|
Differential Amplifier
A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs. It is an analog circuit with two inputs V_\text^- and V_\text^+ and one output V_\text, in which the output is ideally Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the difference between the two voltages: : V_\text = A(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where A is the Gain (electronics), gain of the amplifier. Single amplifiers are usually implemented by either adding the appropriate feedback resistors to a standard Operational amplifier, op-amp, or with a dedicated integrated circuit containing internal feedback resistors. It is also a common sub-component of larger integrated circuits handling analog signals. Mathematics of the amplifier : V_\text = A_\text(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where V_\text^+ and V_\text^- are the input voltages, and A_\text is the differential gain. In practice, however, the gain is not quite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Op-amp Symbol
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a direct coupling, DC-coupled Electronic component, electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input, a (usually) Single-ended signaling, single-ended output, and an extremely high gain (electronics), gain. Its name comes from its original use of performing mathematical operations in analog computers. By using negative feedback, an Op amp circuits, op amp circuit's characteristics (e.g. its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth, and functionality) can be determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or engineering tolerance in the op amp itself. This flexibility has made the op amp a popular building block in analog circuits. Today, op amps are used widely in consumer, industrial, and scientific electronics. Many standard integrated circuit op amps cost only a few cents; however, some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Common Emitter
In electronics, a common-emitter amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar-junction-transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage amplifier. It offers high current gain (typically 200), medium input resistance and a high output resistance. The output of a common emitter amplifier is inverted; i.e. for a sine wave input signal, the output signal is 180 degrees out of phase with respect to the input. In this circuit, the base terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the collector is the output, and the emitter is ''common'' to both (for example, it may be tied to ground reference or a power supply rail), hence its name. The analogous FET circuit is the common-source amplifier, and the analogous tube circuit is the common-cathode amplifier. Emitter degeneration Common-emitter amplifiers give the amplifier an inverted output and can have a very high gain that may vary widely from one transistor to the next. The gain is a strong f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Long Tailed Pair
A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs. It is an analog circuit with two inputs V_\text^- and V_\text^+ and one output V_\text, in which the output is ideally proportional to the difference between the two voltages: : V_\text = A(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where A is the gain of the amplifier. Single amplifiers are usually implemented by either adding the appropriate feedback resistors to a standard op-amp, or with a dedicated integrated circuit containing internal feedback resistors. It is also a common sub-component of larger integrated circuits handling analog signals. Mathematics of the amplifier : V_\text = A_\text(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where V_\text^+ and V_\text^- are the input voltages, and A_\text is the differential gain. In practice, however, the gain is not quite equal for the two inputs. This means, for instance, that if V_\text^+ an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Breakdown Voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator (electrical), insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to experience electrical breakdown and become electrically Conductor (material), conductive. For diodes, the breakdown voltage is the minimum reverse voltage that makes the diode conduct appreciably in reverse. Some devices (such as TRIACs) also have a ''forward breakdown voltage''. Electrical breakdown Materials are often classified as electrical conductor, conductors or Insulator (electricity), insulators based on their resistivity. A conductor is a substance which contains many mobile charged particles called charge carriers which are free to move about inside the material. An electric field is created across a piece of the material by applying a voltage difference between electrical contacts on different sides of the material. The force of the field causes the charge carriers within the material to move, creating an electric current from the positive co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Emitter-coupled Logic
In electronics, emitter-coupled logic (ECL) is a high-speed integrated circuit bipolar transistor logic family. ECL uses a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) differential amplifier with single-ended input and limited emitter current to avoid the saturated (fully on) region of operation and the resulting slow turn-off behavior. As the current is steered between two legs of an emitter-coupled pair, ECL is sometimes called ''current-steering logic'' (CSL), ''current-mode logic'' (CML) or ''current-switch emitter-follower'' (CSEF) logic. In ECL, the transistors are never in saturation, the input and output voltages have a small swing (0.8 V), the input impedance is high and the output impedance is low. As a result, the transistors change states quickly, gate delays are low, and the fanout capability is high. In addition, the essentially constant current draw of the differential amplifiers minimizes delays and glitches due to supply-line inductance and capacitance, and the compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Common-emitter
In electronics, a common-emitter amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar-junction-transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage amplifier. It offers high current gain (typically 200), medium input resistance and a high output resistance. The output of a common emitter amplifier is inverted; i.e. for a sine wave input signal, the output signal is 180 degrees out of phase with respect to the input. In this circuit, the base terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the collector is the output, and the emitter is ''common'' to both (for example, it may be tied to ground reference or a power supply rail), hence its name. The analogous FET circuit is the common-source amplifier, and the analogous tube circuit is the common-cathode amplifier. Emitter degeneration Common-emitter amplifiers give the amplifier an inverted output and can have a very high gain that may vary widely from one transistor to the next. The gain is a strong functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Common Collector
In electronics, a common collector amplifier (also known as an emitter follower) is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer. In this circuit, the base terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the emitter is the output, and the collector is ''common'' to both (for example, it may be tied to ground reference or a power supply rail), hence its name. The analogous field-effect transistor circuit is the common drain amplifier and the analogous tube circuit is the cathode follower. Basic circuit The circuit can be explained by viewing the transistor as being under the control of negative feedback. From this viewpoint, a common-collector stage (Fig. 1) is an amplifier with full series negative feedback. In this configuration (Fig. 2 with β = 1), the entire output voltage ''V''out is placed contrary and in series with the input voltage ''V''in. Thus the two voltages are subtracted ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Virtual Ground
In electronics, a virtual ground (or virtual earth) is a node of a circuit that is maintained at a steady reference potential, without being connected directly to the reference potential. In some cases the reference potential is considered to be that of the surface of the earth, and the reference node is called "ground" or "earth" as a consequence. The virtual ground concept aids circuit analysis in operational amplifiers and other circuits and provides useful practical circuit effects that would be difficult to achieve in other ways. In circuit theory, a node may have any value of current or voltage but physical implementations of a virtual ground will have limitations in terms of current handling ability and a non-zero impedance which may have practical side effects. Construction A voltage divider, using two resistors, can be used to create a virtual ground node. If two voltage sources are connected in series with two resistors, it can be shown that the midpoint becomes a vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bipolar Transistor Biasing
Biasing is the setting of the DC operating point of an electronic component. For bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), the operating point is defined as the steady-state DC collector-emitter voltage (V_) and the collector current (I_) with no input signal applied. Bias circuits for BJTs are discussed in this article. Properties of bias circuits In discrete circuits, bias circuits primarily consist of resistors. In integrated circuits, bias circuits are often more complicated – especially for bandgap voltage references and current mirrors. A bias circuit may also include elements such as temperature-dependent resistors, diodes, or additional voltage sources, depending on the expected range of operating conditions. Modes of operation In class-A amplifiers, the operating point is chosen such that the transistor stays in forward-active mode across the input signal's range. The operating point is often set near the center of the forward-active region, allowing for equal pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
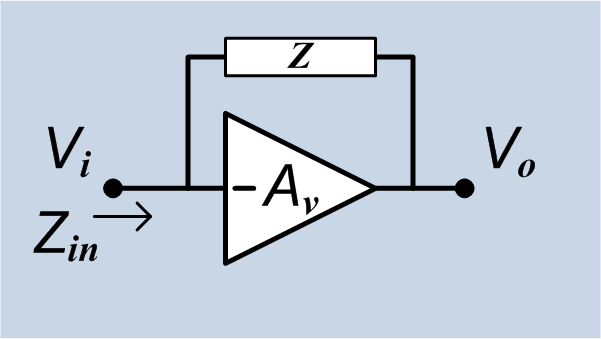
Miller Effect
In electronics, the Miller effect (named after its discoverer John Milton Miller) accounts for the increase in the equivalent input capacitance of an inverting voltage amplifier due to amplification of the effect of capacitance between the amplifier's input and output terminals, and is given by :C_=C (1+A_v)\, where -A_v is the voltage gain of the inverting amplifier (A_v positive) and C is the feedback capacitance. Although the term ''Miller effect'' normally refers to capacitance, any impedance connected between the input and another node exhibiting gain can modify the amplifier input impedance via this effect. These properties of the Miller effect are generalized in the Miller theorem. The Miller capacitance due to undesired parasitic capacitance between the output and input of active devices like transistors and vacuum tubes is a major factor limiting their gain at high frequencies. History When Miller published his work in 1919, he was working on vacuum tube triodes. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Figure 3
Figure may refer to: General *A shape, drawing, depiction, or geometric configuration *Figure (wood), wood appearance *Figure (music), distinguished from musical motif *Noise figure, in telecommunication *Dance figure, an elementary dance pattern *A person's figure, human physical appearance *Figure–ground (perception), the distinction between a visually perceived object and its surroundings Arts *Figurine, a miniature statuette representation of a creature *Action figure, a posable jointed solid plastic character figurine *Figure painting, realistic representation, especially of the human form *Figure drawing *Model figure, a scale model of a creature Writing *figure, in writing, a type of floating block (text, table, or graphic separate from the main text) *Figure of speech, also called a rhetorical figure *Christ figure, a type of character * in typesetting, text figures and lining figures Accounting *Figure, a synonym for number *Significant figures in a decimal numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phase Splitter
A phase splitter is a device that separates a signal into multiple phases (or polarities). The term is most often applied to amplifiers that produce two "balanced" voltage outputs: of equal amplitude but opposite polarity (i.e. 180 degrees phase difference), but sometimes is used to refer to the generation of quadrature signals (i.e. differing by 90 degrees). The term is not used for logic circuits producing complementary outputs, nor applied to differential amplifiers that have balanced inputs ''and'' outputs. Methods * using a unity gain inverting amplifier to provide an inverted copy of its input signal; * a split-load amplifier (also known as a "cathodyne" or "concertina phase splitter", especially in the context of vacuum tube implementations); a transistor implementation is shown in the diagram; * a differential pair amplifier can form a phase splitter in two ways: ** if the shared emitter (or cathode or source, for triode vacuum tube A vacuum tube, electron tub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |