|
Dee Why-class Ferry
The ''Dee Why'' and ''Curl Curl'', were two identical steam ferries servicing Sydney Harbour's Circular Quay to Manly service. Both commissioned in 1928, they were the largest ferries on Sydney Harbour until the 1938 introduction of the ''South Steyne''. ''Curl Curl'' was the fastest ferry on the harbour, able to do the Manly run in 22 minutes. ''Dee Why'' was only marginally slower. The two ferries were built in Scotland and steamed to Sydney under their own power. The cost to build them in Australia was too high, so the company looked to Scotland for their new ships. ''Curl Curl'' served until 1960 while ''Dee Why'' was in service until 1968. The ferries were named after the Sydney suburbs of Dee Why and Curl Curl that lie north of Manly. Background In the 1920s, the Port Jackson & Manly Steamship Company ran a seven-ship fleet comprising the '' Kuring-gai'' and six similar Sydney-built double-ended screw steamers: ''Binngarra'' (1905), '' Burra Bra'' (1908), ''Bellubera'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manly Ferry Wharf
Manly Wharf is a heritage-listed passenger terminal wharf and recreational area located at West Esplanade and serving Manly, a Sydney suburb in the Northern Beaches Council local government area of New South Wales, Australia. Since the 1850s, it has served as the Manly embarkation and disembarkation point for the Manly to Sydney ferry service. The wharf has been redeveloped a number of times since the first structure was constructed in 1856. New facilities were added in the early 20th century, and it was rebuilt in a modernist style in the early 1940s, the basic form of which remains today. The wharf was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 18 April 2000. In addition to passenger services, a cargo service was also run to Manly until the 1928-opening of the Spit Bridge. Following the closure of the cargo service, an amusement park, Manly Fun Pier, was opened on the east wharf in 1931 which closed prior to the 1990 redevelopment of the wharf. Services To th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
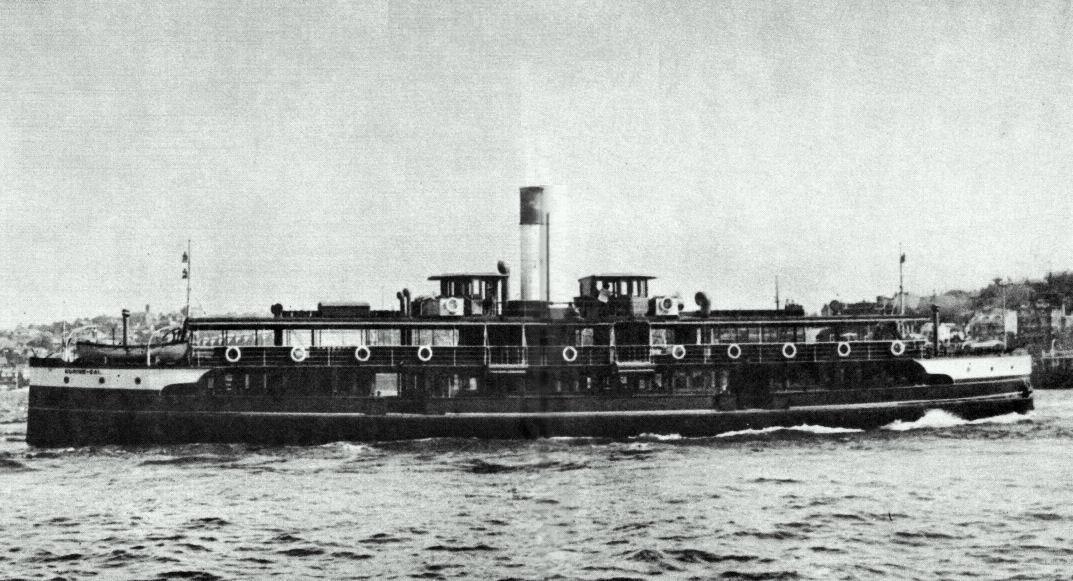
Binngarra
''Binngarra'' was a ferry operated by Port Jackson & Manly Steamship Company on the Manly service. Launched in 1905, she was the first of six similar vessels built for the company–the ''Binngarra'' class—the success of which saw three of her sister vessels serving through to the 1970s and 1980s. Built by Mort's Dock and Engineering Co Ltd, in Woolwich, she was a double-ended screw steamer with steel hull and timber superstructure. She was decommissioned from ferry service in 1930. "Binngarra" is thought to be an Australia Aboriginal word for "spring" or "returning". It is sometimes misspelled as "Bingarra". Background The Port Jackson & Manly Steamship Company's fleet transitioned comparatively late to screw propelled vessels and the fleet comprised mostly paddle steamers until the early years of the twentieth century. The difficulty of turning in the narrow bays of Sydney Harbour - particularly in the busy Circular Quay terminus in Sydney Cove - required the use of doub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firth Of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde is the mouth of the River Clyde. It is located on the west coast of Scotland and constitutes the deepest coastal waters in the British Isles (it is 164 metres deep at its deepest). The firth is sheltered from the Atlantic Ocean by the Kintyre peninsula, which encloses the outer firth in Argyll and Ayrshire. The Kilbrannan Sound is a large arm of the Firth of Clyde, separating the Kintyre Peninsula from the Isle of Arran. Within the Firth of Clyde is another major island – the Isle of Bute. Given its strategic location at the entrance to the middle and upper Clyde, Bute played a vital naval military role during World War II. Geography At its entrance, the firth is about wide. At one area in its upper reaches, it is joined by Loch Long and the Gare Loch. This area includes the large anchorage off of Greenock that is known as the Tail of the Bank. (The “Bank” is a reference to the sandbank and shoal that separates the firth from the estuary of the Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amidships
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water (mostly though not necessarily on the sea). Some remain current, while many date from the 17th to 19th centuries. The word nautical derives from the Latin ''nauticus'', from Greek ''nautikos'', from ''nautēs'': "sailor", from ''naus'': "ship". Further information on nautical terminology may also be found at Nautical metaphors in English, and additional military terms are listed in the Multiservice tactical brevity code article. Terms used in other fields associated with bodies of water can be found at Glossary of fishery terms, Glossary of underwater diving terminology, Glossary of rowing terms, and Glossary of meteorology. This glossary is split into two articles: * terms starting with the letters A to L are at Glossary of nautical terms (A-L) * terms starting with the letters M to Z are at Glossary of nautical terms (M-Z). __N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are the mechanical horsepower (or imperial horsepower), which is about 745.7 watts, and the metric horsepower, which is approximately 735.5 watts. The term was adopted in the late 18th century by Scottish engineer James Watt to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses. It was later expanded to include the output power of other types of piston engines, as well as turbines, electric motors and other machinery. The definition of the unit varied among geographical regions. Most countries now use the SI unit watt for measurement of power. With the implementation of the EU Directive 80/181/EEC on 1 January 2010, the use of horsepower in the EU is permitted only as a supplementary unit. History The development of the stea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phantom (ferry)
''Phantom'' was an iron paddle steamer on Sydney Harbour that ran the Circular Quay to Manly run. Built in 1858, she was the first large double-ended Manly ferry, a basic configuration that has continued through to the contemporary Manly ferries. Service history ''Phantom'' was built by JF Dow and Co of Melbourne. Her 50 hp steam engines were supplied by the builder and could push her to over 12 knots. She could carry up to 166 passengers. She steamed up to Sydney over four days arriving on 19 May 1859. She is thought to be the first vessel to wear the long-standing Manly ferry livery of dark green hull and white funnel with black topping. This livery was discontinued in the 1970s when the ferries came under the control of the NSW State Government's Public Transport Commission. She was bought in 1864 by the newly-created Brighton and Manly Steam Ferry Company. Being long (36.3 m) and narrow (beam 4.0 m) with a shallow draft, rides across the Sydney Heads in bad weather co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Architecture
Naval architecture, or naval engineering, is an engineering discipline incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software and safety engineering as applied to the engineering design process, shipbuilding, maintenance, and operation of marine vessels and structures. Naval architecture involves basic and applied research, design, development, design evaluation (classification) and calculations during all stages of the life of a marine vehicle. Preliminary design of the vessel, its detailed design, construction, trials, operation and maintenance, launching and dry-docking are the main activities involved. Ship design calculations are also required for ships being modified (by means of conversion, rebuilding, modernization, or repair). Naval architecture also involves formulation of safety regulations and damage-control rules and the approval and certification of ship designs to meet statutory and non-statutory requirements. Main subjects The word "vessel" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PS Brighton
PS ''Brighton'' was a ferry used on the Sydney to Manly run. The biggest Manly ferry at the time and the largest paddle steamer to operate on Sydney Harbour, she was well-appointed and popular with passengers. Background In the late 1800s, the Manly to Circular Quay (Sydney) ferry service was growing, and the Port Jackson Steamboat Company was expanding. In 1878, the double-ended '' Fairlight'' was ordered from England and tug-ferry ''Commodore'' soon followed. Following an 1881 name change to Port Jackson Steamship Company, the ''Brighton'' was ordered. Design and construction The ship was constructed by T.B. Seath & Co. of Rutherglen, Scotland in 1883. She was said to be a copy of the ''Primrose'' and ''Daisy'' which ran on the River Mersey, England. Her paddle wheels were driven by two A. Campbell & Son compound diagonal oscillating steam engines generating 160 hp and then 230 hp in the 1890s. She could reach a speed of 15 knots. She had a summer capacity of 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier And Miller
Napier & Miller Ltd. (also Messrs Napier & Miller) were Scottish shipbuilders based at Old Kilpatrick, Glasgow, Scotland. Company history The company was founded in 1898 at a yard at Yoker. In 1906 it moved to a new site a few miles downriver at Old Kilpatrick after its yard was acquired by the Clyde Navigation Trust to build a new dock (subsequently named Rothesay Dock). During World War I the company built sloops and minesweepers for the Royal Navy, along with merchant ships. It also assembled a number of Royal Aircraft Factory B.E.2 aircraft. In the 1920s the company built passenger ships and Great Lakes traders for United States, Canadian and Norwegian companies. The company also did contract work for other shipbuilders, for example being subcontracted by A. & J. Inglis to build the hull for the paddle steamer for Buchanan Steamers. During the Great Depression the company went out of business, having built over 120 ships. The last ship was completed in 1930, and the yard w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baragoola
MV ''Baragoola'' was a ferry formerly operated by the Port Jackson & Manly Steamship Company and its successors on the Manly service. The sixth and final of the -type Manly ferries, the vessel entered service in 1922. Built with a triple-expansion steam engine, she was converted to diesel-electric propulsion in 1961. Since its decommissioning as a ferry in 1983, the vessel had a number of owners who attempted to find a new role and restore it. In 2003, it was laid up at Balls Head Bay on the north side of Sydney Harbour as attempts to restore the vessel continued. However, in January 2022, she sank at her mooring alongside the Balls Head Coal Loader, with the decision then made that the vessel would be scrapped. ''Baragoola'' is an Australian Aboriginal word for "flood tide". Background The Port Jackson & Manly Steamship Company's fleet transitioned comparatively late to screw-propelled vessels and the fleet comprised mostly paddle steamers until the early years of the twe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MV North Head
The MV ''North Head'' (formerly SS ''Barrenjoey'') was a ferry operated by the Port Jackson & Manly Steamship Company and its successors on the Manly service from 1913 until 1985. The vessel was launched as ''Barrenjoey'', a steamer and one of the six ''Binngarra''-type Manly ferries which were built between 1905 and 1922. In 1951, she was converted to diesel-electric power, completely rebuilt and renamed ''North Head''. She was removed from service in 1985 following the introduction of the ''Freshwater''-class ferries. She spent time in Hobart as a floating restaurant and, in 2000, she was taken to Cairns where she remains grounded and in deteriorating condition. The name "Barrenjoey" was taken from the headland at the northern tip of Pittwater. "North Head" is the northern headland at the entrance to Sydney Harbour. Background The Port Jackson & Manly Steamship Company's fleet transitioned comparatively late to screw propelled vessels and the fleet comprised mostly pad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.png)




