|
Depth Contour
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of seabed, ocean floors (''seabed topography''), lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago. Bathymetric (or hydrography, hydrographic) charts are typically produced to support safety of surface or sub-surface navigation, and usually show seafloor relief or terrain as contour lines (called depth contours or isobaths) and selected depths (''Depth sounding, soundings''), and typically also provide surface navigational information. Bathymetric maps (a more general term where navigational safety is not a concern) may also use a Digital Terrain Model and artificial illumination techniques to illustrate the depths being portrayed. The global bathymetry is sometimes combined with topography data to yield a global relief model. Paleobathymetry is the study of past underwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) is a combat support agency within the United States Department of Defense whose primary mission is collecting, analyzing, and distributing geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) in support of national security. Initially known as the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA) from 1996 to 2003, it is a member of the United States Intelligence Community. NGA headquarters, also known as NGA Campus East or NCE, is located at Fort Belvoir North Area in Springfield, Virginia. The agency also operates major facilities in the St. Louis, Missouri area (referred to as NGA Campus West or NCW), as well as support and liaison offices worldwide. The NGA headquarters, at , is the third-largest government building in the Washington metropolitan area after The Pentagon and the Ronald Reagan Building. In addition to using GEOINT for U.S. military and intelligence efforts, NGA provides assistance during natural and man-made disasters, aids in security ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary purpose of safety of navigation and in support of all other marine activities, including economic development, security and defense, scientific research, and environmental protection. History The origins of hydrography lay in the making of charts to aid navigation, by individual mariners as they navigated into new waters. These were usually the private property, even closely held secrets, of individuals who used them for commercial or military advantage. As transoceanic trade and exploration increased, hydrographic surveys started to be carried out as an exercise in their own right, and the commissioning of surveys was increasingly done by governments and special hydrographic offices. National organizations, particularly navies, realized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Terrain Models
A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refers to a discrete global grid. DEMs are used often in geographic information systems (GIS), and are the most common basis for digitally produced relief maps. A digital terrain model (DTM) represents specifically the ground surface while DEM and DSM may represent tree top canopy or building roofs. While a DSM may be useful for landscape modeling, city modeling and visualization applications, a DTM is often required for flood or drainage modeling, land-use studies, geological applications, and other applications, and in planetary science. Terminology There is no universal usage of the terms ''digital elevation model'' (DEM), ''digital terrain model'' (DTM) and ''digital surface model'' (DSM) in scientific literature. In most cases the term ''digita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephonic or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. The GPS project was started by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1973. The first prototype spacecraft was lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
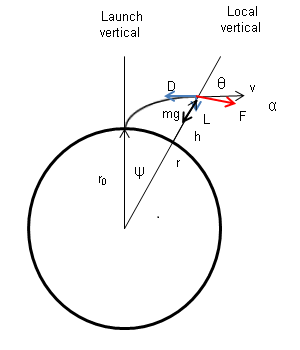
Flight Dynamics
Flight dynamics in aviation and spacecraft, is the study of the performance, stability, and control of vehicles flying through the air or in outer space. It is concerned with how forces acting on the vehicle determine its velocity and attitude with respect to time. For a fixed-wing aircraft, its changing orientation with respect to the local air flow is represented by two critical angles, the angle of attack of the wing ("alpha") and the angle of attack of the vertical tail, known as the sideslip angle ("beta"). A sideslip angle will arise if an aircraft yaws about its centre of gravity and if the aircraft sideslips bodily, i.e. the centre of gravity moves sideways.Flightwise - Volume 2 - Aircraft Stability And Control, Chris Carpenter 1997, Airlife Publishing Ltd., , p.145 These angles are important because they are the principal source of changes in the aerodynamic forces and moments applied to the aircraft. Spacecraft flight dynamics involve three main forces: propulsive (ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation of the energy of a photon, via the Planck relation ''E'' = ''hν'', where ''E'' is the photon's energy, ''ν'' is its freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Resolution
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major determinant of image resolution. It is used in optics applied to light waves, in antenna theory applied to radio waves, and in acoustics applied to sound waves. The colloquial use of the term "resolution" sometimes causes confusion; when an optical system is said to have a high resolution or high angular resolution, it means that the perceived distance, or actual angular distance, between resolved neighboring objects is small. The value that quantifies this property, ''θ,'' which is given by the Rayleigh criterion, is low for a system with a high resolution. The closely related term spatial resolution refers to the precision of a measurement with respect to space, which is directly connected to angular resolution in imaging instruments. The Rayleigh criterion shows th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
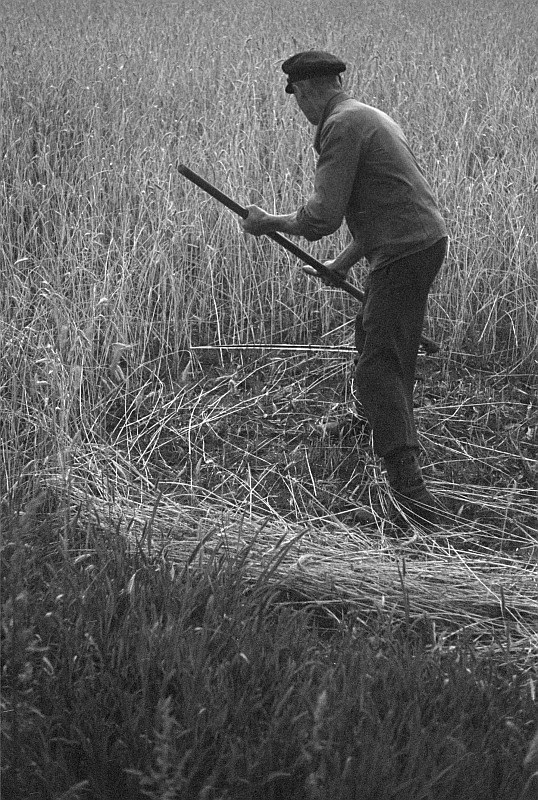
Swath Width
A swathe (; rhymes with "bathe") or swath (; rhymes with "cloth") is the width of a scythe stroke or a mowing-machine blade, the path of this width made in mowing or the mown grass or grain lying on such a path. The mower with a scythe moves along the mowing-edge with the uncut grass to the right and the cut grass laid in a neat row to the left, on the previously mown land. The swathe width depends on the blade length, the nature of the crop and the mower but is usually about 1.5 metres wide. Mowing may be done by a team of mowers, usually starting at the edges of a meadow then proceeding clockwise leaving a series of staggered swathes and finishing in the middle. The mower swings the scythe steadily in long, left handed arcs ending in front of the mower and depositing the cut grass neatly to the left. The mower takes a small step forward and repeats the motion, proceeding with a steady rhythm, stopping at frequent intervals to hone the blade. The correct technique has a slici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multibeam Echosounder
A multibeam echosounder (MBES) is a type of sonar that is used to map the seabed. It emits acoustic waves in a fan shape beneath its transceiver. The time it takes for the sound waves to reflect off the seabed and return to the receiver is used to calculate the water depth. Unlike other sonars and echo sounders, MBES uses beamforming to extract directional information from the returning soundwaves, producing a swath of depth soundings from a single ping. History and progression Multibeam sonar sounding systems, also known as ''swathe'' (British English) or ''swath'' (American English), originated for military applications. The Sonar Array Sounding System (SASS) was developed in the early 1960s by the US Navy, in conjunction with General Instrument to map large swaths of the ocean floor to assist the underwater navigation of its submarine force. SASS was tested aboard the USS ''Compass Island'' (AG-153). The final array system, composed of sixty-one one degree beams with a swa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)