|
Data Quality
Data quality refers to the state of qualitative or quantitative pieces of information. There are many definitions of data quality, but data is generally considered high quality if it is "fit for tsintended uses in operations, decision making and planning". Moreover, data is deemed of high quality if it correctly represents the real-world construct to which it refers. Furthermore, apart from these definitions, as the number of data sources increases, the question of internal data consistency becomes significant, regardless of fitness for use for any particular external purpose. People's views on data quality can often be in disagreement, even when discussing the same set of data used for the same purpose. When this is the case, data governance is used to form agreed upon definitions and standards for data quality. In such cases, data cleansing, including standardization, may be required in order to ensure data quality. Definitions Defining data quality is difficult due to the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualitative Data
Qualitative properties are properties that are observed and can generally not be measured with a numerical result. They are contrasted to quantitative properties which have numerical characteristics. Some engineering and scientific properties are qualitative. A test method can result in qualitative data about something. This can be a categorical result or a binary classification (e.g., pass/fail, go/no go, conform/non-conform). It can sometimes be an engineering judgement. The data that all share a qualitative property form a nominal category. A variable which codes for the presence or absence of such a property is called a binary categorical variable, or equivalently a dummy variable. In businesses Some important qualitative properties that concern businesses are: Human factors, 'human work capital' is probably one of the most important issues that deals with qualitative properties. Some common aspects are work, motivation, general participation, etc. Although all of thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customer Service
Customer service is the assistance and advice provided by a company to those people who buy or use its products or services. Each industry requires different levels of customer service, but in the end, the idea of a well-performed service is that of increasing revenues. The perception of success of the customer service interactions is dependent on employees "who can adjust themselves to the personality of the customer". Customer service is often practiced in a way that reflects the strategies and values of a firm. Good quality customer service is usually measured through customer retention. Customer service for some firms is part of the firm’s intangible assets and can differentiate it from others in the industry. One good customer service experience can change the entire perception a customer holds towards the organization. Customer service does not only focus on the external aspect of the organization, but also the internal relations that facilitate the business activity. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Record Linkage
Record linkage (also known as data matching, data linkage, entity resolution, and many other terms) is the task of finding records in a data set that refer to the same entity across different data sources (e.g., data files, books, websites, and databases). Record linkage is necessary when joining different data sets based on entities that may or may not share a common identifier (e.g., database key, URI, National identification number), which may be due to differences in record shape, storage location, or curator style or preference. A data set that has undergone RL-oriented reconciliation may be referred to as being ''cross-linked''. Naming conventions "Record linkage" is the term used by statisticians, epidemiologists, and historians, among others, to describe the process of joining records from one data source with another that describe the same entity. However, many other terms are used for this process. Unfortunately, this profusion of terminology has led to few cross-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Rules Engine
A business rules engine is a software system that executes one or more business rules in a runtime production environment. The rules might come from legal regulation ("An employee can be fired for any reason or no reason but not for an illegal reason"), company policy ("All customers that spend more than $100 at one time will receive a 10% discount"), or other sources. A business rule system enables these company policies and other operational decisions to be defined, tested, executed and maintained separately from application code. Rule engines typically support rules, facts, priority (score), mutual exclusion, preconditions, and other functions. Rule engine software is commonly provided as a component of a business rule management system which, among other functions, provides the ability to: register, define, classify, and manage all the rules, verify consistency of rules definitions (”Gold-level customers are eligible for free shipping when order quantity > 10” and “m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Profiling
Data profiling is the process of examining the data available from an existing information source (e.g. a database or a file) and collecting statistics or informative summaries about that data. The purpose of these statistics may be to: # Find out whether existing data can be easily used for other purposes # Improve the ability to search data by tagging it with keywords, descriptions, or assigning it to a category # Assess data quality, including whether the data conforms to particular standards or patterns # Assess the risk involved in integrating data in new applications, including the challenges of joins # Discover metadata of the source database, including value patterns and distributions, key candidates, foreign-key candidates, and functional dependencies # Assess whether known metadata accurately describes the actual values in the source database # Understanding data challenges early in any data intensive project, so that late project surprises are avoided. Finding d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shadow System
Shadow system is a term used in information services for any application relied upon for business processes that is not under the jurisdiction of a centralized information systems department. That is, the information systems department did not create it, was not aware of it, and does not support it. Overview Shadow systems (a.k.a. shadow data systems, data shadow systems, shadow information technology, shadow accounting systems or in short: Shadow IT) consist of small scale databases and/or spreadsheets developed for and used by end users, outside the direct control of an organization's IT department. The design and development process for these systems tends to fall into one of two categories. In the first case, these systems are developed on an adhoc basis rather than as part of a formal project and are not tested, documented or secured with the same rigor as more formally engineered reporting solutions. This makes them comparatively quick and cheap to develop, but unsuitable in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Migration
Data migration is the process of selecting, preparing, extracting, and transforming data and permanently transferring it from one computer storage system to another. Additionally, the validation of migrated data for completeness and the decommissioning of legacy data storage are considered part of the entire data migration process. Data migration is a key consideration for any system implementation, upgrade, or consolidation, and it is typically performed in such a way as to be as automated as possible, freeing up human resources from tedious tasks. Data migration occurs for a variety of reasons, including server or storage equipment replacements, maintenance or upgrades, application migration, website consolidation, disaster recovery, and data center relocation. The standard phases , "nearly 40 percent of data migration projects were over time, over budget, or failed entirely." As such, to achieve an effective data migration, proper planning is critical. While the specifics of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply Chain Management
In commerce, supply chain management (SCM) is the management of the flow of goods and services including all processes that transform raw materials into final products between businesses and locations. This can include the movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, finished goods, and end to end order fulfilment from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Interconnected, interrelated or interlinked networks, channels and node businesses combine in the provision of products and services required by end customers in a supply chain. Supply-chain management has been defined as the "design, planning, execution, control, and monitoring of supply chain activities with the objective of creating net value, building a competitive infrastructure, leveraging worldwide logistics, synchronising supply with demand and measuring performance globally". SCM practice draws heavily on industrial engineering, systems engineering, operations management, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customer Relationship Management
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a process in which a business or other organization administers its interactions with customers, typically using data analysis to study large amounts of information. CRM systems compile data from a range of different communication channels, including a company's website, telephone, email, live chat, marketing materials and more recently, social media. They allow businesses to learn more about their target audiences and how to best cater for their needs, thus retaining customers and driving sales growth. CRM may be used with past, present or potential customers. The concepts, procedures, and rules that a corporation follows when communicating with its consumers are referred to as CRM. This complete connection covers direct contact with customers, such as sales and service-related operations, forecasting, and the analysis of consumer patterns and behaviors, from the perspective of the company. According to Gartner, the global CRM market ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Intelligence
Business intelligence (BI) comprises the strategies and technologies used by enterprises for the data analysis and management of business information. Common functions of business intelligence technologies include reporting, online analytical processing, analytics, dashboard development, data mining, process mining, complex event processing, business performance management, benchmarking, text mining, predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics. BI tools can handle large amounts of structured and sometimes unstructured data to help identify, develop, and otherwise create new strategic business opportunities. They aim to allow for the easy interpretation of these big data. Identifying new opportunities and implementing an effective strategy based on insights can provide businesses with a competitive market advantage and long-term stability, and help them take strategic decisions. Business intelligence can be used by enterprises to support a wide range of business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
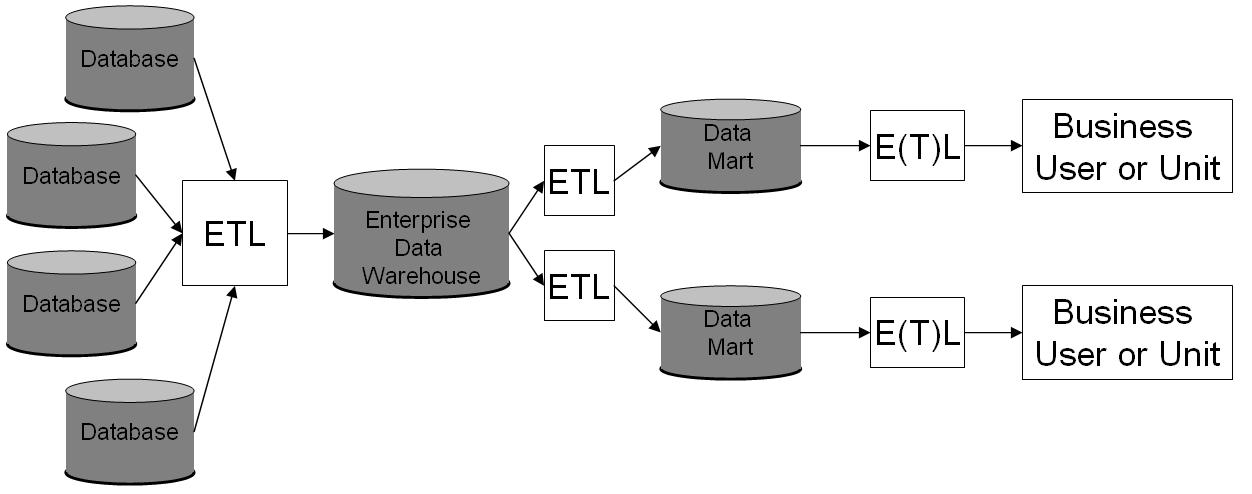
Data Warehousing
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. The data stored in the warehouse is uploaded from the operational systems (such as marketing or sales). The data may pass through an operational data store and may require data cleansing for additional operations to ensure data quality before it is used in the DW for reporting. Extract, transform, load (ETL) and extract, load, transform (ELT) are the two main approaches used to build a data warehouse system. ETL-based data warehousing The typical extract, transform, load (ETL)-based data warehouse uses staging, data integration, and access layers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of System Quality Attributes
Within systems engineering, quality attributes are realized non-functional requirements used to evaluate the performance of a system. These are sometimes named architecture characteristics, or "ilities" after the suffix many of the words share. They are usually Architecturally Significant Requirements that require architects' attention. Quality attributes Notable quality attributes include: * accessibility * accountability * accuracy * adaptability * administrability * affordability * agility * auditability * autonomy rl* availability * compatibility * composability rl* confidentiality * configurability * correctness * credibility * customizability * debuggability * degradability * determinability * demonstrability * dependability * deployability * discoverability rl* distributability * durability * effectiveness * efficiency * evolvability * extensibility * failure transparency * fault-tolerance * fidelity * flexibility * inspectability * instal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)