|
Day Of The Vow
The Day of the Vow ( af, Geloftedag) is a religious public holiday in South Africa. It is an important day for Afrikaners, originating from the Battle of Blood River on 16 December 1838, before which about 400 Voortrekkers made a promise to God that if He rescued them out of the hands of the approximately 20,000 Zulu warriors they were facing, they would honour that day as a sabbath day in remembrance of what God did for them. Initially called Dingane's Day ( af, Dingaansdag), 16 December was made an annual national holiday in 1910, before being renamed Day of the Vow in 1982. In 1994, after the end of Apartheid, it was officially replaced by the Day of Reconciliation, an annual holiday also on 16 December. However, many still celebrate it unofficially. Origin The day of the Vow traces its origin as an annual religious holiday to The Battle of Blood River on 16 December 1838. The besieged Voortrekkers took a public vow (or covenant) together before the battle, led by Sare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Reformed Church
The Dutch Reformed Church (, abbreviated NHK) was the largest Christian denomination in the Netherlands from the onset of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century until 1930. It was the original denomination of the Dutch Royal Family and the foremost Protestant denomination until 2004. It was the larger of the two major Reformed denominations, after the Reformed Churches in the Netherlands (''Gereformeerde kerk'') was founded in 1892. It spread to the United States, South Africa, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Brazil, and various other world regions through Dutch colonization. Allegiance to the Dutch Reformed Church was a common feature among Dutch immigrant communities around the world and became a crucial part of Afrikaner nationalism in South Africa. The Dutch Reformed Church was founded in 1571 during the Protestant Reformation in the Calvinist tradition, being shaped theologically by John Calvin, but also other major Reformed theologians. The church was influenced by vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Thompson (author)
Leonard Monteath Thompson (born 6 March 1916, in Cranborne, Dorset, England - died June 2004) was Charles J. Stillé Professor of History Emeritus at Yale and director of the former Yale Southern African Research Program. He is well known for his work on the formation of the Union of South Africa and the two-volume '' The Oxford History of South Africa'', a collaboration with N.M. Wilson., and has written and edited many books, including ''The Political Mythology of Apartheid'', ''The Frontier in History'' (with Howard Lamar), ''A History of South Africa'', and ''South African Politics'' (with Andrew Prior), all published by Yale University Press. Life Born in England in 1916, Thompson was educated in both England and South Africa, and was a Rhodes Scholar at Oxford University from 1937 to 1939. He was a lieutenant in the Royal Navy during the Second World War, and was awarded many medals for distinguished service. After the war, he taught at the University of Cape Town. Thompson w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covenant Monument
The Covenant Monument is a provincial heritage site in Belfast in the Mpumalanga province of South Africa. In 1982 it was described in the Government Gazette A government gazette (also known as an official gazette, official journal, official newspaper, official monitor or official bulletin) is a periodical publication that has been authorised to publish public or legal notices. It is usually establis ... as References South African Heritage Resource Agency database Monuments and memorials in South Africa Buildings and structures in Mpumalanga {{SouthAfrica-struct-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
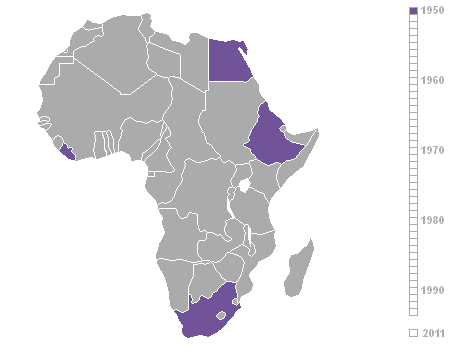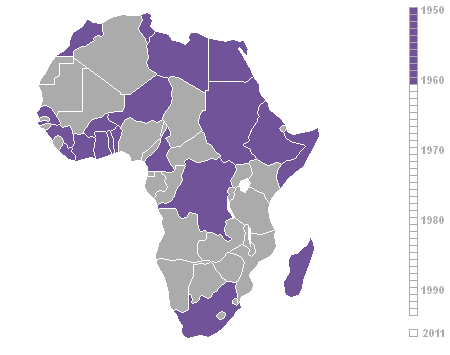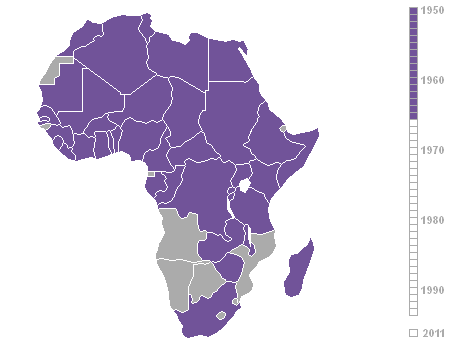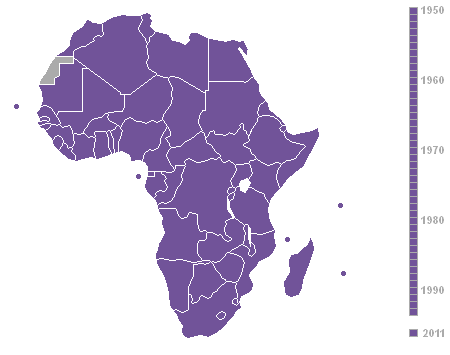
Decolonisation Of Africa
The decolonisation of Africa was a process that took place in the Scramble for Africa, mid-to-late 1950s to 1975 during the Cold War, with radical government changes on the continent as Colonialism, colonial governments made the transition to Sovereign state, independent states. The process was often marred with violence, political turmoil, widespread unrest, and organised revolts in both northern and sub-Saharan countries including the Algerian War in French Algeria, the Angolan War of Independence in Portuguese Angola, the Congo Crisis in the Belgian Congo, the Mau Mau Uprising in Kenya Colony, British Kenya, the Zanzibar Revolution in the Sultanate of Zanzibar, and the Nigerian Civil War in the secessionist state of Biafra. Background The "Scramble for Africa" between 1870 and 1914 was a significant period of European imperialism in Africa that ended with almost all of Africa, and its natural resources, being controlled as colonies by a small number of European states. Racin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Institute Of Southern Africa
The Christian Institute of Southern Africa was an ecumenical progressive organisation founded by English and Afrikaans clergy in December 1963 to unite South African Christians against apartheid. The CI became deeply involved with black activists such as Steve Biko, and was banned by the state in 1977. History The Christian Institute of Southern Africa was founded in 1963 by 280 Christians (Hexham 1980) that included Albert Geyser, Ben Marais, D. C. S. Oosthuizen, and John de Gruchy. Factors that contributed to the founding was the need to continue dialogue after the disastrous conclusion of the 1960 Cottesloe Consultation, the last time that all South African churches met until 1990. Reformed members of the CI could also critique official Dutch Reformed policies, which included support for apartheid. The 1963 South Transvaal Synod of the Dutch Reformed Church had forbidden unofficial comments that were not submitted through official channels (Maritz 2003:56). The first nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boer
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape Colony, Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled Dutch Cape Colony, this area, but the United Kingdom incorporated it into the British Empire in 1806. The name of the group is derived from "boer", which means "farmer" in Dutch language, Dutch and Afrikaans language, Afrikaans. In addition, the term also applied to those who left the British Cape Colony, Cape Colony Great Trek, during the 19th century to colonise in the Orange Free State, South African Republic, Transvaal (together known as the Boer Republics), and to a lesser extent Natalia Republic, Natal. They emigrated from the Cape to live beyond the reach of the British colonial administration, with their reasons for doing so primarily being the new Anglophone common law system being introduced into the Cape and the Slavery Abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Turnhalle Alliance
The Popular Democratic Movement (PDM), formerly the Democratic Turnhalle Alliance (DTA), is an amalgamation of political parties in Namibia, registered as one singular party for representation purposes. In coalition with the United Democratic Front, it formed the official opposition in Parliament until the parliamentary elections in 2009. The party currently holds 16 seats in the Namibian National Assembly and one seat in the Namibian National Council and is the official opposition. McHenry Venaani is president of the PDM. The PDM is an associate member of the International Democrat Union, a transnational grouping of national political parties generally identified with political conservatism, and a member of the Democrat Union of Africa, which was relaunched in Accra, Ghana in February 2019. The president of the party, McHenry Venaani, is the current chairperson of the Democrat Union of Africa. History The party was formed as the Democratic Turnhalle Alliance (DTA) on 5 Nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. Although Kazungula, it does not border Zimbabwe, less than 200 metres (660 feet) of the Botswanan right bank of the Zambezi, Zambezi River separates the two countries. Namibia gained independence from South Africa on 21 March 1990, following the Namibian War of Independence. Its capital and largest city is Windhoek. Namibia is a member state of the United Nations (UN), the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the African Union (AU) and the Commonwealth of Nations. The driest country in sub-Saharan Africa, Namibia has been inhabited since pre-historic times by the San people, San, Damara people, Damara and Nama people. Around the 14th century, immigration, immigrating Bantu peoples arrived as part of the Bantu expansion. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Party (South Africa)
The National Party ( af, Nasionale Party, NP), also known as the Nationalist Party, was a political party in South Africa South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ... founded in 1914 and disbanded in 1997. The party was an Afrikaner ethnic nationalist party that promoted Afrikaner interests in South Africa. However, in 1990 it became a South African civic nationalist party seeking to represent all South Africans. It first became the governing party of the country in 1924. It merged with its rival, the SAP, during the Great Depression, and a splinter faction became the official opposition during World War II and returned to power and governed South Africa from 4 June 1948 until 9 May 1994. Beginning in 1948 following the 1948 South African general election, general electi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel François Malan
Daniël François Malan (; 22 May 1874 – 7 February 1959) was a South African politician who served as the fourth prime minister of South Africa from 1948 to 1954. The National Party implemented the system of apartheid, which enforced racial segregation laws, during his tenure as Prime Minister. Early life Malan was born in Riebeek-West in the Cape Colony. The progenitor of the Malan name in the South African region was a French Huguenot refugee named Jacques Malan from Provence (Mérindol), France, who arrived at the Cape before 1689. The Malan name is one of a number of Afrikaans names of French origin which have retained their original spelling. Malan's older sister, Cinie, later became a missionary and linguist. Malan obtained a B.A. in Music and Science from Victoria College, Stellenbosch, whereafter he entered the Stellenbosch seminary in order to train as a minister in the Dutch Reformed Church. Along with his studies in theology, he obtained a M.A. in Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |