meaning they require a specific stimulus to cause the channel to open and close. These ion channel types regulate the flow of charged ions across the membrane and therefore mediate membrane potential of the cell. Molecules that act as channel blockers are important in the field of pharmacology, as a large portion of drug desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Hyperthermia
Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is a type of severe reaction that occurs in response to particular medications used during General anaesthesia, general anesthesia, among those who are susceptible. Symptoms include tetany, muscle rigidity, hyperthermia, fever, and a tachycardia, fast heart rate. Complications can include rhabdomyolysis, muscle breakdown and hyperkalemia, high blood potassium. Most people who are susceptible to MH are generally unaffected when not exposed to triggering agents. Exposure to triggering agents (certain inhalational anaesthetic, volatile anesthetic agents or Suxamethonium chloride, succinylcholine) can lead to the development of MH in those who are susceptible. Susceptibility can occur due to at least six genetic mutations, with the most common one being of the RYR1 gene. These genetic variations are often inherited from a person's parents in an Dominance (genetics), autosomal dominant manner. The condition may also occur as a new mutation or be associated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (HYPP, HyperKPP) is an inherited autosomal dominant disorder that affects sodium channels in muscle cells and the ability to regulate potassium levels in the blood. It is characterized by muscle hyperexcitability or weakness which, exacerbated by potassium, heat or cold, can lead to uncontrolled shaking followed by paralysis. Onset usually occurs in early childhood, but it still occurs with adults. The mutation which causes this disorder is dominant on SCN4A with linkage to the sodium channel expressed in muscle. The mutation causes single amino acid changes in parts of the channel which are important for inactivation. These mutations impair "ball and chain" fast inactivation of SCN4A following an action potential. Signs and symptoms Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis causes episodes of extreme muscle weakness, with attacks often beginning in childhood. Depending on the type and severity of the HyperKPP, it can increase or stabilize until the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resting Potential
A relatively static membrane potential which is usually referred to as the ground value for trans-membrane voltage. The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response to environmental or intracellular stimuli. The resting potential exists due to the differences in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from functional activity of various ion channels, ion transporters, and exchangers. Conventionally, resting membrane potential can be defined as a relatively stable, ground value of transmembrane voltage in animal and plant cells. Beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
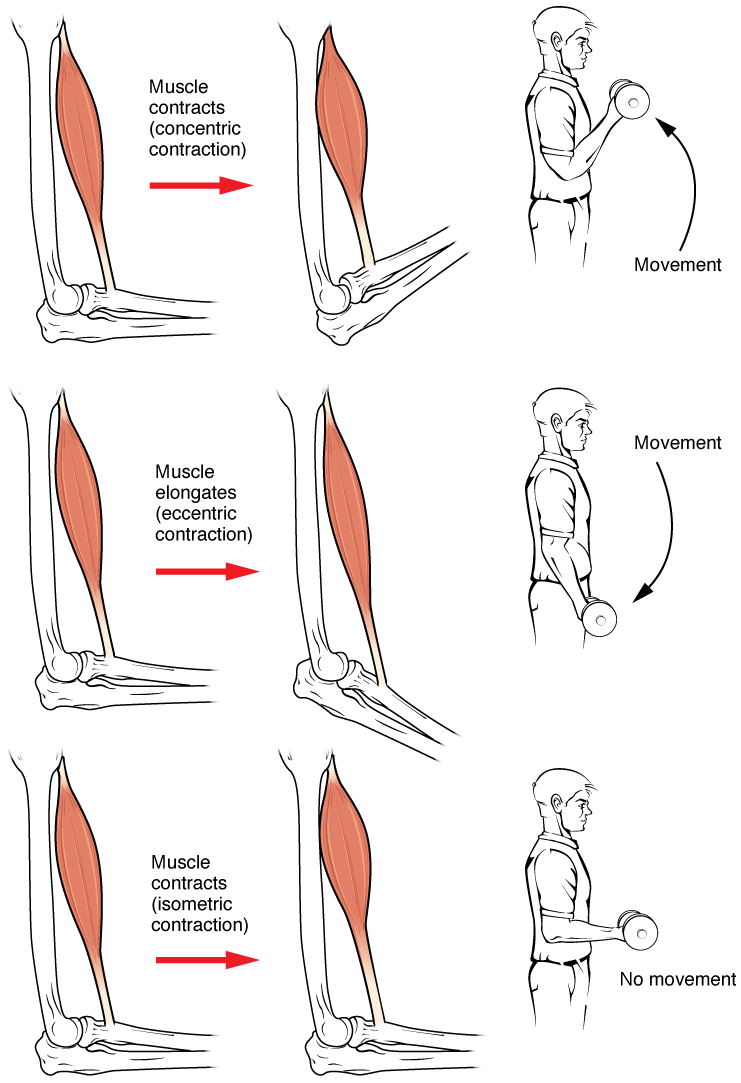
Excitation-contraction Coupling
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the interaction of two types of filaments which are the thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are two strands of actin coiled around each, and thick filaments consist of mostly elongated proteins called myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils which are important organelles in the skeletal muscle system. Muscle contraction can also be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and in some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell-cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect with other neurons at synapses, or to motor cells or glands. In other types of cells, their main function is to activate intracellular processes. In muscle cells, for example, an action potential is the first step in the chain of events l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
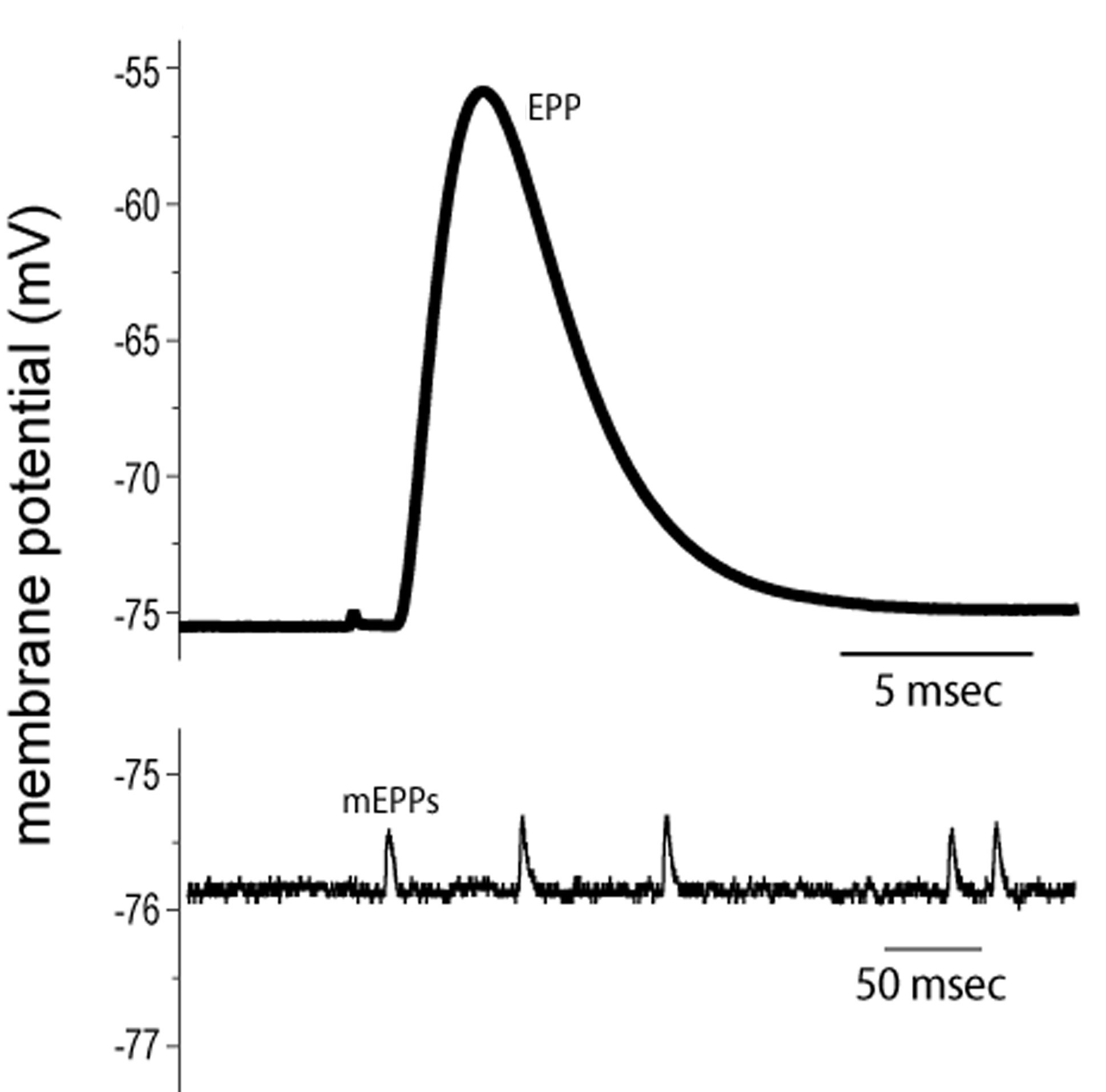
End-plate Potential
End plate potentials (EPPs) are the voltages which cause depolarization of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called "end plates" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.4mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
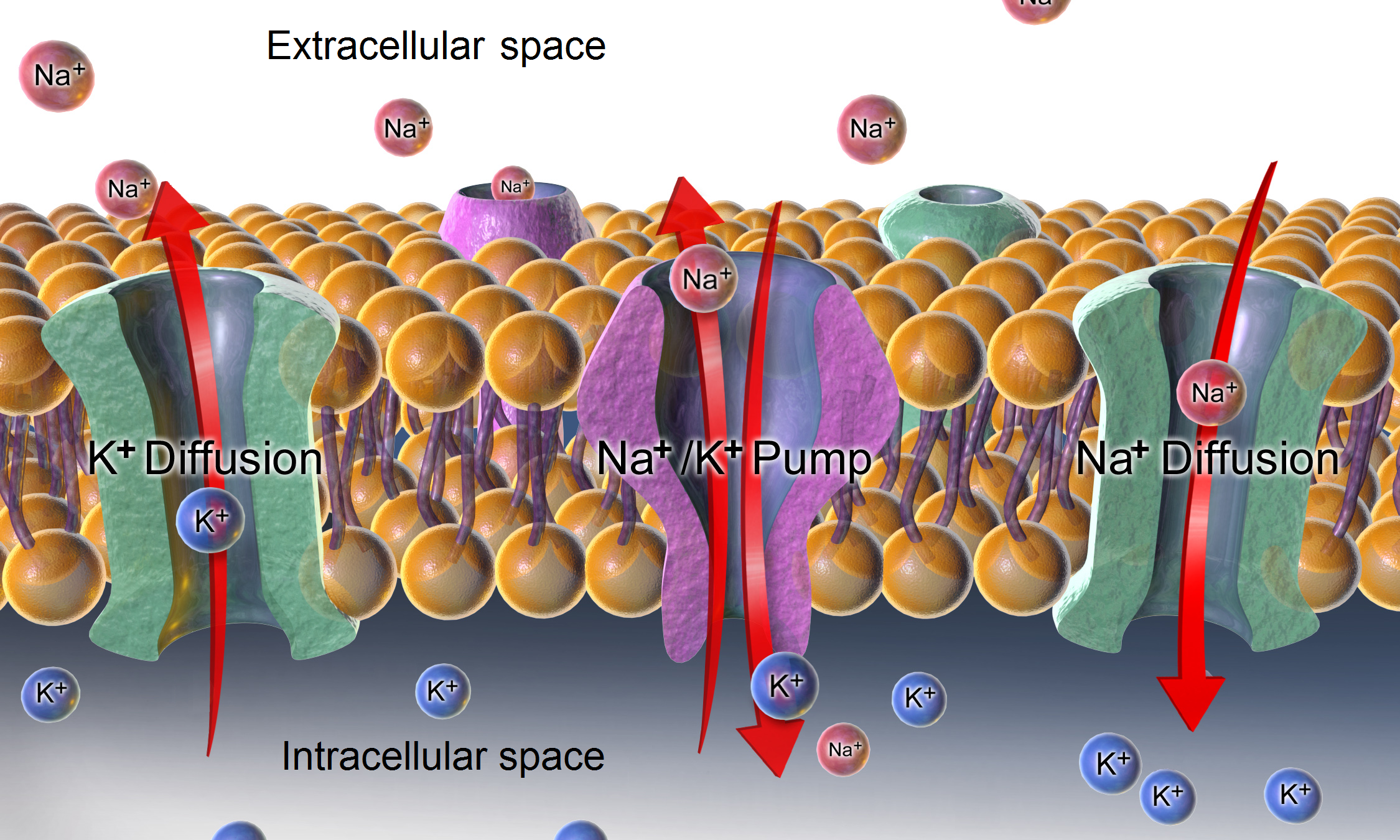
Membrane Potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges to move from the internal to exterior cellular environments and vice versa, as long as there is no acquisition of kinetic energy or the production of radiation. The concentration gradients of the charges directly determine this energy requirement. For the exterior of the cell, typical values of membrane potential, normally given in units of milli volts and denoted as mV, range from –80 mV to –40 mV. All animal cells are surrounded by a membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. The membrane serves as both an insulator and a diffusion barrier to the movement of ions. Transmembrane proteins, also known as ion transporter or ion pump proteins, actively push ions across the membrane and establish concentration gradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryanodine Receptor
Ryanodine receptors (RyR for short) form a class of intracellular calcium channels in various forms of excitable animal tissue like muscles and neurons. There are three major isoforms of the ryanodine receptor, which are found in different tissues and participate in different signaling pathways involving calcium release from intracellular organelles. The RYR2 ryanodine receptor isoform is the major cellular mediator of calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) in animal cells. Etymology The ryanodine receptors are named after the plant alkaloid ryanodine which shows a high affinity to them. Isoforms There are multiple isoforms of ryanodine receptors: * RyR1 is primarily expressed in skeletal muscle * RyR2 is primarily expressed in myocardium (heart muscle) * RyR3 is expressed more widely, but especially in the brain. * Non-mammalian vertebrates typically express two RyR isoforms, referred to as RyR-alpha and RyR-beta. * Many invertebrates, including the model organisms Dros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |