|
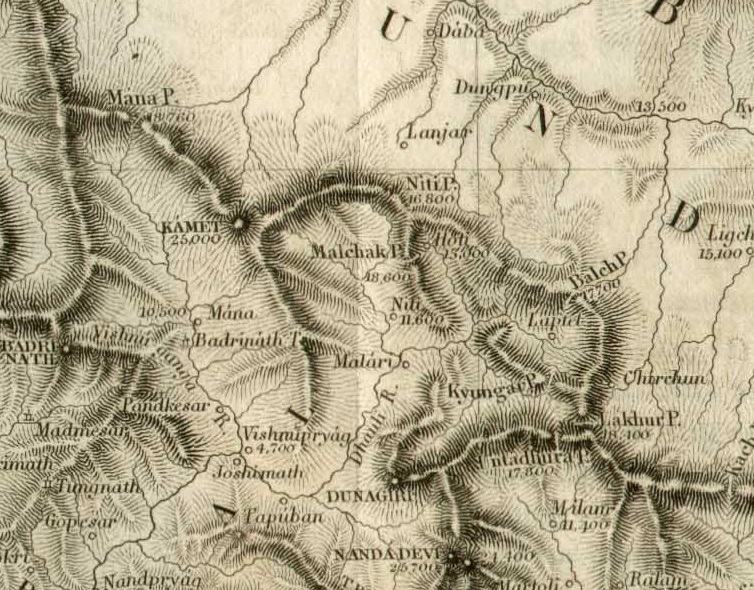
Daba, Zanda County
Daba (; ) or Danbab () is a township under the administration of Zanda County in the Tibet region of China, centred at the Daba village. Geography The Daba village is on the bank of the Daba Chu river, a tributary of the Sutlej River. The township of Daba spans both the banks of the Sutlej river, up to the Burang County and the Manasarovar region. It stretches to the south until the Indian border. Daba village and township are close to the Indian border. On the Indian side of the border are Garhwal and Kumaon regions of India's Uttarakhand state. The Niti Pass and the have served as the main historical trade routes. Since 1954, China has disputed the Indian control over the Barahoti region along the border. , the Daba township has two other villages in addition to Daba: * Dongbo Village (, ) * Kyunglung Village (, ) History In the mid-19th century, Henry Strachey mentioned that Daba Dzong was one of the two dzongs in the Guge region of Ngari, the other being Tsaparan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townships Of The People's Republic Of China
Townships (), formally township-level divisions (), are the basic level (fourth-level administrative units) of political divisions in China. They are similar to municipalities and communes in other countries and in turn may contain village committees and villages. In 1995 there were 29,502 townships and 17,532 towns (a total of 47,034 township-level divisions) in China. Much like other levels of government in mainland China, the township's governance is divided between the Communist Party Township Secretary, and the " county magistrate" (). The township party secretary, along with the township's party committee, determines policy. The magistrate is in charge of administering the daily affairs of government and executing policies as determined by the party committee. A township official is the lowest-level ranked official in the civil service hierarchy; in practice, however, the township party secretary and magistrate can amass high levels of personal power. A township governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niti Pass
Niti Valley is a remote valley located in the northernmost region of Uttarakhand, India at a height of 3, 600 m (11, 811 ft). It is close to the Chinese border and Niti is the last village in the valley before the border with south Tibet. The Niti Pass was an ancient trade route between India and Tibet, and it was sealed after the 1962 Sino-Indian War. Since then, the border has remained sealed. The villages in the valley include Lata, Kaga, Dronagiri, Garpak, Malari, Bampa, Gamshali and Niti. They are mostly inhabited by Bhotiyas of Uttarakhand of Chamoli district ,namely Marchas, a community of Mongoloid origin, and Tolcchas, both known as Rongpa. The language spoken by Marchas is mix of Tibetan and Garhwali , while Tolcchas speak Garhwali Rongpa . Due to adverse weather conditions in the winter, the villages in the valley are only hospitable for about six to eight months. Villagers migrate to lower regions during the winters. Various medicinal plants and herbs grow in the valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panwar Dynasty
The Panwar dynasty ( ) ruled the Garhwal Kingdom (present day Uttarakhand). The dynasty independently ruled Garhwal from the ninth to nineteenth century until the Kingdom of Nepal attacked the Kumaon Kingdom in 1791 and Garhwal in 1804. With the help of the British troops, Garhwal and Kumaon gained independence from Nepal. Unable to pay the military cost of British-ruled India, the then-Garhwali king gave part of his territory to the Raj and ruled until 1949. The last king of Garhwal, Manabendra Shah, decided to join India after it became independent. Garhwal and Kumaon became part of India as the then-state of Uttar Pradesh, which is now Uttarakhand. Pt. Harikrishna Raturi king Bhanu Pratap was the first ruler of Panwar dynasty in Garhwal who founded Chandpur-Garhi as his capital. This was is strongest Garh for the fifty-two Garhs of Garhwal. See also * Panwar * Paramara dynasty The Paramara dynasty (IAST: Paramāra) was an Indian dynasty that ruled Malwa and surroundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garhwal Kingdom
Garhwal Kingdom was an independent Himalayan kingdom in the current north-western Himalayan state of Uttarakhand, India, founded in 688 CE by Kanak Pal, the progenitor of the Panwar dynasty that ruled over the kingdom uninterrupted until 1803 CE. The kingdom was divided into two parts during the British Raj, namely: the princely state ''of Garhwal and'' the ''Garhwal District'' of British India. During this period, the princely state of Garhwal was one of the States of the Punjab Hills which became part of the Punjab Hill States Agency although it was not under the Punjab Province administration. The princely state of Garhwal or Independent Garhwal consisted of the present day Tehri Garhwal district and most of the Uttarkashi district. This former state acceded to the Union of India in August 1949 CE. Etymology The exact origin of the word 'Garhwal' is unknown, though it is believed to be derived from the title ‘''Garh-wala''’ (Owner of Forts) given to the rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fateh Shah
Fateh Shah was the Hindu Rajput king of Garhwal, a small kingdom in North India, from 1684 to 1716. Campaigns H. G. Walton states that Fateh Shah led an attack from Dehradun on Saharanpur in 1692. Pundirs and Gurjars were expelled out of Dehradun and areas of Saharanpur. According to research by G.R.C. Williams, Fateh Shah established a township called Fateh Pur in Haraura Pargana of Saharanpur. According to Rahul Sankrityayan and Fateh Prakash, Raja Fateh Shah also invaded Tibet, where his sword and armour were preserved in the monastery at Daba for a long time. The ruler of Daba(area of Tibet ) refused to pay its taxes to the Fateh Shah so he again conquered Daba .Some areas of Tibet accepted dominance of Pawar kings of Uttarakhand . Battle of Bhangani Dabral and Bhakt Darshan believe that Fateh Shah invaded Sirmur in 1692. Ajay Singh Rawat writes that the year of invasion mentioned by these writers is not correct, and the animosity between Fateh Shah and Raja of Sirmur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogra–Tibetan War
The Dogra–Tibetan War or Sino-Sikh War was fought from May 1841 to August 1842, between the forces of the Dogra nobleman Gulab Singh of Jammu, under the suzerainty of the Sikh Empire, and those of Tibet. Gulab Singh's commander was the able general Zorawar Singh Kahluria, who, after the conquest of Ladakh, attempted to extend its boundaries in order to control the trade routes into Ladakh. Zorawar Singh's campaign, suffering from the effects of inclement weather, suffered a defeat at Minsar (or Missar) and Singh was killed. The Tibetans then advanced on Ladakh. Gulab Singh sent reinforcements under the command of his nephew Jawahir Singh. A subsequent battle near Leh in 1842 led to a Tibetan defeat. The Treaty of Chushul was signed in 1842 maintaining the ''status quo ante bellum''. Background Ladakh trade In the 19th century, Ladakh was the hub of trade routes that branched out into Turkestan and Tibet. Its trade with Tibet was governed by the 1684 Treaty of Tingmosgang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Quarterly Review
The ''Quarterly Review'' was a literary and political periodical founded in March 1809 by London publishing house John Murray. It ceased publication in 1967. It was referred to as ''The London Quarterly Review'', as reprinted by Leonard Scott, for an American edition. Early years Initially, the ''Quarterly'' was set up primarily to counter the influence on public opinion of the ''Edinburgh Review''. Its first editor, William Gifford, was appointed by George Canning, at the time Foreign Secretary, later Prime Minister. Early contributors included Secretaries of the Admiralty John Wilson Croker and Sir John Barrow, Poet Laureate Robert Southey, poet-novelist Sir Walter Scott, Italian exile Ugo Foscolo, Gothic novelist Charles Robert Maturin, and the essayist Charles Lamb. Under Gifford, the journal took the Canningite liberal-conservative position on matters of domestic and foreign policy, if only inconsistently. It opposed major political reforms, but it supported the gradual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Moorcroft (explorer)
William Moorcroft (176727 August 1825) was an English veterinarian and explorer employed by the East India Company. Moorcroft travelled extensively throughout the Himalayas, Tibet and Central Asia, eventually reaching Bukhara, in present-day Uzbekistan. Early life and education Moorcroft was born in Ormskirk, Lancashire, the illegitimate son of Ann Moorcroft, daughter of a local farmer. He was baptised in 1767 in St Peter & St Paul, the Parish Church of Ormskirk, where there is a commemorative plaque to his life. His family had sufficient means to secure an apprenticeship with a surgeon in Liverpool but during this time an unknown disease decimated cattle herds in Lancashire and young William was recruited to treat stricken animals. His proficiency so impressed the county landowners they offered to underwrite his education if he would abandon surgery to attend a veterinarian college in Lyon, France. He arrived in France in the revolutionary year of 1789 and became the first En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gartok
Gartok (), is made of twin encampment settlements of Gar Günsa and Gar Yarsa (, Wade–Giles: ''Ka-erh-ya-sha'') in the Gar County in the Ngari Prefecture of Tibet. Gar Gunsa served as the winter encampment and Gar Yarsa as the summer encampment. But in British nomenclature, the name Gartok was applied only to Gar Yarsa and the practice continues till date. Gartok was established as Lhasa's administrative headquarters for Western Tibet (Ngari) after it conquered it from Ladakh in 1684. A senior official called Garpön was stationed here. Gartok (Gar Yarsa) also served as Western Tibet's principal trade-market. But the village itself was small and said to have been quite poor. After the Chinese annexation of Tibet, the headquarters of Western Tibet was moved to Shiquanhe. Gar Yarsa is situated on the bank of the Gartang River, one of the headwaters of the Indus River, at the base of the Kailash Range, at an elevation of . Name Gar () means "encampment". During the 15th an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsaparang
Tsaparang was the capital of the ancient kingdom of Guge in the Garuda Valley, through which the upper Sutlej River flows, in Ngari Prefecture (Western Tibet) near the border of Ladakh. It is 278 km south-southwest of Senggezangbo Town and 26 km west of the 11th-century monastery at Tholing, and not far west of Mount Kailash and Lake Manasarovar. The Tsaparang Dzong was located here. Nearby is the Bon monastery of Gurugem. Tsaparang is a huge fortress perched on a pyramid-shaped rock rising about 500 to 600 feet (152 to 183 m) at the end of a long narrow spur. It contains numerous tunnels and caves that have been carved out of the rock. At its base was a village where the common people lived. Above them were two public temples - the Lhakhang Marpo (Red Chapel) and the Lhakhang Karpo (White Chapel), and quarters for the monks. Further up, ascending a twisting stone staircase in a tunnel, were the royal quarters, and at the very top, the summer palace. The English TV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngari
Ngari Prefecture () or Ali Prefecture () is a prefecture of China's Tibet Autonomous Region covering Western Tibet, whose traditional name is Ngari Khorsum. Its administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Shiquanhe. History Ngari was once the heart of the ancient kingdom of Guge. Later Ngari, along with Ü and Tsang, composed Ü-Tsang, one of the traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo and Kham. The lowlands of Ngari is known as Maryul. During the 10th century, the kingdom of Maryul was founded, taking the name Ladakh, lasted until 1842. The prefecture has close cultural links with Kinnaur and Lahaul and Spiti district of the bordering Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. Geography and climate The paved Xinjiang-Tibet Highway () passes through this area. There are well-known prehistoric petroglyphs near the far western town of Rutog. The town of Ngari lies above sea level in northwest Tibet some west of the capital, Lhasa. Ngari Gunsa Airport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guge
Guge (; ) was an ancient dynastic kingdom in Western Tibet. The kingdom was centered in present-day Zanda County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region. At various points in history after the 10th century AD, the kingdom held sway over a vast area including south-eastern Zanskar, Upper Kinnaur district, and Spiti Valley, either by conquest or as tributaries. The ruins of the former capital of the Guge kingdom are located at Tsaparang in the Sutlej valley, not far from Mount Kailash and westwards from Lhasa. History Founding Guge was founded in the 10th century. Its capitals were located at Tholing and Tsaparang. Kyide Nyimagon, a great-grandson of Langdarma, the last monarch of the Tibetan Empire, fled from the insecure conditions in Ü-Tsang in 910 to arrive in Ngari (West Tibet). He established a kingdom around 912, annexing Purang and Guge. He established his capital in Guge. Nyimagon later divided his lands into three parts. The king's eldest son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |