|
Digital Solid State Propulsion
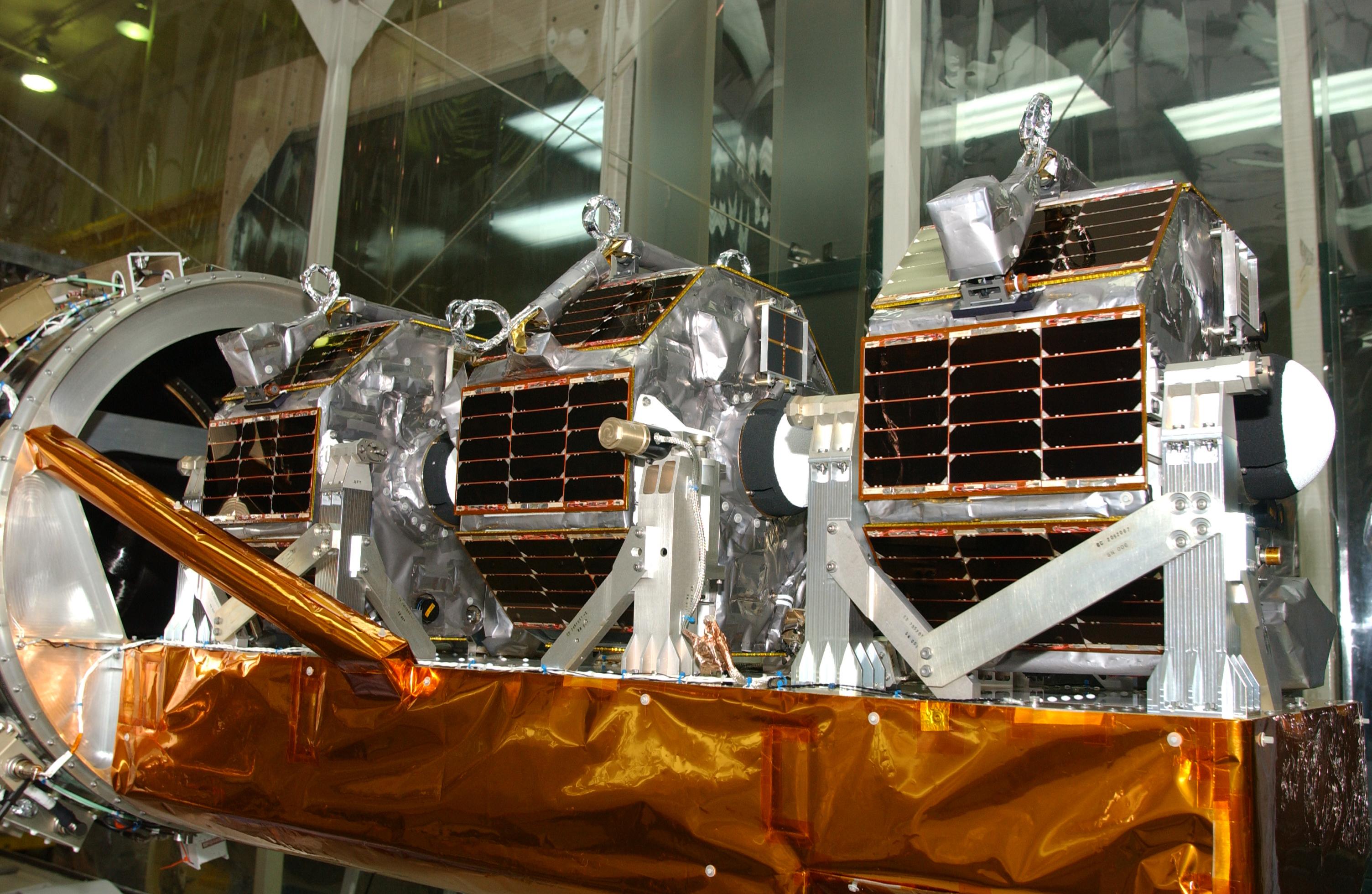
Digital Solid State Propulsion (DSSP) is an aerospace company developing microthruster propulsion technology for small satellites. DSSP's technology utilizes Electric Solid Propellants (ESPs) to enable small satellites to make orbital maneuvers that have generally not been possible in the very small, mass-constrained satellites such as CubeSats and nanosats. DSSP's first flight was aboard the NRL SPINSAT, launched as a secondary payload on SpaceX CRS-4 and deployed from the Kibo module airlock on 28 November 2014. NASA safety experts approved the mission because the satellite's 12 thruster-clusters burn an inert solid fuel, that only ignite when an electric charge is passed across it. In July 2012, DSSP won second place in the ''2012 NewSpace Business Plan Competition'' in Silicon Valley, sponsored by the Space Frontier Foundation The Space Frontier Foundation is an American space advocacy nonprofit corporation organized to promote the interests of increased involvement of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 7th-most extensive, the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 32nd-most populous, and the List of U.S. states and territories by population density, 9th-least densely populated of the U.S. states. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's people live in Clark County, Nevada, Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise, NV MSA, Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area, including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities. Nevada's capital is Carson City, Nevada, Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state. Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Propulsion
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallsat
A small satellite, miniaturized satellite, or smallsat is a satellite of low mass and size, usually under . While all such satellites can be referred to as "small", different classifications are used to categorize them based on mass. Satellites can be built small to reduce the large economic cost of launch vehicles and the costs associated with construction. Miniature satellites, especially in large numbers, may be more useful than fewer, larger ones for some purposes – for example, gathering of scientific data and radio relay. Technical challenges in the construction of small satellites may include the lack of sufficient power storage or of room for a propulsion system. Rationales One rationale for miniaturizing satellites is to reduce the cost; heavier satellites require larger rockets with greater thrust that also have greater cost to finance. In contrast, smaller and lighter satellites require smaller and cheaper launch vehicles and can sometimes be launched in multipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Maneuver
In spaceflight, an orbital maneuver (otherwise known as a burn) is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft. For spacecraft far from Earth (for example those in orbits around the Sun) an orbital maneuver is called a ''deep-space maneuver (DSM)''. The rest of the flight, especially in a transfer orbit, is called ''coasting''. General Rocket equation The Tsiolkovsky rocket equation, or ideal rocket equation is an equation that is useful for considering vehicles that follow the basic principle of a rocket: where a device that can apply acceleration to itself (a thrust) by expelling part of its mass with high speed and moving due to the conservation of momentum. Specifically, it is a mathematical equation that relates the delta-v (the maximum change of speed of the rocket if no other external forces act) with the effective exhaust velocity and the initial and final mass of a rocket (or other reaction engine.) For any such maneuver (or journey involvin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
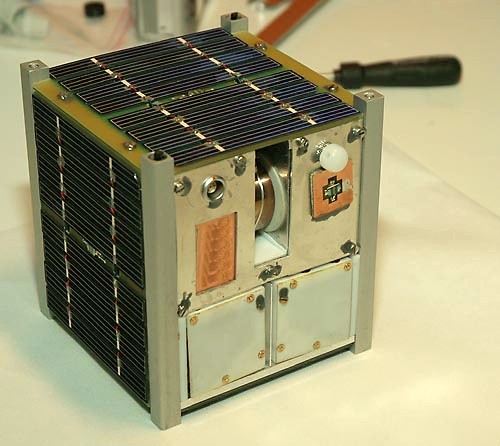
CubeSat
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are put into orbit by deployers on the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. , more than 1,600 CubeSats have been launched. In 1999, California Polytechnic State University (Cal Poly) professor Jordi Puig-Suari and Bob Twiggs, a professor at Stanford University Space Systems Development Laboratory, developed the CubeSat specifications to promote and develop the skills necessary for the design, manufacture, and testing of small satellites intended for low Earth orbit (LEO) that perform a number of scientific research functions and explore new space technologies. Academia accounted for the majority of CubeSat launches until 2013, when more than half of launches were for non-academic purposes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanosat
A small satellite, miniaturized satellite, or smallsat is a satellite of low mass and size, usually under . While all such satellites can be referred to as "small", different classifications are used to categorize them based on mass. Satellites can be built small to reduce the large economic cost of launch vehicles and the costs associated with construction. Miniature satellites, especially in large numbers, may be more useful than fewer, larger ones for some purposes – for example, gathering of scientific data and radio relay. Technical challenges in the construction of small satellites may include the lack of sufficient power storage or of room for a propulsion system. Rationales One rationale for miniaturizing satellites is to reduce the cost; heavier satellites require larger rockets with greater thrust that also have greater cost to finance. In contrast, smaller and lighter satellites require smaller and cheaper launch vehicles and can sometimes be launched in multip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPINSAT
SpaceX CRS-4, also known as SpX-4, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station (ISS), contracted to NASA, which was launched on 21 September 2014 and arrived at the space station on 23 September 2014. It was the sixth flight for SpaceX's uncrewed Dragon cargo spacecraft, and the fourth SpaceX operational mission contracted to NASA under a Commercial Resupply Services contract. The mission brought equipment and supplies to the space station, including the first 3D printer to be tested in space, a device to measure wind speed on Earth, and small satellites to be launched from the station. It also brought 20 mice for long-term research aboard the ISS. Launch history After a scrub due to poor weather conditions on 20 September 2014, the launch occurred on 21 September 2014 at 05:52 UTC from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. Primary payload NASA contracted for the CRS-4 mission and therefore determined the primary payload ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX CRS-4
SpaceX CRS-4, also known as SpX-4, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station (ISS), contracted to NASA, which was launched on 21 September 2014 and arrived at the space station on 23 September 2014. It was the sixth flight for SpaceX's uncrewed Dragon cargo spacecraft, and the fourth SpaceX operational mission contracted to NASA under a Commercial Resupply Services contract. The mission brought equipment and supplies to the space station, including the first 3D printer to be tested in space, a device to measure wind speed on Earth, and small satellites to be launched from the station. It also brought 20 mice for long-term research aboard the ISS. Launch history After a scrub due to poor weather conditions on 20 September 2014, the launch occurred on 21 September 2014 at 05:52 UTC from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. Primary payload NASA contracted for the CRS-4 mission and therefore determined the primary pay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibo Module
Kibo may refer to: * Kibō (ISS module), Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), component of the International Space Station * Kibo, a volcanic cone forming the main summit of Mount Kilimanjaro * An alias of James Parry, who as "Kibo" became a cult figure on Usenet in the early 1990s for posting numerous humorous messages * ''Kibo'' (spider), a genus of jumping spiders * Kibō no Tō, a political party in Japan * Board game record A board game record is a game record for a board game. ''Kifu'' (棋譜) is the Japanese term for an abstract strategy game record. In China, people named this kind of record "qipu" (. In Korea, people named this kind of record "Gibo" ({{zh, t ... See also * Kybo, scouting term for an outhouse {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo County and Santa Clara County. San Jose is Silicon Valley's largest city, the third-largest in California, and the tenth-largest in the United States; other major Silicon Valley cities include Sunnyvale, Santa Clara, Redwood City, Mountain View, Palo Alto, Menlo Park, and Cupertino. The San Jose Metropolitan Area has the third-highest GDP per capita in the world (after Zurich, Switzerland and Oslo, Norway), according to the Brookings Institution, and, as of June 2021, has the highest percentage of homes valued at $1 million or more in the United States. Silicon Valley is home to many of the world's largest high-tech corporations, including the headquarters of more than 30 businesses in the Fortune 1000, and thousands of startup companies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Frontier Foundation
The Space Frontier Foundation is an American space advocacy nonprofit corporation organized to promote the interests of increased involvement of the private sector, in collaboration with government, in the exploration and development of space. Its advocate members design and lead a collection of projects with goals that align to the organization's goals as described by its credo. History The foundation was founded in 1988 by space activists led by Rick Tumlinson, Bob Werb and Jim Muncy who felt that: "it was technically possible to realize their shared vision of large-scale...settlement of the inner solar system... utthey knew this was not happening (and couldn't happen) under the status-quo centrally planned and exclusive U.S. government space program." Since 2005 the foundation has relied heavily on NASA funding, including a recent $110,000 award for business competition. Thomas Olson appeared on The Space Show to promote the competition. The competition takes place duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerospace Companies Of The United States
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astronautics. Aerospace organizations research, design, manufacture, operate, or maintain both aircraft and spacecraft. The beginning of space and the ending of the air is considered as 100 km (62 mi) above the ground according to the physical explanation that the air pressure is too low for a lifting body to generate meaningful lift force without exceeding orbital velocity. Overview In most industrial countries, the aerospace industry is a cooperation of the public and private sectors. For example, several states have a civilian space program funded by the government, such as NASA, National Aeronautics and Space Administration in the United States, European Space Agency in Europe, the Canadian Space Agency in Canada, Indian Space Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)



.jpg)

