|
Dark Fermentation
Dark fermentation is the fermentative conversion of organic substrate to biohydrogen. It is a complex process manifested by diverse groups of bacteria, involving a series of biochemical reactions using three steps similar to anaerobic conversion. Dark fermentation differs from photofermentation in that it proceeds without the presence of light. Overview Fermentative/hydrolytic microorganisms hydrolyze complex organic polymers to monomers which are further converted to a mixture of lower-molecular-weight organic acids and alcohols by obligatory producing acidogenic bacteria. Utilization of wastewater as a potential substrate for biohydrogen production has been drawing considerable interest in recent years especially in the dark fermentation process. Industrial wastewater as a fermentative substrate for H2 production addresses most of the criteria required for substrate selection viz., availability, cost and biodegradability. Chemical wastewater (Venkata Mohan, ''et al.'', 2007a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentative Hydrogen Production
Fermentative hydrogen production is the fermentative conversion of organic substrates to H2. Hydrogen produced in this manner is often called biohydrogen. The conversion is effected by bacteria and protozoa, which employ enzymes. Fermentative hydrogen production is one of several anaerobic conversions. Dark vs photofermentation Dark fermentation reactions do not require light energy. These are capable of constantly producing hydrogen from organic compounds throughout the day and night. Typically these reactions are coupled to the formation of carbon dioxide or formate. Important reactions that result in hydrogen production start with glucose, which is converted to acetic acid: :C6H12O6 + 2 H2O → 2 CH3CO2H + 2 CO2 + 4 H2 A related reaction gives formate instead of carbon dioxide: :C6H12O6 + 2 H2O → 2 CH3CO2H + 2 HCO2H + 2 H2 These reactions are exergonic by 216 and 209 kcal/mol, respectively. Using synthetic biology, bacteria can be genetically altered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. Gluco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biohydrogen
Biohydrogen is H2 that is produced biologically. Interest is high in this technology because H2 is a clean fuel and can be readily produced from certain kinds of biomass. Many challenges characterize this technology, including those intrinsic to H2, such as storage and transportation of a noncondensible gas. Hydrogen producing organisms are poisoned by O2. Yields of H2 are often low. Biochemical principles The main reactions involve fermentation of sugars. Important reactions start with glucose, which is converted to acetic acid: :C6H12O6 + 2 H2O -> 2 CH3COOH + 2 CO2 + 4 H2 A related reaction gives formate instead of carbon dioxide: :C6H12O6 + 2 H2O -> 2 CH3COOH + 2 HCOOH + 2 H2 These reactions are exergonic by 216 and 209 kcal/mol, respectively. H2 production is catalyzed by two hydrogenases. One is called eFehydrogenase; the other is called iFehydrogenase. Many organisms express these enzymes. Notable examples are members of the genera Clostridium, Desulfovibr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogas
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste and food waste. It is a renewable energy source. Biogas is produced by anaerobic digestion with anaerobic organisms or methanogen inside an anaerobic digester, biodigester or a bioreactor. Biogas is primarily methane () and carbon dioxide () and may have small amounts of hydrogen sulfide (), moisture and siloxanes. The gases methane, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide () can be combusted or oxidized with oxygen. This energy release allows biogas to be used as a fuel; it can be used in fuel cells and for any heating purpose, such as cooking. It can also be used in a gas engine to convert the energy in the gas into electricity and heat. Biogas can be compressed after removal of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, the same way as natural gas is compressed to CN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanogenic
Methanogenesis or biomethanation is the formation of methane coupled to energy conservation by microbes known as methanogens. Organisms capable of producing methane for energy conservation have been identified only from the Domain (biology), domain Archaea, a group Phylogenetics, phylogenetically distinct from both eukaryotes and bacteria, although many live in close association with anaerobic bacteria. Other forms of methane production that are not coupled to ATP synthesis exist within all three domains of life. The production of methane is an important and widespread form of microbial metabolism. In Hypoxia (environmental), anoxic environments, it is the final step in the decomposition of biomass (ecology), biomass. Methanogenesis is responsible for significant amounts of natural gas accumulations, the remainder being thermogenic. Biochemistry Methanogenesis in microbes is a form of anaerobic respiration. Methanogens do not use oxygen to respire; in fact, oxygen inhibits the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
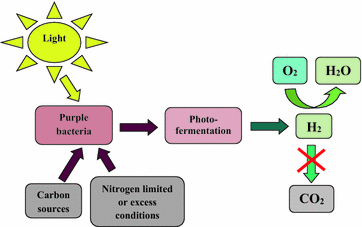
Photo-fermentative
Photofermentation is the fermentative conversion of organic substrate to biohydrogen manifested by a diverse group of photosynthetic bacteria by a series of biochemical reactions involving three steps similar to anaerobic conversion. Photofermentation differs from dark fermentation because it only proceeds in the presence of light. For example, photo-fermentation with ''Rhodobacter sphaeroides'' SH2C (or many other purple non-sulfur bacteria) can be employed to convert small molecular fatty acids into hydrogen and other products. Light-dependent pathways Phototropic bacteria Phototropic bacteria produce hydrogen gas via photofermentation, where the hydrogen is sourced from organic compounds. C6H12O6 + 6H2O ->[] 6CO2 + 12H2 Photolytic producers Photolysis, Photolytic producers are similar to phototrophs, but source hydrogen from water molecules that are broken down as the organism interacts with light. Photolytic producers consist of algae and certain photosynthetic bact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Description The combining capacity, or affinity of an ...—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent bond, covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, Carbon-12, C and Carbon-13, C being stable, while Carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the Timeline of chemical element discoveries#Ancient discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the Abundance of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidogenesis
Acidogenesis is the second stage in the four stages of anaerobic digestion: * Hydrolysis: A chemical reaction where particulates are solubilized and large polymers converted into simpler monomers; * Acidogenesis: A biological reaction where simple monomers are converted into volatile fatty acids; * Acetogenesis: A biological reaction where volatile fatty acids are converted into acetic acid, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen * Methanogenesis: A biological reaction where acetates are converted into methane and carbon dioxide, while hydrogen is consumed. Anaerobic digestion is a complex biochemical process of biologically mediated reactions by a consortium of microorganisms to convert organic compounds into methane and carbon dioxide. It is a stabilization process, reducing odor, pathogens, and mass reduction. Hydrolytic bacteria form a variety of reduced end-products from the fermentation of a given substrate. One fundamental question that arises concerns the metabolic features t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioaugmentation
Biological augmentation is the addition of archaea or bacterial cultures required to speed up the rate of degradation of a contaminant. Organisms that originate from contaminated areas may already be able to break down waste, but perhaps inefficiently and slowly. Bioaugmentation is a type of bioremediation in which it requires studying the indigenous varieties present in the location to determine if biostimulation is possible. After discovering the indigenous bacteria found in the location, if the indigenous bacteria can metabolize the contaminants, more of the indigenous bacterial cultures will be implemented into the location to boost the degradation of the contaminants. Bioaugmentation is the introduction of more archaea or bacterial cultures to enhance the contaminant degradation whereas biostimulation is the addition of nutritional supplements for the indigenous bacteria to promote the bacterial metabolism. If the indigenous variety do not have the metabolic capability to perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyric Acid
Butyric acid (; from grc, βούτῡρον, meaning "butter"), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2CO2H. It is an oily, colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Isobutyric acid (2-methylpropanoic acid) is an isomer. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. The acid does not occur widely in nature, but its esters are widespread. It is a common industrial chemical and an important component in the mammalian gut. History Butyric acid was first observed in impure form in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. However, Chevreul did not publish his early research on butyric acid; instead, he deposited his findings in manuscript form with the secretary of the Academy of Sciences in Paris, France. Henri Braconnot, a French chemist, was also researching the composition of butter and was publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
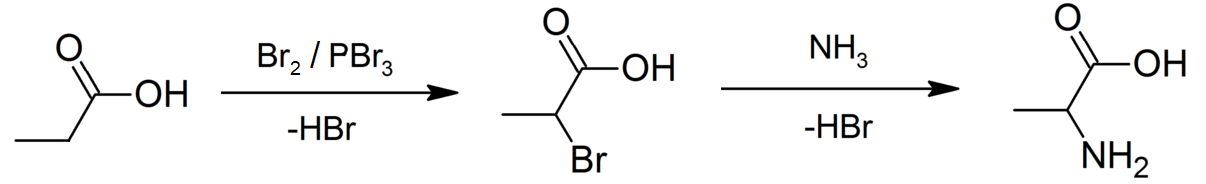
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion CH3CH2CO2− as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the same compound, which he called propionic acid, from the Greek words πρῶτος (prōtos), meaning ''first'', and πίων (piōn), meaning ''fat'', because it is the smallest H(CH2)''n''COOH acid that exhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |