|
Delustrant
A delustrant is a substance that reduces the lustre (sheen) of synthetic fibres. The most common delustrant is anatase titanium dioxide. Synthetic fibres such as nylon are normally extremely shiny and transparent when extruded. Adding powdered titanium dioxide causes the surface of the fibres to be rougher, reducing the sheen; at the same time, being opaque, it reduces the transparency of the fibre. To be effective as a delustrant, titanium dioxide must be powdered 0.1-1.0 µm, depending on the size of the fibre, and varying amounts (up to about 2%) can be used depending on the level of lustre required. Some of the words used to describe different lustre levels are: clear, bright, semi-dull, semi-matt, dull, matt, extra dull, and super dull. See also * Luster (textiles) * Hand feel Hand feel (Hand, Fabric hand, Fabric feel) is the property of fabrics related to the touch that expresses sensory comfort. It refers to the way fabrics feel against the skin or in the hand an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Fiber
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres (in British English; see spelling differences) are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants (like cotton) or fur from animals. They are the result of extensive research by scientists to replicate naturally occurring animal and plant fibers. In general, synthetic fibers are created by extruding fiber-forming materials through spinnerets, forming a fiber. These are called synthetic or artificial fibers. The word polymer comes from a Greek prefix "poly" which means "many" and suffix "mer" which means "single units". (Note: each single unit of a polymer is called a monomer). Early experiments The first fully synthetic fiber was glass. Joseph Swan invented one of the first artificial fibers in the early 1880s; today it would be called semisynthetic in precise usage. His fiber was drawn from a cellulose liquid, formed by chemically modifying th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
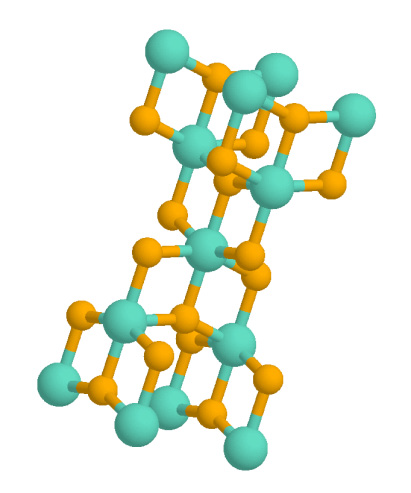
Anatase
Anatase is a metastable mineral form of titanium dioxide (TiO2) with a tetragonal crystal structure. Although colorless or white when pure, anatase in nature is usually a black solid due to impurities. Three other polymorphs (or mineral forms) of titanium dioxide are known to occur naturally: brookite, akaogiite, and rutile, with rutile being the most common and most stable of the bunch. Anatase is formed at relatively low temperatures and found in minor concentrations in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Thin films of TiO2-coated glass show antifogging and self-cleaning properties under ultraviolet radiation. Anatase is always found as small, isolated, and sharply developed crystals, and like rutile, it crystallizes in a tetragonal system. Anatase is metastable at all temperatures and pressures, with rutile being the equilibrium polymorph. Nevertheless, anatase is often the first titanium dioxide phase to form in many processes due to its lower surface energy, with a transforma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble to water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structure of rutile is tetragonal in symmetry whereas anatase and brookite are orthorhombic. The oxygen substructures are all slight distort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lustre (mineralogy)
Lustre (British English) or luster (American English; see spelling differences) is the way light interacts with the surface of a crystal, rock, or mineral. The word traces its origins back to the Latin ''lux'', meaning "light", and generally implies radiance, gloss, or brilliance. A range of terms are used to describe lustre, such as ''earthy'', ''metallic'', ''greasy'', and ''silky''. Similarly, the term ''vitreous'' (derived from the Latin for glass, ''vitrum'') refers to a glassy lustre. A list of these terms is given below. Lustre varies over a wide continuum, and so there are no rigid boundaries between the different types of lustre. (For this reason, different sources can often describe the same mineral differently. This ambiguity is further complicated by lustre's ability to vary widely within a particular mineral species). The terms are frequently combined to describe intermediate types of lustre (for example, a "vitreous greasy" lustre). Some minerals exhibit unus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers composed of polyamides ( repeating units linked by amide links).The polyamides may be aliphatic or semi-aromatic. Nylon is a silk-like thermoplastic, generally made from petroleum, that can be melt-processed into fibers, films, or shapes. Nylon polymers can be mixed with a wide variety of additives to achieve many property variations. Nylon polymers have found significant commercial applications in fabric and fibers (apparel, flooring and rubber reinforcement), in shapes (molded parts for cars, electrical equipment, etc.), and in films (mostly for food packaging). History DuPont and the invention of nylon Researchers at DuPont began developing cellulose based fibers, culminating in the synthetic fiber rayon. DuPont's experience with rayon was an important precursor to its development and marketing of nylon. DuPont's invention of nylon spanned an eleven-year period, ranging from the initial research pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luster (textiles)
In textiles, lustre or luster is a physical property that makes them appear bright, glossy, and shiny. The amount of light reflected from the surface of a fiber is referred to as its luster.The level of luster is determined by how light reflects off the surface. For example, round surfaced fiber reflects more light and appears shinier than fiber with an irregular surface. Synthetic fibers with a more regular surface seem brighter than natural fibers with an irregular surface, with the exception of silk, which has a regular surface. Objective Luster is the degree of gloss or sheen possessed by the fiber or textile surface. Luster adds aesthetic values in fabrics, contributes to their attractiveness. Occasionally, this adds value to their quality assessment. In some cases, when lustre is undesirable, fibres are purposefully dulled by the addition of substances. Factors Factors affecting ''lustre (the way light reflects)'' lie with fiber properties, but various processes can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand Feel
Hand feel (Hand, Fabric hand, Fabric feel) is the property of fabrics related to the touch that expresses sensory comfort. It refers to the way fabrics feel against the skin or in the hand and conveys information about the cloth's softness and smoothness. Hand feel is an estimated and subjective property of different fabrics, but nowadays, hand feel could be measured and assessed statistically. Tactile senses Our daily life experiences are profoundly influenced by the sense of touch. Touch is the first sense to develop, beginning in the first trimester of pregnancy. During the next few months in the womb, the baby's entire body develops touch receptors. Around 7 weeks into pregnancy, touch is the first sense to develop in the fetus. Therefore, hand feel is an important characteristic of clothing that provides sensory comfort. Hand feel (also called handle or drape) is one of the basic characteristics that are necessary for sensory comfort that is related to tactile comfort. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
