|
Denaʼina People
The Denaʼina ( ; own name: in the Inland dialect ənʌʔɪnʌ in the Upper Inlet dialect ənʌ͡ɪnʌ russian: денаʼина), or formerly Tanaina (russian: Танаина; кенайтце), are an Alaska Native Athabaskan people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group. They are the original inhabitants of the south central Alaska region ranging from Seldovia in the south to Chickaloon in the northeast, Talkeetna in the north, Lime Village in the Northwest and Pedro Bay in the Southwest. The Denaʼina homeland (''Denaʼina Ełnena'') is more than 41,000 square miles in area.Patricia H. Partnow 2013Denaʼinaqʼ Huchʼulyeshi: The Denaʼina Way of Living. Anchorage Museum. They arrived in the Southcentral Alaska sometime between 1,000 and 1,500 years ago. They were the only Alaskan Athabaskan group to live on the coast. Denaʼina culture is a hunter-gatherer culture and have a matrilineal system. The Iditarod Trail's antecedents were the native trails of the De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Indian Languages Alaska
Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early Branch, a stream in Missouri * Early County, Georgia Other uses * Early (Scritti Politti album), ''Early'' (Scritti Politti album), 2005 * Early (A Certain Ratio album), ''Early'' (A Certain Ratio album), 2002 * Early (name) * Early effect, an effect in transistor physics * Early Records, a record label * the early part of the morning See also * Earley (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chickaloon, Alaska
Chickaloon (''Nay’dini’aa Na’'' in Ahtna Athabascan; ''Nuk'din'itnu'' in Dena'ina) is a census-designated place (CDP) in Matanuska-Susitna Borough, Alaska, United States. It is part of the Anchorage, Alaska Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 254 at the 2020 census, down from 272 in 2010. The Alaska Native people of Chickaloon are a mixture of Ahtna and Dena'ina Athabaskan. On May 31, 2021 a M6.1 Earthquake struck Chickaloon. Geography Chickaloon is located at (61.793994, -148.482733). According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , of which is land and (1.05%) is water. Demographics Chickaloon first appeared on the 1930 U.S. Census as an unincorporated village. It appeared again on the 1940 & 1960 censuses, but was not returned separately in 1950, 1970 & 1980. It returned again beginning in 1990, when it was made a census-designated place. As of the census of 2000, there were 213 people, 87 households, and 58 fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alutiiq People
The Alutiiq people (pronounced in English; from Promyshlenniki Russian Алеутъ, "Aleut"; plural often "Alutiit"), also called by their ancestral name ( or ; plural often "Sugpiat"), as well as Pacific Eskimo or Pacific Yupik, are a southern coastal people of Alaska Natives. Their traditional homelands include Prince William Sound and outer Kenai Peninsula (), the Kodiak Archipelago and the Alaska Peninsula (). In the early 1800s there were more than 60 Alutiiq villages in the Kodiak archipelago, with an estimated population of 13,000 people. Today more than 4,000 Alutiiq people live in Alaska. Terminology At present, the most commonly used title is (singular), (dual), (plural). These terms derive from the names (, ) that Russian fur traders and settlers gave to the native people in the region. Russian occupation began in 1784, following their massacre of hundreds of Sugpiat at Refuge Rock () just off the coast of Sitkalidak Island near the present-day village of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chugach Sugpiaq
Chugach , Chugach Sugpiaq or Chugachigmiut is the name of an Alaska Native people in the region of the Kenai Peninsula and Prince William Sound on the southern coast of Alaska. The Chugach people are an Alutiiq (Pacific Eskimo) people who speak the Chugach dialect of the Alutiiq language. Name Their autonym ''Sugpiaq'' derives from ''suk'', meaning "person" and -''piaq'', meaning "real." The term ''Alutiiq'' derives from the Russian term for the Aleut people. According to Ethnologue, earlier terms for the Chugach such as Chugach Eskimo, South Alaska Eskimo, Sugpiak Eskimo, and Sugpiaq Eskimo, are pejorative. Settlements Chugach villages include Chenega Bay, Eyak, Alaska, Eyak, Nanwalek, Alaska, Nanwalek (English Bay), Port Graham, Alaska, Port Graham, and Tatitlek, Alaska, Tatitlek. History The Chugach people have lived in the region around Prince William Sound for millennia, according to archaeological finds. They were the first indigenous Alaskans to encounter the Russian ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alutiiq
The Alutiiq people (pronounced in English; from Promyshlenniki Russian Алеутъ, "Aleut"; plural often "Alutiit"), also called by their ancestral name ( or ; plural often "Sugpiat"), as well as Pacific Eskimo or Pacific Yupik, are a southern coastal people of Alaska Natives. Their traditional homelands include Prince William Sound and outer Kenai Peninsula (), the Kodiak Archipelago and the Alaska Peninsula (). In the early 1800s there were more than 60 Alutiiq villages in the Kodiak archipelago, with an estimated population of 13,000 people. Today more than 4,000 Alutiiq people live in Alaska. Terminology At present, the most commonly used title is (singular), (dual), (plural). These terms derive from the names (, ) that Russian fur traders and settlers gave to the native people in the region. Russian occupation began in 1784, following their massacre of hundreds of Sugpiat at Refuge Rock () just off the coast of Sitkalidak Island near the present-day village of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanana Peoples
The Tanana Athabaskans, Tanana Athabascans or Tanana Athapaskans are an Alaskan Athabaskan peoples of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group. They are the original inhabitants of the Tanana River (in Tanana languages , literally 'straight water', in Koyukon language , literally 'trail water') drainage basin in east-central Alaska Interior, United States and a little part (White River First Nation) lived in Yukon, Canada. Tanana River Athabaskan peoples are called in Lower Tanana and Koyukon language (literally 'trail people'), in Gwich'in language (literally 'people of Tanana River'). In Alaska, where they are the oldest, there are three or four groups identified by the languages they speak. These are the Tanana proper or Lower Tanana () and/or Middle Tanana, Tanacross or Tanana Crossing (), and Upper Tanana (). The Tanana Athabaskan culture is a hunter-gatherer culture and have a matrilineal system. Tanana Athabaskans were semi-nomadic and as living in semi-permanen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koyukon People
The Koyukon (russian: Коюконы) are an Alaska Native Athabascan people of the Athabascan-speaking ethnolinguistic group. Their traditional territory is along the Koyukuk and Yukon rivers where they subsisted for thousands of years by hunting and trapping. Many Koyukon live in a similar manner today. The Koyukon language belongs to a large family called Na-Dené or Athabascan, traditionally spoken by numerous groups of native people throughout northwestern North America. In addition, due to ancient migrations of related peoples, other Na-Dené languages, such as Navajo and Apachean varieties, are spoken in the American Southwest and in Mexico. History The first Europeans to enter Koyukon territory were Russians, who came up the Yukon River to Nulato in 1838. When they arrived, they found that items such as iron pots, glass beads, cloth apparel, and tobacco had already reached the people through their trade with coastal Eskimos, who had long traded with Russians. An ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Kuskokwim Language
The Upper Kuskokwim language (also called Kolchan or Goltsan or Dinak'i) is an Athabaskan language of the Na-Dené language family. It is spoken by the Upper Kuskokwim people in the Upper Kuskokwim River villages of Nikolai, Telida, and McGrath, Alaska. About 40 of a total of 160 Upper Kuskokwim people (Dichinanek’ Hwt’ana) still speak the language. A practical orthography of the language was established by Raymond Collins, who in 1964 began linguistic work at Nikolai. Since 1990s, the language has also been documented by a Russian linguist Andrej Kibrik Andrej Kibrik (russian: Андре́й Алекса́ндрович Ки́брик; born June 18, 1963) is a Russian linguist, the director of the Institute of Linguistics of the Russian Academy of Sciences (since 2017), and professor at the Phil .... Bibliography Alaska Native Language Center Retrieved on 2007-03-14. * Collins, Raymond and Sally Jo Collins. 2004. Dichinanek' Hwt'ana: A History of the people of the Uppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
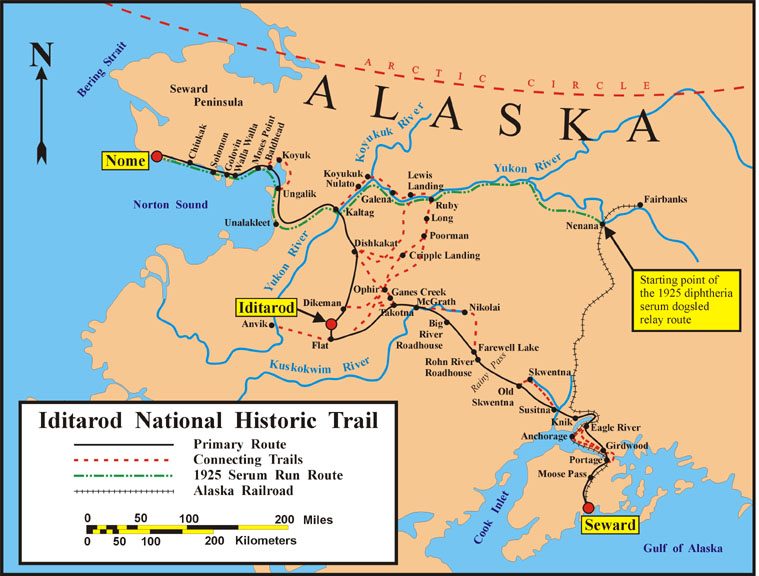
Iditarod Trail
The Iditarod Trail, also known historically as the Seward-to-Nome Trail, is a thousand-plus mile (1,600 km) historic and contemporary trail system in the US state of Alaska. The trail began as a composite of trails established by Alaskan native peoples. Its route crossed several mountain ranges and valleys and passed through numerous historical settlements en route from Seward to Nome. The discovery of gold around Nome brought thousands of people over this route beginning in 1908. Roadhouses for people and dog barns sprang up every 20 or so miles. By 1918 World War I and the lack of 'gold fever' resulted in far less travel. The trail might have been forgotten except for the 1925 diphtheria outbreak in Nome. In one of the final great feats of dog sleds, twenty drivers and teams carried the life-saving serum in 127 hours. Today, the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race serves to commemorate the part the trail and its dog sleds played in the development of Alaska, and the route an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrilineality
Matrilineality is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which each person is identified with their matriline – their mother's lineage – and which can involve the inheritance of property and/or titles. A matriline is a line of descent from a female ancestor to a descendant (of either sex) in which the individuals in all intervening generations are mothersin other words, a "mother line". In a matrilineal descent system, an individual is considered to belong to the same descent group as their mother. This ancient matrilineal descent pattern is in contrast to the currently more popular pattern of patrilineal descent from which a family name is usually derived. The ''matriline'' of historical nobility was also called their enatic or uterine ancestry, corresponding to the patrilineal or "agnatic" ancestry. Early human kinship In the late 19th century, almost all prehistorians and anthropologists believed, followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, honey, or anything safe to eat, and/or by hunting game (pursuing and/or trapping and killing wild animals, including catching fish), roughly as most animal omnivores do. Hunter-gatherer societies stand in contrast to the more sedentary agricultural societies, which rely mainly on cultivating crops and raising domesticated animals for food production, although the boundaries between the two ways of living are not completely distinct. Hunting and gathering was humanity's original and most enduring successful competitive adaptation in the natural world, occupying at least 90 percent of human history. Following the invention of agriculture, hunter-gatherers who did not change were displaced or conquered by farming or pastoralist groups in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |