|
DB Class 216
The Class V 160 (after 1968: Class 216) is a class of diesel-hydraulic locomotives of the German railways. It is the first variant of the V160 family, built for the Deutsche Bundesbahn for medium/heavy trains. The Class were successful locomotives, eventually leading to a family of similar locomotives (see DB V 160 family). Due to them having steam heating, and a lack in later years of suitable coaching stock they were amongst the first of the family to be withdrawn, no examples being operated by Deutsche Bahn by 2004. A few examples were converted to the short lived DBAG Class 226, with other examples being rebuilt and still in service with private operators. Background and history Following good performance from the diesel-hydraulic locomotive the DB Class V 80, in the period of history of the German Railways sometimes known as Epoch III, the Deutsche Bundesbahn planned (in 1953) to build several types of new diesel locomotive, primarily to replace steam powered locomotive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krupp
The Krupp family (see pronunciation), a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, is notable for its production of steel, artillery, ammunition and other armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG (Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp after acquiring Hoesch AG in 1991 and lasting until 1999), was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century, and was the premier weapons manufacturer for Germany in both world wars. Starting from the Thirty Years' War until the end of the Second World War, it produced battleships, U-boats, tanks, howitzers, guns, utilities, and hundreds of other commodities. The dynasty began in 1587 when trader Arndt Krupp moved to Essen and joined the merchants' guild. He bought and sold real estate, and became one of the city's richest men. His descendants produced small guns during the Thirty Years' War and eventually acquired fulling mills, coal mines and an iron forge. During the Napoleonic Wars, Friedrich Kr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
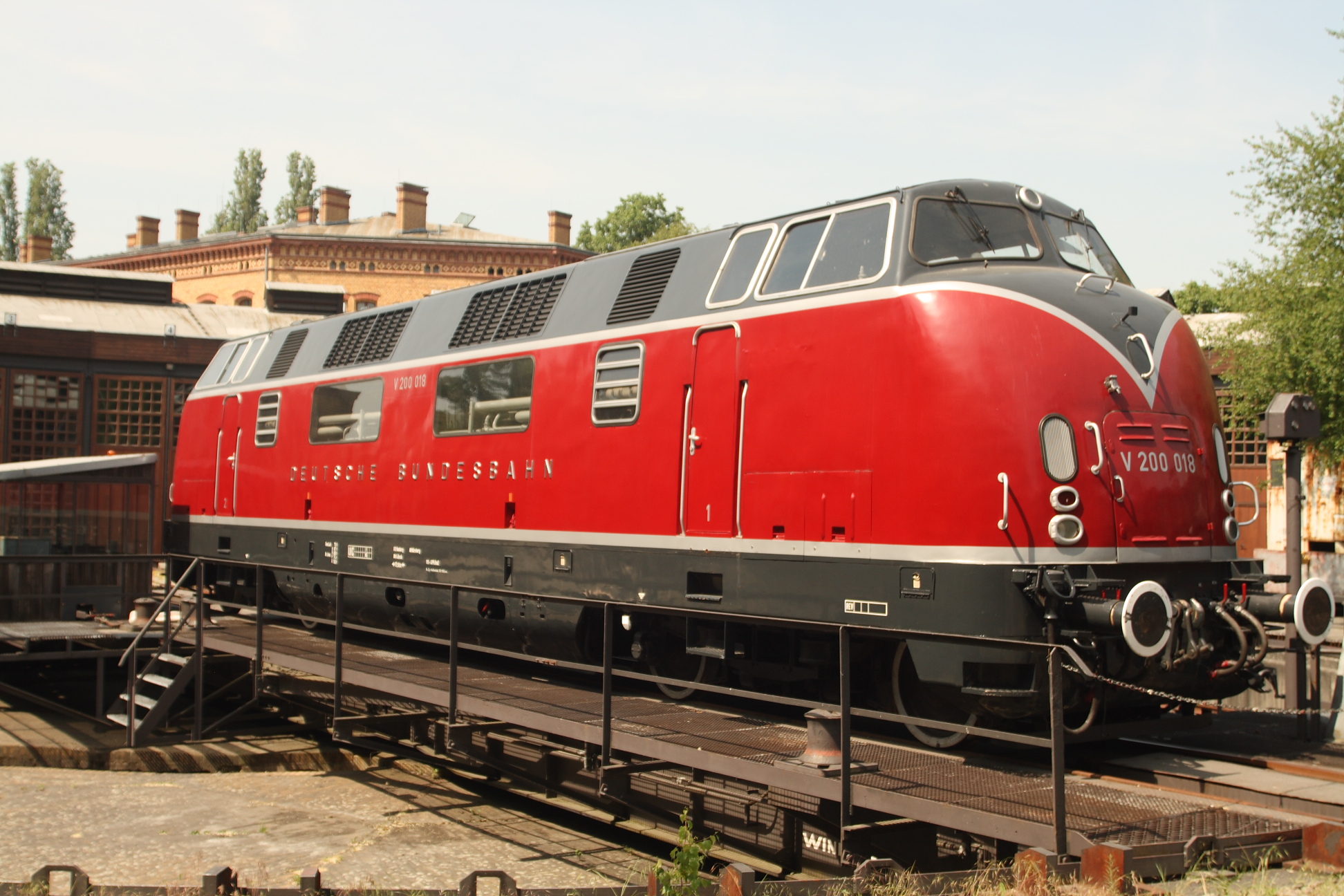
DB Class V 200
DB Class V 200 (also known as Class 220) was the first series production diesel-hydraulic express locomotive of the German Deutsche Bundesbahn and – as Am 4/4 – of the SBB-CFF-FFS in Switzerland. History DB Service Five prototypes of the V 200 were built by Krauss-Maffei in 1953/1954. Full production began in 1956, with 61 engines being built by Krauss-Maffei and 20 by MaK. These five V 200 prototypes were put through extensive testing, the aim being to ensure the production locomotives would be as reliable as the technology and maintenance standards of the 1950s allowed. In 1955 one locomotive travelled under its own power through Yugoslavia, Greece and Turkey partly as a test and partly to demonstrate the locomotive's capability to potential customers in those countries. Initially the V 200 hauled express trains on all main lines, replacing the DRG Class 05, DRG Class 03 and DRG Class 01. Following the electrification of many main lines the V 200 was used increasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sifa
Sifa is a type of deadman's control system used on German-influenced European railways.{{cite web , url = http://www.virtualmarket.innotrans.de/index.php5?id=1022238&highlight=&fid=523&offset=0&Action=showProduct , title = Deadman's control system UDB , accessdate=2008-12-24 Although deadman's pedals are commonly used on railways worldwide, Sifa systems are specifically those codified by German Industrial Norms VDE 0119-207-5. In Switzerland the equivalent system is called 'safety control' (''Sicherheitssteuerung'').Eidgenössisches Departement für Umwelt, Verkehr, Energie und Kommunikation''Ausführungsbestimmungen zur Eisenbahnverordnung (AB-EBV)', as at: 01July 2016 Description Sifa is short for ''Sicherheitsfahrschaltung'', German for "safety driving circuit". It is usually a pedal and/or large press button, which monitors the alertness of the driver. The driver has to repeatedly press a button after a fixed interval; if they fail to do so, the train will carry out an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voith
The Voith Group is a German manufacturer of machines for the pulp and paper industry, technical equipment for hydropower plants and drive and braking systems. The family-owned company, which operates worldwide and has its headquarters in Heidenheim an der Brenz, was founded in 1867. Company history Laying the foundations for industrial paper production In 1825, Johann Matthäus Voith took over his father's locksmith's workshop in Heidenheim with five employees, mainly carrying out repairs to water wheels and paper mills. Around 1830 in Heidenheim, there were about 600 people working in 15 factories, mostly textile factories that had been established by wealthy merchants and publishers. The necessary maintenance and repair of the expensive machinery offered a source of income to several workshops, particularly the locksmiths and metalworkers in what was still a small town at the time. In 1830, Johann Matthäus Voith and his workshop were involved in the construction of a pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB Locomotive Classification
Originally, both Deutsche Bundesbahn and Deutsche Reichsbahn continued the classification system of the Deutsche Reichsbahn (DRG) – see also a short overview of the numbering system of the German railways. When UIC introduced a new classification system that could be processed by the computers of the late 1960s, DB did a major modification of their system, effective 1 January 1968. This system is still in use and now includes the engines of the former GDR railways as well. (See List of Deutsche Bahn AG locomotives and railbuses for a current list.) Basics Since January 1, 1968, all vehicles are identified by a seven-digit vehicle number that consists of a three-digit class number, a three-digit serial number, and a check digit, the latter separated by a dash. Series with more than 1,000 vehicles are assigned ascending class numbers. The first digit of the class number denotes the vehicle type using a scheme that is summarized in the following table, along with the correspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gina Lollobrigida
Luigia "Gina" Lollobrigida (born 4 July 1927) is an Italian actress, photojournalist, and politician. She was one of the highest-profile European actresses of the 1950s and early 1960s, a period in which she was an international sex symbol. As of 2022, Lollobrigida is among the last living, high-profile international actors from the Golden Age of Hollywood cinema. As her film career slowed, Lollobrigida established a second career as a photojournalist. In the 1970s, she achieved a scoop by gaining access to Fidel Castro for an exclusive interview. Lollobrigida has continued as an active supporter of Italian and Italian American causes, particularly the National Italian American Foundation (NIAF). In 2008, she received the NIAF Lifetime Achievement Award at the Foundation's Anniversary Gala. In 2013, she sold her jewelry collection, and donated the nearly $5 million from the sale to benefit stem-cell therapy research. Youth Born Luigia Lollobrigida in Subiaco, she was the daugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian T 18
The Prussian T 18 was the last class of tank locomotives developed for the Prussian state railways. They were originally intended for services on the island of Rügen as replacements for Class T 12 and T 10 engines. They emerged when a class of locomotive was conceived in 1912 that was to handle express and passenger trains in border areas or in shuttle services on short routes. A tank engine design with symmetrical running gear was envisaged because, unlike a tender locomotive, it could run equally fast forwards and backwards and could be operated on return journeys without having to be turned on a turntable. Its power and top speed were to be the same as those of the P 8. Robert Garbe designed this 4-6-4 (2′C2′) tank locomotive for 100 km/h with a 17-ton axle load and contracted the ''Vulkan Werke'' in Stettin to build it. It was given the designation T 18. A total of 534 engines were built from 1912 to 1927, mainly by the Stettiner Maschinenbau AG Vulc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian G 10
The Prussian G 10 was a German goods train, steam locomotive, whose design was based on a combination of the running and valve gear from the Prussian T 16 and the boiler from the Prussian P 8. In developing the G 10, however, the T 16 running gear with side play on the first and fifth axles was modified. The T 16 was also subsequently built with this modified configuration and called the Prussian T 16.1. The G 10 was intended for heavy goods train duties on main lines, but as a result of its low axle load it could be employed more flexibly than its equally powerful cousin, the Prussian G 8.1. The G 10 was occasionally even used in passenger train service. Between 1910 and 1924 no less than 2,615 Class G 10s were delivered to the Prussian state railways and the Deutsche Reichsbahn, 35 to the Imperial Railways in Alsace-Lorraine (see Alsace-Lorraine G 10) and 27 to the Saar Railway. Another 350 were sent to railway companies in Turkey, Romania, Poland and Lithuania. The Deutsche R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRB Class 50
The DRB Class 50Wartime locomotives classes are prefixed DRB (Deutsche Reichsbahn) to distinguish them from those introduced by the DRG (prefixed DRG), which became defunct in 1937, and those introduced later by the East German Deutsche Reichsbahn (prefixed DR). is a German class of 2-10-0 locomotive, built from 1939 as a standard locomotive (''Einheitsdampflokomotive'') for hauling goods trains. It had one leading axle and five coupled axles and was one of the most successful designs produced for the Deutsche Reichsbahn. This class was procured as part of the German Nazi party's preparations for war that led into the Second World War. Up to 1948, 3,164 Class 50 engines were built by almost all the European locomotive factories – towards the end as so-called provisional war locomotives (''Übergangskriegslokomotiven'') and classified as 50 ÜK. At the end of the steam locomotive era, they became virtually a universal class of mixed-traffic steam engine that, thanks to their lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian P 10
The Prussian state railways' Class P 10 were 2-8-2 "Mikado" type passenger-hauling steam locomotives built for hauling heavy express trains in the hilly terrain of the ''Mittelgebirge''. They were the last Prussian passenger train steam locomotives to be developed in Prussia before the state railways were merged into the Deutsche Reichsbahn (German Imperial Railway), who eventually designated them as DRG Class 39. The design by Borsig, under the supervision of chief engineer August Meister, was ready in 1919 but, due to material shortages, no locomotives were produced until 1922. They were three-cylinder locomotives, all cylinders driving the second coupled axle. Three sets of Walschaerts valve gear were used, the one for the inside cylinder being mainly located inside the frame, but driven from the same eccentric crank as the valve gear on the left-hand side; two eccentric rods of different lengths being attached to the same crank. The locomotives' heavy axle-load exceeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |