|
Decision Downloading
Decision downloadingClampitt,P. & Williams, M.(2007)Decision Downloading, MIT Sloan Management Review, Jan 1, 2 refers to communicating a decision to those who have not been involved in the decision-making process. The term “decision downloading” is used to set apart those special situations in which decision-makers communicate a decision that has already been made. It applies when the communicators cannot, for whatever reason, keep everyone informed in real-time about the decision-making process. Types of "downloaders" Decision downloaders can be classified into three groups: robust, restricted, and remedial.Clampitt,P. & Williams, M.(2007)Decision Downloading, MIT Sloan Management Review, Jan 1, 9 Robust downloaders discuss: # how the decision was made # why it was made # what alternatives were considered # how it fits in with the organizational mission # how it impacts the organization # how it impacts employees. Restricted downloaders discuss some of the above i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DD Logo
DD, dd, or other variants may refer to: Arts and entertainment *"D.D.", a track on mixtape ''Echoes of Silence'' by The Weeknd * DD (character), a character in ''The Saga of Seven Suns'' novels by Kevin J. Anderson *DD National or DD1, an Indian national television channel *Dancing Dolls, a Japanese all-female pop group *Daredevil (Marvel Comics character), a Marvel Comics character **Matt Murdock (Marvel Cinematic Universe), the Marvel Cinematic Universe counterpart * Decorative Designers * Donegal Daily, an Irish news website * Doordarshan, a public service broadcaster in India *Erann DD, a Danish singer and songwriter *DD, the production code for the 1966 ''Doctor Who'' serial ''The Tenth Planet'' Business * DuPont, which trades shares on the New York Stock Exchange as DD * Dunkin' Donuts, a company Military * DD tank, an amphibious tank * Dishonorable discharge, a punitive discharge in the U.S. military * DD, the U.S. Navy hull classification for destroyers * DD F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillip G
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularized the name include kings of Macedonia and one of the apostles of early Christianity. ''Philip'' has many alternative spellings. One derivation often used as a surname is Phillips. It was also found during ancient Greek times with two Ps as Philippides and Philippos. It has many diminutive (or even hypocoristic) forms including Phil, Philly, Lip, Pip, Pep or Peps. There are also feminine forms such as Philippine and Philippa. Antiquity Kings of Macedon * Philip I of Macedon * Philip II of Macedon, father of Alexander the Great * Philip III of Macedon, half-brother of Alexander the Great * Philip IV of Macedon * Philip V of Macedon New Testament * Philip the Apostle * Philip the Evangelist Others * Philippus of Croton (c. 6th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT Sloan Management Review
The ''MIT Sloan Management Review'' is a research-based magazine and digital platform for business executives published at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. The print edition is published quarterly; the digital edition is updated daily. Background The magazine (originally known as the ''Industrial Management Review'') was established in 1959 by the MIT Sloan School of Management. In 2001, the magazine added the university (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) to its official name and the magazine has been called ''MIT Sloan Management Review'' since then. It has transformed from its original, print-only, form to a multi-format platform. The magazine distributes content on the web, in print, on mobile platforms, in podcast format, and via licensees and libraries around the world. Sections Content is presented in five main sections: * Editor's Column: A one-page article from the editor-in-chief exploring a topic of current interest for business executives. * Frontiers: Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty
Uncertainty refers to epistemic situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown. Uncertainty arises in partially observable or stochastic environments, as well as due to ignorance, indolence, or both. It arises in any number of fields, including insurance, philosophy, physics, statistics, economics, finance, medicine, psychology, sociology, engineering, metrology, meteorology, ecology and information science. Concepts Although the terms are used in various ways among the general public, many specialists in decision theory, statistics and other quantitative fields have defined uncertainty, risk, and their measurement as: Uncertainty The lack of certainty, a state of limited knowledge where it is impossible to exactly describe the existing state, a future outcome, or more than one possible outcome. ;Measurement of uncertainty: A set of possible states or outc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either Rationality, rational or irrational. The decision-making process is a reasoning process based on assumptions of value (ethics and social sciences), values, preferences and beliefs of the decision-maker. Every decision-making process produces a final choice, which may or may not prompt action. Research about decision-making is also published under the label problem solving, particularly in European psychological research. Overview Decision-making can be regarded as a Problem solving, problem-solving activity yielding a solution deemed to be optimal, or at least satisfactory. It is therefore a process which can be more or less Rationality, rational or Irrationality, irrational and can be based on explicit knowledge, explicit or tacit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
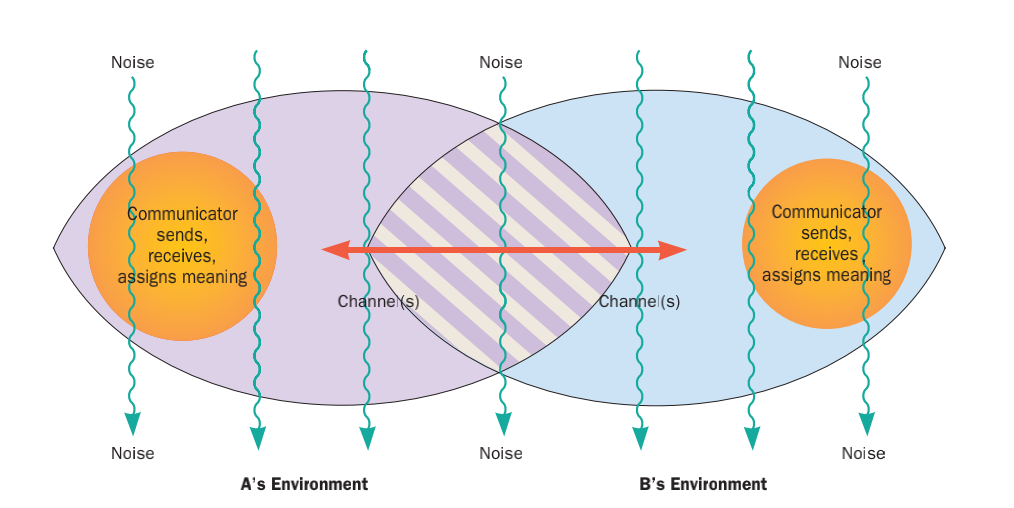
Communication Studies
Communication studies or communication science is an academic discipline that deals with processes of human communication and behavior, patterns of communication in interpersonal relationships, social interactions and communication in different cultures. Communication is commonly defined as giving, receiving or exchanging ideas, information, signals or messages through appropriate media, enabling individuals or groups to persuade, to seek information, to give information or to express emotions effectively. Communication studies is a social science that uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge that encompasses a range of topics, from face-to-face conversation at a level of individual agency and interaction to social and cultural communication systems at a macro level. Scholarly communication theorists focus primarily on refining the theoretical understanding of communication, examining statistics in order to help subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either rational or irrational. The decision-making process is a reasoning process based on assumptions of values, preferences and beliefs of the decision-maker. Every decision-making process produces a final choice, which may or may not prompt action. Research about decision-making is also published under the label problem solving, particularly in European psychological research. Overview Decision-making can be regarded as a problem-solving activity yielding a solution deemed to be optimal, or at least satisfactory. It is therefore a process which can be more or less rational or irrational and can be based on explicit or tacit knowledge and beliefs. Tacit knowledge is often used to fill the gaps in complex decision-making processes. Usually, both o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Making Software
Decision may refer to: Law and politics *Judgment (law), as the outcome of a legal case *Landmark decision, the outcome of a case that sets a legal precedent * ''Per curiam'' decision, by a court with multiple judges Books * ''Decision'' (novel), a 1983 political novel by Allen Drury * ''The Decision'' (novel), a 1998 book in the ''Animorphs'' series Sports *Decision (baseball), a statistical credit earned by a baseball pitcher * Decisions in combat sports *Decisions (professional wrestling), by which a wrestler scores a point against his opponent Film and TV * ''Decision'' (TV series), an American anthology TV series * ''The Decision'' (play), by the 20th-century German dramatist Bertolt Brecht * ''The Decision'' (TV special), in which NBA player LeBron James announced that he would switch teams * "The Decision" (song), by English indie rock band Young Knives Music Albums * ''Decisions'' (George Adams and Don Pullen album), 1984 * ''Decisions'' (The Winans album), 1987 Songs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Dynamics
Group dynamics is a system of behaviors and psychological processes occurring within a social group (''intra''group dynamics), or between social groups ( ''inter''group dynamics). The study of group dynamics can be useful in understanding decision-making behaviour, tracking the spread of diseases in society, creating effective therapy techniques, and following the emergence and popularity of new ideas and technologies. These applications of the field are studied in psychology, sociology, anthropology, political science, epidemiology, education, social work, leadership studies, business and managerial studies, as well as communication studies. History The history of group dynamics (or group processes) has a consistent, underlying premise: 'the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.' A social group is an entity that has qualities which cannot be understood just by studying the individuals that make up the group. In 1924, Gestalt psychologist Max Wertheimer proposed ‘There are e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish a number of personal and relational goals. Interpersonal communication research addresses at least six categories of inquiry: 1) how humans adjust and adapt their verbal communication and nonverbal communication during face-to-face communication; 2) how messages are produced; 3) how uncertainty influences behavior and information-management strategies; 4) deceptive communication; 5) relational dialectics; and 6) social interactions that are mediated by technology. A large number of scholars have described their work as research into interpersonal communication. There is considerable variety in how this area of study is conceptually and operationally defined.Knapp & Daly, 2011) Researchers in interpersonal communication come from many different research paradigms and theoretical tradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizational Communication
Within the realm of communication studies, organizational communication is a field of study surrounding all areas of communication and information flow that contribute to the functioning of an organization. Organizational communication is constantly evolving and as a result, the scope of organizations included in this field of research have also shifted over time. Now both traditionally profitable companies, as well as NGO's and non-profit organizations, are points of interest for scholars focused on the field of organizational communication. Organizations are formed and sustained through continuous communication between members of the organization and both internal and external sub-groups who possess shared objectives for the organization. The flow of communication encompasses internal and external stakeholders and can be formal or informal. History The field traces its lineage through business information, business communication, and early mass communication studies published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small-group Communication
Communication in small groups consists of three or more people who share a common goal and communicate collectively to achieve it. During small group communication, interdependent participants analyze data, evaluate the nature of the problem(s), decide and provide a possible solution or procedure. Additionally, small group communication provides strong feedback, unique contributions to the group as well as a critical thinking analysis and self-disclosure from each member. Small groups communicate through an interpersonal exchange process of information, feelings and active listening in both two types of small groups: primary groups and secondary groups. Group communication The first important research study of small group communication was performed in front of a live studio audience in Hollywood California by social psychologist Robert Bales and published in a series of books and articles in the early and mid 1950s .Bales, R. F. (1950). ''Interaction process analysis''. Page 33. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |