|
Diane Kelly (computer Scientist)
Diane Kelly is an American computer scientist, notable for her work on the analysis of information seeking behaviours, and the development of experimental methods to support further research in the field. She is director of the faculties of Information Sciences and Communication & Information at the University of Tennessee Knoxville. Kelly's work is strongly user-oriented, with human behaviour and interaction at the centre of her research. She received a simultaneous PhD in Information and Library Science and Cognitive Science Certificate from Rutgers University in 2004. She graduated with an MLS from Rutgers in 1999 and a BA in Psychology & English from the University of Alabama in 1996. Other contributions made by Kelly include user modeling using implicit indicators of relevance, interface development and analysis for enhanced user interest and interaction, and new methodologies for designing and evaluating interactive retrieval systems. She was the recipient of the 2012 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Search Process
In library and information science, the information search process (ISP) is a six-stage process of information seeking behavior. The ISP was first suggested by Carol Kuhlthau in 1991. It describes the thoughts, feelings and actions of the searcher, and is often used to describe students. Stages Stage 1: Initiation During the first stage, ''initiation'', the information seeker recognizes the need for new information to complete an assignment. As they think more about the topic, they may discuss the topic with others and brainstorm the topic further.Shannon, Donna. "Kuhlthau's Information Search Process." School Library Media Activities Monthly, Vol. 19, no. 2, October 2002: p. 19-23. This stage of the information seeking process is filled with feelings of apprehension and uncertainty. Stage 2: Selection In the second stage, ''selection'', the individual begins to decide what topic will be investigated and how to proceed. Some information retrieval may occur at this point, resulting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Methods
Research is "creativity, creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, Discovery (observation), discovery, interpretation (philosophy), interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemology, epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Seeking Behavior
Information behavior is a field of information science research that seeks to understand the way people search for and use information in various contexts. It can include information seeking and information retrieval, but it also aims to understand why people seek information and how they use it. The term 'information behavior' was coined by Thomas D. Wilson in 1981 and sparked controversy upon its introduction. The term has now been adopted and Wilson's model of information behavior is widely cited in information behavior literature. In 2000, Wilson defined information behavior as "the totality of human behavior in relation to sources and channels of information". A variety of theories of information behavior seek to understand the processes that surround information seeking. An analysis of the most cited publications on information behavior during the early 21st century shows its theoretical nature. Information behavior research can employ various research methodologies gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Tennessee, Knoxville
The University of Tennessee (officially The University of Tennessee, Knoxville; or UT Knoxville; UTK; or UT) is a public land-grant research university in Knoxville, Tennessee. Founded in 1794, two years before Tennessee became the 16th state, it is the flagship campus of the University of Tennessee system, with ten undergraduate colleges and eleven graduate colleges. It hosts more than 30,000 students from all 50 states and more than 100 foreign countries. It is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". UT's ties to nearby Oak Ridge National Laboratory, established under UT President Andrew Holt and continued under the UT–Battelle partnership, allow for considerable research opportunities for faculty and students. Also affiliated with the university are the Howard H. Baker Jr. Center for Public Policy, the University of Tennessee Anthropological Research Facility, and the University of Tennessee Arboretum, which occupies of nearby Oak R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Friendly
Usability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a software can be used by specified consumers to achieve quantified objectives with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a quantified context of use. The object of use can be a software application, website, book, tool, machine, process, vehicle, or anything a human interacts with. A usability study may be conducted as a primary job function by a ''usability analyst'' or as a secondary job function by designers, technical writers, marketing personnel, and others. It is widely used in consumer electronics, communication, and knowledge transfer objects (such as a cookbook, a document or online help) and mechanical objects such as a door handle or a hammer. Usability includes methods of measuring usability, such as needs analysis and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Modeling
User modeling is the subdivision of human–computer interaction which describes the process of building up and modifying a conceptual understanding of the user. The main goal of user modeling is customization and adaptation of systems to the user's specific needs. The system needs to "say the 'right' thing at the 'right' time in the 'right' way". To do so it needs an internal representation of the user. Another common purpose is modeling specific kinds of users, including modeling of their skills and declarative knowledge, for use in automatic software-tests. User-models can thus serve as a cheaper alternative to user testing but should not replace user testing. Background A user model is the collection and categorization of personal data associated with a specific user. A user model is a (data) structure that is used to capture certain characteristics about an individual user, and a user profile is the actual representation in a given user model. The process of obtaining the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interface (computing)
In computing, an interface is a shared boundary across which two or more separate components of a computer system exchange information. The exchange can be between software, computer hardware, peripheral devices, humans, and combinations of these. Some computer hardware devices, such as a touchscreen, can both send and receive data through the interface, while others such as a mouse or microphone may only provide an interface to send data to a given system. Hardware interfaces Hardware interfaces exist in many components, such as the various buses, storage devices, other I/O devices, etc. A hardware interface is described by the mechanical, electrical, and logical signals at the interface and the protocol for sequencing them (sometimes called signaling). See also: A standard interface, such as SCSI, decouples the design and introduction of computing hardware, such as I/O devices, from the design and introduction of other components of a computing system, thereby allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karen Spärck Jones
Karen Sparck Jones is a computer science researcher and innovator who pioneered the search engine algorithm known as inverse document frequency (IDF). While many early information scientists and computer engineers were focused on developing programming languages and coding computer systems, Sparck-Jones thought it more beneficial to develop information retrieval systems that could understand human language. /sup> Background Karen Sparck-Jones was born in Huddersfield, Yorkshire, England in 1935 and attended school through university at Girton College in Cambridge. While she did not study computer science in school, she began her research career in a niche organization known as the Cambridge Language Research Unit (CLRU). Through her work at the CLRU, Sparck-Jones began pursuing her Ph.D. At the time of submission, her Ph.D thesis was cast aside as uninspired and lacking original thought but was later published in its entirety as a book. /sup> Professional Career � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
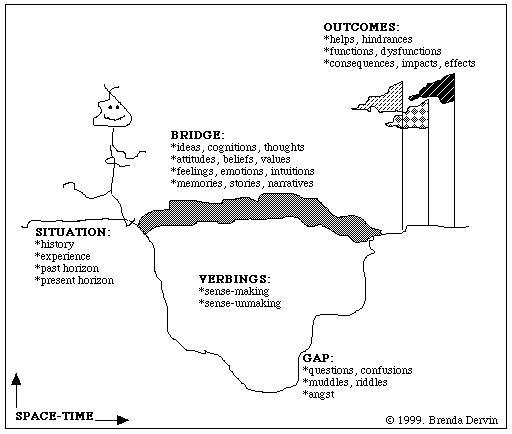
Brenda Dervin
Brenda Dervin, was a professor of communication at Ohio State University, working in the fields communication and library and information science. Her research about information seeking and information use led to the development of the sense-making methodology (Ross, Nilsen, & Dewdney, 2003, p. 93). Dervin received a bachelor's degree in journalism and home economics from Cornell University, with a minor in philosophy of religion, and her M.S. and PhD degrees in communication research from Michigan State University. In 1986 she acted as the first president of the International Communication Association The International Communication Association (ICA) is an academic association for scholars interested in the study, teaching and application of all aspects of human and mediated communication. ICA communicates within the association and with ot .... Dervin reviews articles and also is on editorial boards for communication and library and information science journals. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Kingsley Zipf
George Kingsley Zipf (; January 7, 1902 – September 25, 1950), was an American linguist and philologist who studied statistical occurrences in different languages.. Zipf earned his bachelors, masters, and doctoral degrees from Harvard University, although he also studied at the University of Bonn and the University of Berlin. He was Chairman of the German Department and University Lecturer (meaning he could teach any subject he chose) at Harvard University. He worked with Chinese and demographics, and much of his effort can explain properties of the Internet, distribution of income within nations, and many other collections of data. Zipf's law He is the eponym of Zipf's law, which states that while only a few words are used very often, many or most are used rarely, :P_n \sim 1/n^a where ''Pn'' is the frequency of a word ranked ''n''th and the exponent ''a'' is almost 1. This means that the second item occurs approximately 1/2 as often as the first, and the third item 1/3 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Computer Scientists
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |