|
Density Contrast
Density contrast is a parameter used in galaxy formation to indicate where there are local enhancements in matter density. :\Delta=\frac It is believed that after inflation In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ..., although the universe was mostly uniform, some regions were slightly denser than others with contrast densities on the order of 1 trillionth. As the horizon distance expanded, the enclosed causally connected (i.e. gravitationally connected) masses increased until they reached the Jeans mass and began to collapse, which allowed galaxies, galaxy clusters, superclusters, and filaments to form. References Physical cosmology Inflation (cosmology) {{physical-cosmology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Formation
The study of galaxy formation and evolution is concerned with the processes that formed a heterogeneous universe from a homogeneous beginning, the formation of the first galaxies, the way galaxies change over time, and the processes that have generated the variety of structures observed in nearby galaxies. Galaxy formation is hypothesized to occur from structure formation theories, as a result of tiny quantum fluctuations in the aftermath of the Big Bang. The simplest model in general agreement with observed phenomena is the Lambda-CDM model—that is, that clustering and merging allows galaxies to accumulate mass, determining both their shape and structure. Commonly observed properties of galaxies Because of the inability to conduct experiments in outer space, the only way to “test” theories and models of galaxy evolution is to compare them with observations. Explanations for how galaxies formed and evolved must be able to predict the observed properties and types of galax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation (cosmology)
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation, is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the early universe. The inflationary epoch lasted from seconds after the conjectured Big Bang singularity to some time between and seconds after the singularity. Following the inflationary period, the universe continued to expand, but at a slower rate. The acceleration of this expansion due to dark energy began after the universe was already over 7.7 billion years old (5.4 billion years ago). Inflation theory was developed in the late 1970s and early 80s, with notable contributions by several theoretical physicists, including Alexei Starobinsky at Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Alan Guth at Cornell University, and Andrei Linde at Lebedev Physical Institute. Alexei Starobinsky, Alan Guth, and Andrei Linde won the 2014 Kavli Prize "for pioneering the theory of cosmic inflation." It was developed further in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Horizon
The particle horizon (also called the cosmological horizon, the comoving horizon (in Dodelson's text), or the cosmic light horizon) is the maximum distance from which light from particles could have traveled to the observer in the age of the universe. Much like the concept of a terrestrial horizon, it represents the boundary between the observable and the unobservable regions of the universe, so its distance at the present epoch defines the size of the observable universe. Due to the expansion of the universe, it is not simply the age of the universe times the speed of light (approximately 13.8 billion light-years), but rather the speed of light times the conformal time. The existence, properties, and significance of a cosmological horizon depend on the particular cosmological model. Conformal time and the particle horizon In terms of comoving distance, the particle horizon is equal to the conformal time \eta that has passed since the Big Bang, times the speed of light c. In g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeans Mass
In stellar physics, the Jeans instability causes the collapse of interstellar gas clouds and subsequent star formation, named after James Jeans. It occurs when the internal gas pressure is not strong enough to prevent gravitational collapse of a region filled with matter. For stability, the cloud must be in hydrostatic equilibrium, which in case of a spherical cloud translates to: :\frac = -\frac, where M_\text(r) is the enclosed mass, p is the pressure, \rho(r) is the density of the gas (at radius r), G is the gravitational constant, and r is the radius. The equilibrium is stable if small perturbations are damped and unstable if they are amplified. In general, the cloud is unstable if it is either very massive at a given temperature or very cool at a given mass; under these circumstances, the gas pressure cannot overcome gravity, and the cloud will collapse. The Jeans instability likely determines when star formation occurs in molecular clouds. Jeans mass The Jeans mass is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Clusters
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after galaxy filaments and were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. One of the key features of clusters is the intracluster medium (ICM). The ICM consists of heated gas between the galaxies and has a peak temperature between 2–15 keV that is dependent on the total mass of the cluster. Galaxy clusters should not be confused with ''galactic clusters'' (also known as open clusters), which are star clusters ''within'' galaxies, or with globular clusters, which typically orbit galaxies. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. The galaxy groups and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
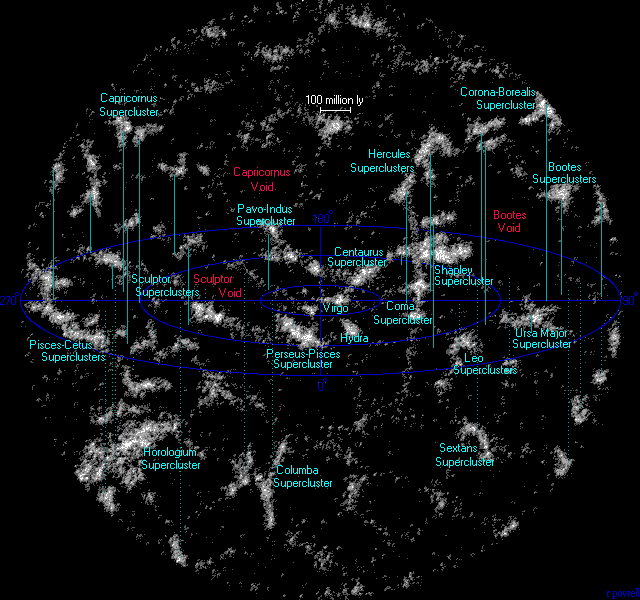
Superclusters
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster."Earth's new address: 'Solar System, Milky Way, Laniakea '''' The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the |
Galaxy Filament
In cosmology, galaxy filaments (subtypes: supercluster complexes, galaxy walls, and galaxy sheets) Boris V. Komberg, Andrey V. Kravtsov, Vladimir N. Lukash; "The search and investigation of the Large Groups of Quasars" ; ;R.G. Clowes; "Large Quasar Groups - A Short Review"; ''The New Era of Wide Field Astronomy'', ASP Conference Series, vol. 232.; 2001; Astronomical Society of the Pacific; ; are the largest known structures in the universe, consisting of walls of gravitationally bound galaxy superclusters. These massive, thread-like formations can reach 80 megaparsecs ''h''−1 (or of the order of 160 to 260 million light-years) and form the boundaries between large voids. Formation In the standard model of the evolution of the universe, galactic filaments form along and follow web-like strings of dark matter—also referred to as the galactic web or cosmic web. It is thought that this dark matter dictates the structure of the Universe on the grandest of scales. Dark matter g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Cosmology
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate.For an overview, see Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed those physical laws to be understood. Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond the Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |