|
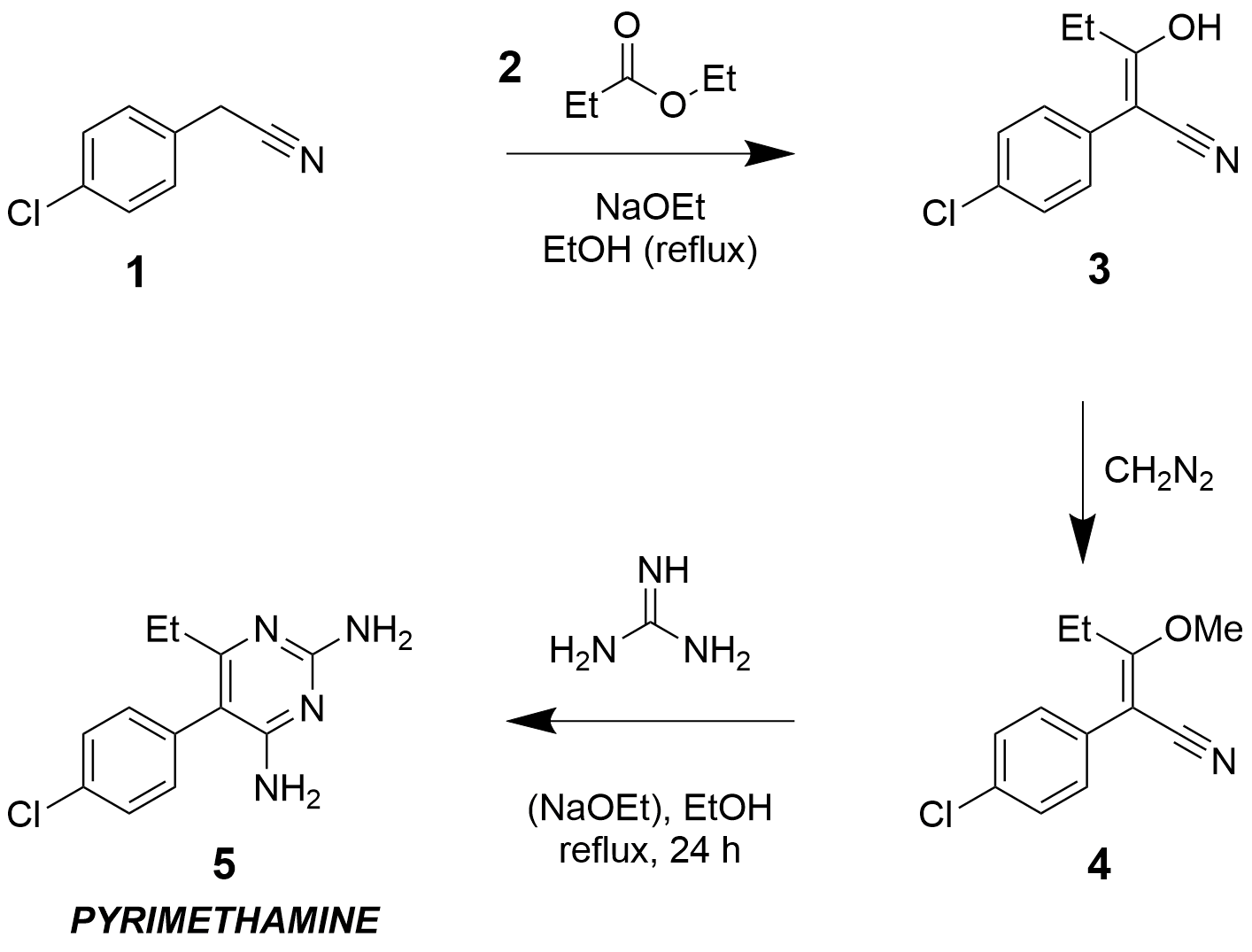
Daraprim
Pyrimethamine, sold under the brand name Daraprim among others, is a medication used with leucovorin (leucovorin is used to decrease side effects of pyrimethamine; it does not have intrinsic anti-parasitic activity) to treat the parasitic diseases toxoplasmosis and cystoisosporiasis. It is also used with dapsone as a second-line option to prevent ''Pneumocystis jiroveci'' pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It was previously used for malaria but is no longer recommended due to resistance. Pyrimethamine is taken by mouth. Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset, severe allergic reactions, and bone marrow suppression. It should not be used by people with folate deficiency that has resulted in anemia. There is concern that it may increase the risk of cancer. While occasionally used in pregnancy it is unclear if pyrimethamine is safe for the baby. Pyrimethamine is classified as a folic acid antagonist. It works by inhibiting folic acid metabolism and therefore the maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folic Acid Antagonist
Antifolates are a class of antimetabolite medications that antagonise (that is, block) the actions of folic acid (vitamin B9). Folic acid's primary function in the body is as a cofactor to various methyltransferases involved in serine, methionine, thymidine and purine biosynthesis. Consequently, antifolates inhibit cell division, DNA/RNA synthesis and repair and protein synthesis. Some such as proguanil, pyrimethamine and trimethoprim selectively inhibit folate's actions in microbial organisms such as bacteria, protozoa and fungi. The majority of antifolates work by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR). Comparison of available agents Mechanism Many are primarily DHFR inhibitors, but raltitrexed is an inhibitor of thymidylate synthase, and pemetrexed inhibits both and a third enzyme. Antifolates act specifically during DNA and RNA synthesis, and thus are cytotoxic during the S-phase of the cell cycle. Thus, they have a greater toxic effect on rapidly dividing cells (such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both developed and developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the complementary list. Some medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
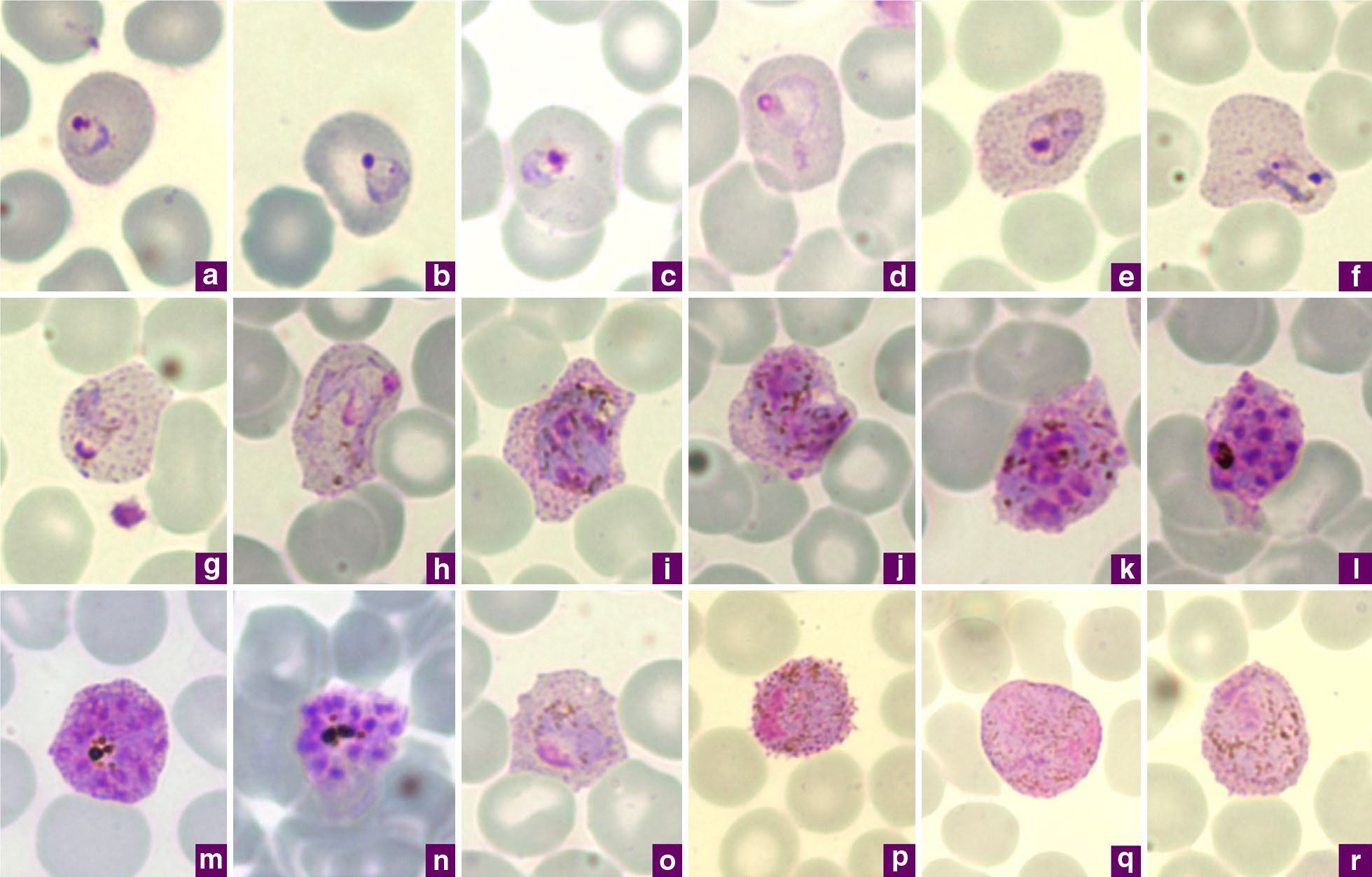
Plasmodium Vivax
''Plasmodium vivax'' is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than ''Plasmodium falciparum'', the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, ''P. vivax'' malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly (a pathologically enlarged spleen). ''P. vivax'' is carried by the female ''Anopheles'' mosquito; the males do not bite. Health Epidemiology ''Plasmodium vivax'' is found mainly in Asia, Latin America, and in some parts of Africa. ''P. vivax'' is believed to have originated in Asia, but recent studies have shown that wild chimpanzees and gorillas throughout central Africa are endemically infected with parasites that are closely related to human ''P. vivax.'' These findings indicate that human P. vivax is of African origin. ''Plasmodium vivax'' accounts for 65% of malaria cases in Asia and South America. Unlike ''Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium Falciparum
''Plasmodium falciparum'' is a Unicellular organism, unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of ''Plasmodium'' that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female ''Anopheles'' mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. It is responsible for around 50% of all malaria cases. ''P. falciparum'' is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer (Burkitt's lymphoma) and is classified as a List of IARC Group 2A carcinogens, Group 2A (probable) carcinogen. The species originated from the malarial parasite ''Laverania'' found in gorillas, around 10,000 years ago. Alphonse Laveran was the first to identify the parasite in 1880, and named it ''Oscillaria malariae''. Ronald Ross discovered its transmission by mosquito in 1897. Giovanni Battista Grassi elucidated the complete transmission from a female Anopheles, anopheline mosquit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxoplasmic Chorioretinitis
Toxoplasma chorioretinitis, more simply known as ocular toxoplasmosis, is possibly the most common cause of infections in the back of the eye (posterior segment) worldwide. The causitive agent is ''Toxoplasma gondii'', and in the United States, most cases are acquired congenitally. The most common symptom is decreased visual acuity in one eye. The diagnosis is made by examination of the eye, using ophthalmoscopy. Sometimes serologic testing is used to rule out the disease, but due to high rates of false positives, serologies are not diagnostic of toxoplasmic retinitis. If vision is not compromised, treatment may not be necessary. When vision is affected or threatened, treatment consists of pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, and folinic acid for 4–6 weeks. Prednisone is sometimes used to decrease inflammation. Signs and symptoms A unilateral decrease in visual acuity is the most common symptom of toxoplasmic retinitis. Under ophthalmic examination, toxoplasmic chorioretinitis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrofolate Reductase
Dihydrofolate reductase, or DHFR, is an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, using NADPH as an electron donor, which can be converted to the kinds of tetrahydrofolate cofactors used in 1-carbon transfer chemistry. In humans, the DHFR enzyme is encoded by the ''DHFR'' gene. It is found in the q11→q22 region of chromosome 5. Bacterial species possess distinct DHFR enzymes (based on their pattern of binding diaminoheterocyclic molecules), but mammalian DHFRs are highly similar. Structure A central eight-stranded beta-pleated sheet makes up the main feature of the polypeptide backbone folding of DHFR. Seven of these strands are parallel and the eighth runs antiparallel. Four alpha helices connect successive beta strands. Residues 9 – 24 are termed "Met20" or "loop 1" and, along with other loops, are part of the major subdomain that surround the active site. The active site is situated in the N-terminal half of the sequence, which includes a conse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfamethoxazole
Sulfamethoxazole (SMZ or SMX) is an antibiotic. It is used for bacterial infections such as urinary tract infections, bronchitis, and prostatitis and is effective against both gram negative and positive bacteria such as ''Listeria monocytogenes'' and ''E. coli''. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and skin rashes. It is a sulfonamide and bacteriostatic. It resembles a component of folic acid. It prevents folic acid synthesis in the bacteria that must synthesize their own folic acid. Mammalian cells, and some bacteria, do not synthesize but require preformed folic acid (vitamin B9); they are therefore insensitive to sulfamethoxazole. It was introduced to the United States in 1961. It is now mostly used in combination with trimethoprim (abbreviated SMX-TMP). The SMX-TMP combination is on the WHO Model List of Essential medicines as a first-choice treatment for urinary tract infections. Other names include: sulfamethalazole, sulfisomezole,PubChem"Sul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethoprim
Trimethoprim (TMP) is an antibiotic used mainly in the treatment of bladder infections. Other uses include for middle ear infections and travelers' diarrhea. With sulfamethoxazole or dapsone it may be used for ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include nausea, changes in taste, and rash. Rarely it may result in blood problems such as not enough platelets or white blood cells. Trimethoprim may cause sun sensitivity. There is evidence of potential harm during pregnancy in some animals but not humans. It works by blocking folate metabolism via dihydrofolate reductase in some bacteria which results in their death. Trimethoprim was first used in 1962. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. Medical uses It is primarily used in the treatment of urinary tract infections, although it may be used against any susceptible aerobic bacterial species. It may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfadiazine
Sulfadiazine is an antibiotic. Used together with pyrimethamine, a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, it is the treatment of choice for toxoplasmosis, which is caused by a protozoan parasite. It is a second-line treatment for otitis media, prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, chancroid, chlamydia, and infections by ''Haemophilus influenzae''. It is also used as adjunct therapy for chloroquine-resistant malaria and several forms of bacterial meningitis. It is taken by mouth. Sulfadiazine is available in multiple generic tablets of 500 mg. For urinary tract infections, the usual dose is 4 to 6 grams daily in 3 to 6 divided doses. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, headache, fever, rash, depression, and pancreatitis. It should not be used in people who have severe liver problems, kidney problems, or porphyria. If used during pregnancy, it may increase the risk of kernicterus in the baby. While the company that makes it does not recommend use during breastfeeding, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumocystis Jirovecii
''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' (previously ''P. carinii'') is a yeast-like fungus of the genus ''Pneumocystis''. The causative organism of ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia, it is an important human pathogen, particularly among immunocompromised hosts. Prior to its discovery as a human-specific pathogen, ''P. jirovecii'' was known as ''P. carinii''. Lifecycle The complete lifecycles of any of the species of ''Pneumocystis'' are not known, but presumably all resemble the others in the genus. The terminology follows zoological terms, rather than mycological terms, reflecting the initial misdetermination as a protozoan parasite. It is an extracellular fungus. All stages are found in lungs and because they cannot be cultured ''ex vivo'', direct observation of living ''Pneumocystis'' is difficult. The trophozoite stage is thought to be equivalent to the so-called vegetative state of other species (such as ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe''), which like ''Pneumocystis'', belong to the Taphrinomycoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isosporiasis
Isosporiasis, also known as cystoisosporiasis, is a human intestinal disease caused by the parasite ''Cystoisospora belli'' (previously known as ''Isospora belli''). It is found worldwide, especially in tropical and subtropical areas. Infection often occurs in immuno-compromised individuals, notably AIDS patients, and outbreaks have been reported in institutionalized groups in the United States. The first documented case was in 1915. It is usually spread indirectly, normally through contaminated food or water (CDC.gov). Signs and symptoms Infection causes acute, non-bloody diarrhea with crampy abdominal pain, which can last for weeks and result in malabsorption and weight loss. In immunodepressed patients, and in infants and children, the diarrhea can be severe. Eosinophilia may be present (differently from other protozoan infections). at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |