|
Defining Equation (physical Chemistry)
In physical chemistry, there are numerous quantities associated with chemical compounds and reactions; notably in terms of ''amounts'' of substance, ''activity'' or ''concentration'' of a substance, and the ''rate'' of reaction. This article uses SI units. Introduction Theoretical chemistry requires quantities from core physics, such as time, volume, temperature, and pressure. But the highly quantitative nature of physical chemistry, in a more specialized way than core physics, uses molar amounts of substance rather than simply counting numbers; this leads to the specialized definitions in this article. Core physics itself rarely uses the mole, except in areas overlapping thermodynamics and chemistry. Notes on nomenclature ''Entity'' refers to the type of particle/s in question, such as atoms, molecules, complexes, radicals, ions, electrons etc. Conventionally for concentrations and activities, square brackets are used around the chemical molecular formula. For an arbitr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compounds
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. Water co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Bond
A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding. Strong chemical bonding arises from the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. Since opposite electric charges attract, the negatively charged electrons surrounding the nucleus and the positively charged protons within a nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity, the more an atom or a substituent group attracts electrons. Electronegativity serves as a simple way to quantitatively estimate the bond energy, and the sign and magnitude of a bond's chemical polarity, which characterizes a bond along the continuous scale from covalent to ionic bonding. The loosely defined term electropositivity is the opposite of electronegativity: it characterizes an element's tendency to donate valence electrons. On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more "pull" it will have on electrons) and the number and location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
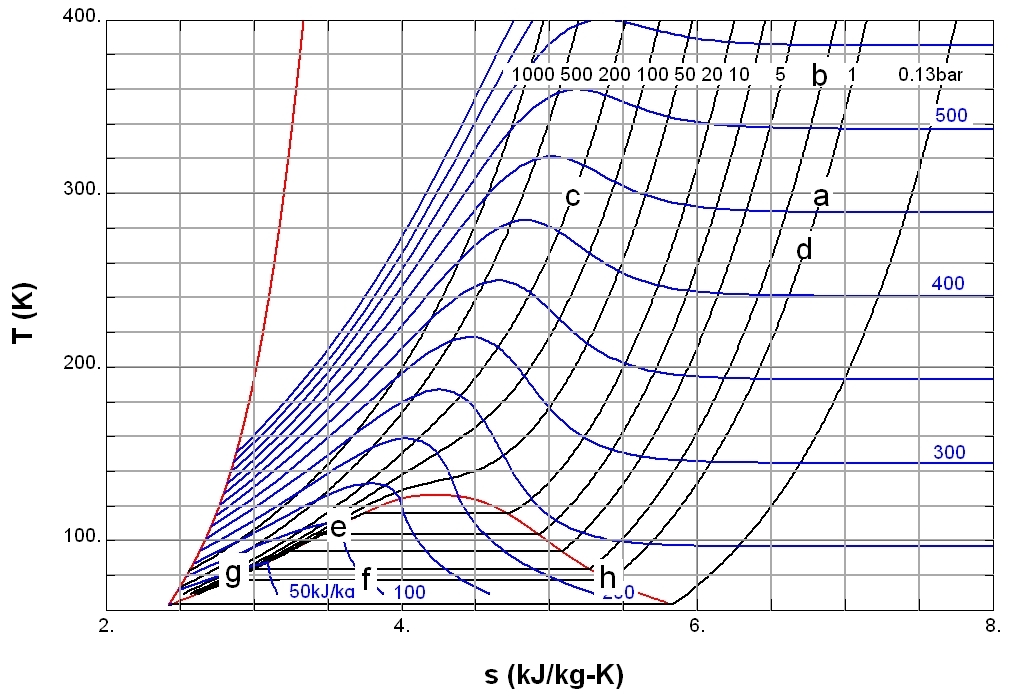
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer William Rankine in 1850 with the names ''thermodynamic function'' and ''heat-potential''. In 1865, German physicist Rudolf Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount of hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure–volume term expresses the work required to establish the system's physical dimensions, i.e. to make room for it by displacing its surroundings. The pressure-volume term is very small for solids and liquids at common conditions, and fairly small for gases. Therefore, enthalpy is a stand-in for energy in chemical systems; bond, lattice, solvation and other "energies" in chemistry are actually enthalpy differences. As a state function, enthalpy depends only on the final configuration of internal energy, pressure, and volume, not on the path taken to achieve it. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement for enthalpy is the joule. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
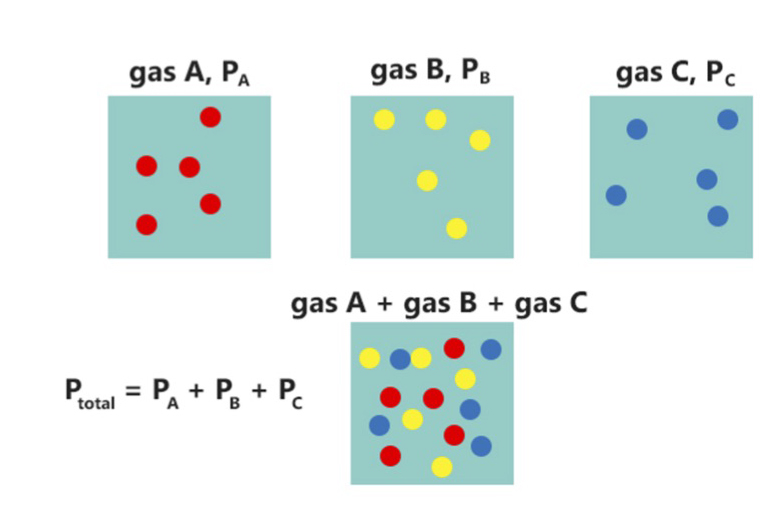
Partial Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture (Dalton's Law). The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of thermodynamic activity of the gas's molecules. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react according to their partial pressures but not according to their concentrations in gas mixtures or liquids. This general property of gases is also true in chemical reactions of gases in biology. For example, the necessary amount of oxygen for human respiration, and the amount that is toxic, is set by the partial pressure of oxygen alone. This is true across a very wide range of different concentrations of oxygen present in various inhaled breathing gases or dissolved in blood; consequently, mixture ratios, like that of breathab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic particles, and in everyday as well as scientific usage, "matter" generally includes atoms and anything made up of them, and any particles (or combination of particles) that act as if they have both rest mass and volume. However it does not include massless particles such as photons, or other energy phenomena or waves such as light or heat. Matter exists in various states (also known as phases). These include classical everyday phases such as solid, liquid, and gas – for example water exists as ice, liquid water, and gaseous steam – but other states are possible, including plasma, Bose–Einstein condensates, fermionic condensates, and quark–gluon plasma. Usually atoms can be imagined as a nucleus of protons and neutrons, and a surro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include Subscript and superscript, subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical nomenclature, chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called ''empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |