|
David C. Phillips
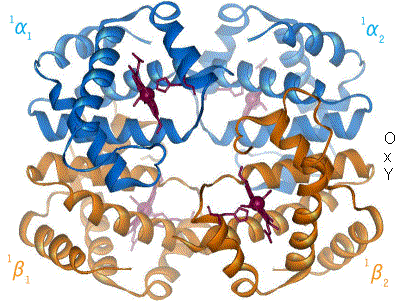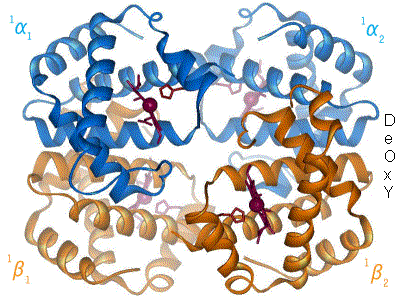
David Chilton Phillips, Baron Phillips of Ellesmere, KBE, FRS (7 March 1924 – 23 February 1999) was a pioneering, British structural biologist and an influential figure in science and government. Research Phillips lead the team which determined in atomic detail the structure of the enzyme lysozyme, which he did in the Davy Faraday Research Laboratories of the Royal Institution in London in 1965. Lysozyme, which was discovered in 1922 by Alexander Fleming, is found in tear drops, nasal mucus, gastric secretions and egg white. Lysozyme exhibits some antibacterial activity so that the discovery of its structure and mode of action were key scientific objectives. David Phillips solved the structure of lysozyme and also explained the mechanism of its action in destroying certain bacteria by a brilliant application of the technique of X-ray crystallography, a technique to which he had been introduced as a PhD student at the University in Cardiff, and to which he later made major in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organisations, and public service outside the civil service. It was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V and comprises five classes across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a knight if male or dame if female. There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with, but not members of, the order. Recommendations for appointments to the Order of the British Empire were originally made on the nomination of the United Kingdom, the self-governing Dominions of the Empire (later Commonwealth) and the Viceroy of India. Nominations continue today from Commonwealth countries that participate in recommending British honours. Most Commonwealth countries ceased recommendations for appointments to the Order of the British Empire when they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Hans Krebs Medal
The Sir Hans Krebs Lecture and Medal is awarded annually by the Federation of European Biochemical Societies (FEBS) for outstanding achievements in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology or related sciences. It was endowed by the Lord Rank Centre for Research and named after the German-born British biochemist Sir Hans Adolf Krebs, well known for identifying the urea and citric acid cycles. The awardee receives a silver medal and presents one of the plenary lectures at the FEBS Congress. List of recipients Source: (1968–2002) *2022 Cecília Rodrigues (University of Lisbon, Portugal) *2019 Mathias Uhlen *2018 Albert J.R. Heck *2017 Carol V. Robinson *2016 Kári Stefánsson *2015 Jürgen Knoblich *2014 Michael N. Hall *2013 Richard J. Roberts *2012 V. Ramakrishnan *2011 Elena Conti *2010 Harald Stenmark *2009 Václav Hořejší *2008 Tim Hunt *2007 Tom Rapoport *2006 Aaron Ciechanover *2005 Thomas Jenuwein *2004 Ryszard Gryglewski *2003 ''No award?'' *2002 Jacques Pouysségur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Finney
Samuel Finney (1857 – 14 April 1935) was a Labour Party politician in the United Kingdom. Life and career Born at Talk-o'-th'-Hill, Finney began working when he was ten years old, and later became a coal miner. In 1881, he was appointed as checkweighman, and he also became active in the North Staffordshire Miners' Federation, serving as its president from 1888 to 1912, and then as its full-time secretary and agent. Finney was a supporter of the Labour Party, and was elected to Burslem Town Council in 1903, and then to Stoke-on-Trent County Borough Council from its establishment. Finney first stood for parliament defending a Labour seat at Hanley in 1912, but came third, losing the seat to the Liberal candidate. He was elected as Member of Parliament (MP) for North West Staffordshire at a by-election in 1916, following the death of Labour MP Albert Stanley. When that constituency was abolished at the 1918 general election, he was returned to Parliament for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Fleming
Sir Alexander Fleming (6 August 1881 – 11 March 1955) was a Scottish physician and microbiologist, best known for discovering the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance, which he named penicillin. His discovery in 1928 of what was later named benzylpenicillin (or penicillin G) from the mould ''Penicillium rubens'' is described as the "single greatest victory ever achieved over disease." For this discovery, he shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain. He also discovered the enzyme lysozyme from his nasal discharge in 1922, and along with it a bacterium he named ''Micrococcus Lysodeikticus'', later renamed ''Micrococcus luteus''. Fleming was knighted for his scientific achievements in 1944. In 1999, he was named in ''Time'' magazine's list of the 100 Most Important People of the 20th century. In 2002, he was chosen in the BBC's television poll for determining the 100 Greatest Britons, and in 2009, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Biology
Structural biology is a field that is many centuries old which, and as defined by the Journal of Structural Biology, deals with structural analysis of living material (formed, composed of, and/or maintained and refined by living cells) at every level of organization. Early structural biologists throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries were primarily only able to study structures to the limit of the naked eye's visual acuity and through magnifying glasses and light microscopes. In the 20th century, a variety of experimental techniques were developed to examine the 3D structures of biological molecules. The most prominent techniques are X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance, and electron microscopy. Through the discovery of X-rays and its applications to protein crystals, structural biology was revolutionized, as now scientists could obtain the three-dimensional structures of biological molecules in atomic detail. Likewise, NMR spectroscopy allowed information about p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographical Memoirs Of Fellows Of The Royal Society
The ''Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society'' is an academic journal on the history of science published annually by the Royal Society. It publishes obituaries of Fellows of the Royal Society. It was established in 1932 as ''Obituary Notices of Fellows of the Royal Society'' and obtained its current title in 1955, with volume numbering restarting at 1. Prior to 1932, obituaries were published in the ''Proceedings of the Royal Society''. The memoirs are a significant historical record and most include a full bibliography of works by the subjects. The memoirs are often written by a scientist of the next generation, often one of the subject's own former students, or a close colleague. In many cases the author is also a Fellow. Notable biographies published in this journal include Albert Einstein, Alan Turing, Bertrand Russell, Claude Shannon, Clement Attlee, Ernst Mayr, and Erwin Schrödinger. Each year around 40 to 50 memoirs of deceased Fellows of the Royal Soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President's Medal (Royal Academy Of Engineering)
The President's Medal, also known as the Royal Academy of Engineering President's Medal, is an award given by the President of the Royal Academy of Engineering. It was first given in 1987. History The award is given at the RAEng's annual awards dinner. Award winners * 2020 - Dervilla Mitchell HonCBE * 2019 - Professor Richard Williams OBE * 2018 - Professor Sir William Wakeham * 2017 - Ian Shott CBE * 2016 - Dr Ian Nussey OBE * 2015 - Sir Richard Olver * 2014 - Dr Dame Sue Ion DBE * 2013 - Terry Hill CBE FREng * 2011 - Professor Anthony Kelly CBE * 2009 - Sir Alan Rudge CBE FREng FRS * 2007 - Rolls-Royce plc * 2006 - Sir David Davies CBE FREng FRS * 2005 - Jonathan Ive * 2004 - Jim Eyre * 2000 - HRH Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh * 1998 - Keith Duckworth OBE * 1995 - Sir William Stewart FRS FRSE * 1994 - Lord Phillips of Ellesmere FRS * 1993 - Sir Neil Cossons OBE * 1990 - Rhys Lloyd, Baron Lloyd of Kilgerran * 1988 - David Sainsbury, Baron Sainsbury of Turville * 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established in 1783. , there are around 1,800 Fellows. The Society covers a broader selection of fields than the Royal Society of London, including literature and history. Fellowship includes people from a wide range of disciplines – science & technology, arts, humanities, medicine, social science, business, and public service. History At the start of the 18th century, Edinburgh's intellectual climate fostered many clubs and societies (see Scottish Enlightenment). Though there were several that treated the arts, sciences and medicine, the most prestigious was the Society for the Improvement of Medical Knowledge, commonly referred to as the Medical Society of Edinburgh, co-founded by the mathematician Colin Maclaurin in 1731. Maclaurin was unhappy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregori Aminoff Prize
The Gregori Aminoff Prize is an international prize awarded since 1979 by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in the field of crystallography, rewarding "a documented, individual contribution in the field of crystallography, including areas concerned with the dynamics of the formation and dissolution of crystal structures. Some preference should be shown for work evincing elegance in the approach to the problem." The prize, which is named in memory of the Swedish scientist and artist Gregori Aminoff (1883–1947), Professor of Mineralogy at the Swedish Museum of Natural History from 1923, was endowed through a bequest by his widow Birgit Broomé-Aminoff. The prize can be shared by several winners. It is considered the Nobel prize for crystallography. Recipients of the Prize SourceRoyal Swedish Academy of Science See also * List of chemistry awards * List of physics awards This list of physics awards is an index to articles about notable awards for physics. The list include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf Prize
The Wolf Prize is an international award granted in Israel, that has been presented most years since 1978 to living scientists and artists for ''"achievements in the interest of mankind and friendly relations among people ... irrespective of nationality, race, colour, religion, sex or political views."'' History The prize is awarded in Israel by the Wolf Foundation, founded by Ricardo Wolf, a German-born inventor and former Cuban ambassador to Israel. It is awarded in six fields: Agriculture, Chemistry, Mathematics, Medicine, Physics, and an Arts prize that rotates between architecture, music, painting, and sculpture. Each prize consists of a diploma and US$100,000. The awards ceremony typically takes place at a session in the Knesset. The prize is described by the Foundation as being "awarded annually", but is not in fact awarded every year: between 2000 and 2010, only six prizes were awarded in most fields, and only four in Physics. The Wolf Prizes in Physics and Chemistry ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |