|
Düben Collection
The Düben collection is a collection of musical manuscripts named after the original collector, Gustaf Düben, held in the Uppsala University Library. It includes much 17th-century baroque music, in particular the only surviving copies of many works by Dieterich Buxtehude. Chronology The collection was compiled starting in the 1640s by Gustaf Düben, and by subsequent members of the family, who held positions at the Swedish Court Chapel. It was ultimately bequeathed to the Uppsala University Library in 1732. Owing to the music it contained being by then mostly out of fashion, it remained there, in neglect but intact, for most of the 18th and 19th centuries. It was ultimately catalogued in the 1880s by librarian Anders Lagerberg, and, upon being noticed by a visiting German musician from Lübeck, gained the attention of musicologists due to it containing copies of previously unknown works by Buxtehude, and later due to its overall significance in assessing 17th-century music history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
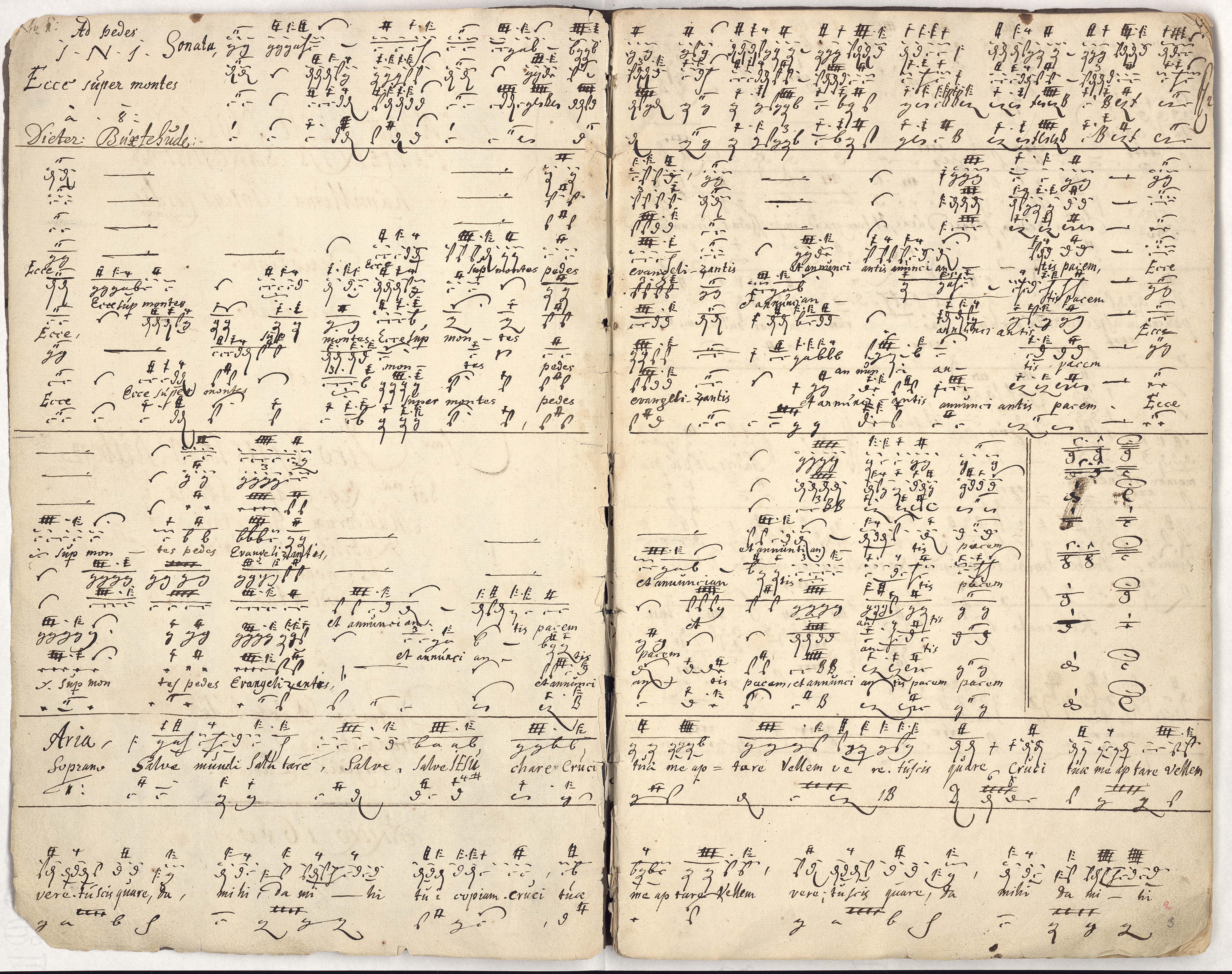
Membra Jesu Nostri
''Membra Jesu nostri'', List of compositions by Dieterich Buxtehude, BuxWV 75, is a cycle of seven cantatas composed in 1680 by Dieterich Buxtehude and dedicated to Gustaf Düben. More specifically and fully it is, in Buxtehude's phrase, a ''“ decantata,”'' or “sung devotion,” titled ''Membra Jesu nostri patientis sanctissima'', which translates from the Latin as ''Limbs Most Holy of Our Suffering Jesus''. Regarding genre, the cycle consists in seven concerto-aria cantatas, a form that had emerged in Germany in the 1660s. The stanzas of its main text are drawn from the medieval hymn ''Salve mundi salutare'', also known as the ''Rhythmica oratio'', formerly ascribed to Bernard of Clairvaux but now thought to be by Arnulf of Leuven. Each cantata addresses a part of Jesus' crucified body: feet, knees, hands, side, breast, heart and face; in each, Bible, Biblical words referring to the limb frame verses of the hymn's text. Structure Each cantata in ''Membra Jesu nostri'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giacomo Carissimi
(Gian) Giacomo Carissimi (; baptized 18 April 160512 January 1674) was an Italian composer and music teacher. He is one of the most celebrated masters of the early Baroque or, more accurately, the Roman School of music. Carissimi established the characteristic features of the Latin oratorio and was a prolific composer of masses, motets, and cantatas. He was highly influential in musical developments in northern European countries through his pupils, like Kerll in Germany and Charpentier in France, and the wide dissemination of his music.Andrew V. Jones, "Giacomo Carissimi", ''Grove Music Online'' Biography Carissimi's exact birthdate is not known, but it was probably in 1604 or 1605 in Marino near Rome, Italy. Of his early life almost nothing is known. Giacomo's parents, Amico (1548–1633, a cooper by trade) and Livia (1565–1622), were married on 14 May 1595 and had four daughters and two sons; Giacomo was the youngest. Nothing is known of his early musical training. His f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala University
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation. Initially founded in the 15th century, the university rose to significance during the rise of Swedish Empire, Sweden as a great power at the end of the 16th century and was then given relative financial stability with a large donation from Monarchy of Sweden, King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus in the early 17th century. Uppsala also has an important historical place in Swedish national culture, and national identity, identity for the Swedish establishment: in historiography, religion, literature, politics, and music. Many aspects of Swedish academic culture in general, such as the white student cap, originated in Uppsala. It shares some peculiarities, such as the student nation system, with Lund University and the University of Helsink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erik Kjellberg
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, Eirik, or Eiríkur is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization). The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* aina(z)'', meaning "one, alone, unique", ''as in the form'' ''Æ∆inrikr'' explicitly, but it could also be from ''* aiwa(z)'' "everlasting, eternity", as in the Gothic form ''Euric''. The second element ''- ríkr'' stems either from Proto-Germanic ''* ríks'' "king, ruler" (cf. Gothic ''reiks'') or the therefrom derived ''* ríkijaz'' "kingly, powerful, rich, prince"; from the common Proto-Indo-European root * h₃rḗǵs. The name is thus usually taken to mean "sole ruler, autocrat" or "eternal ruler, ever powerful". ''Eric'' used in the sense of a proper noun meaning "one ruler" may be the origin of ''Eriksgata'', and if so it would have meant "one ruler's journey". The tour was the medieval Swedish king's journey, when newly el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Düben Family
The Düben family () is a noble family of German descent, originating in Saxony, Holy Roman Empire, whose members were elevated to the Swedish nobility, that rose to prominence with Andreas Düben (–1662), an organist to the German Church in Stockholm, Swedish Empire. During the 17th century, the Düben family exerted a significant influence on music at the Royal Court Orchestra, which experienced a golden age during those years. The family collected and composed various works, resulting in a compilation known as the Düben collection. Gustaf Düben, the son of Andreas Düben, was responsible for compiling this collection. Its members use different surnames; the ennobled individuals and their descendants incorporate a nobiliary particle, "von," into their surnames, as seen in "von Düben" (), while the un-ennobled members do not include this particle in their surnames. Overview The Düben family progenitor, Michael Düben, was an advisor () in Lützen. He had a son, An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vincenzo Albrici
Vincenzo Albrici (26 June 1631 in Rome – 7 September 1687 in Prague) was an Italian composer, brother of Bartolomeo and nephew of Fabio and Alessandro Costantini. Albrici was born as the son of singer who settled from Marche in Rome. In 1641 he became a student at the Collegium Germanicum et Hungaricum under Giacomo Carissimi. In 1647 he was paid as an organist in the Santa Maria in Vallicella. Albrici was one of several musicians and composers residing in the court of Christina of Sweden in the first half of the seventeenth century and arrived to the court of Charles II of England in the 1660s. Then Albrici became joint ''vice-kapellmeister'' with Giovanni Andrea Bontempi under Heinrich Schütz in Dresden (1659). Vincenzo's brother Bartolomeo Albrici, took up the position of organist. Vincenzo and his sister Leonora, also a singer, went to England and became part of the King's Italian Musicke. Bartolomeo joined them in 1666 and remained in England when Vincenzo returned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marco Giuseppe Peranda
Marco Giuseppe Peranda (Macerata, c. 1625 – 12 January 1675 in Dresden) was an Italian musician and composer active in Germany. Life He was one of the most notable Italian musicians in Germany during the early Baroque alongside Vincenzo Albrici, Carlo Pallavicino and Giovanni Andrea Bontempi in Dresden. These four Italian ''Kapellmeisters'' were well rewarded – they earned yearly salaries of 1,200 ''Reichstalers'' while Heinrich Schütz, at this point semi-retired, earned 800 Reichstalers a year.Gina Spagnoli ''Letters and documents of Heinrich Schütz, 1656–1672'' 1990 "In this list, the four Italian Kapellmeisters, Bontempi, Albrici, Peranda, and Pallavicino, are shown to have earned yearly salaries of 1200 Reichstalers while Schutz, by then semiretired, earned 800 Reichstalers. Vice-Kapellmeister Giovanni de ... A contemporary, Agostino Rossi, records him as being a native of Macerata but his musical style shows an education in Rome. From 1651 Perenda was an alto singer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Krieger
Johann Krieger (28 December 1651 – 18 July 1735) was a German composer and organist, younger brother of Johann Philipp Krieger. Born in Nuremberg, he worked at Bayreuth, Zeitz, and Greiz before settling in Zittau. He was one of the most important keyboard composers of his day, highly esteemed by, among others, George Frideric Handel. A prolific composer of church and secular music, he published several dozen of his works, and others survive in manuscript. However, hundreds more were lost when Zittau was destroyed by fire in 1757, during the Seven Years' War. Krieger's keyboard music places him among the most important German composers of his time.Samuel, Grove. The two published collections, ''Sechs musicalische Partien'' (1697) and ''Anmuthige Clavier-Übung'' (1698), contain harpsichord suites, organ toccatas, fugues, ricercars, and other works. Krieger's contemporaries praised his contrapuntal skill, evident in the extant fugues and ricercars. Johann Mattheson was particularl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaspar Förster
Kaspar Förster (also Caspar Foerster) (baptized 28 February 1616 in Danzig – 2 February 1673 in Oliva, near Danzig) was a German singer and composer. Förster studied music under his father Kaspar (1574-1652) and then under Marco Scacchi in Warsaw. He sang bass and conducted choirs at the Polish court in Warsaw from 1638 to about 1643, then served as ''kapellmeister'' to Frederik III of Denmark in Copenhagen between 1652 and 1655. In 1655, a war broke out between Denmark and Sweden, and Förster returned to Danzig, working as ''cantor'' at the Marienkirche there. He returned to the employ of Frederik from 1661 to 1667. During this time he visited Venice several times and played a role in bringing aspects of Italian musical style to northern Europe. He also studied under Giacomo Carissimi in the 1660s. Late in his life he worked briefly in Hamburg before returning to his birthplace. Förster's surviving works are mostly sacred cantatas for three voices, with two violins a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andreas Hammerschmidt
Andreas Hammerschmidt (1611 or 1612 – 29 October 1675) was a German Bohemian composer and organist of the early to middle Baroque era. He was one of the most significant and popular composers of sacred music in Germany in the middle 17th century. He was nicknamed the "Orpheus of Zittau". Life He was born in Brüx to a Saxon father and a Bohemian mother. In 1626 the family had to flee Bohemia, during the Thirty Years' War, after it had become Catholic; they settled in Freiberg, Saxony, where Andreas must have received his musical education. He probably did not study with composer Christoph Demantius, who was ''Kantor'' at Freiberg and the most significant musician in the city while Hammerschmidt was there; however he may have known him. Many famous musicians of the early Baroque spent time in Freiberg but it is uncertain which of them taught Hammerschmidt; at any rate he received a superb musical training while there. Hammerschmidt left Freiberg in 1633, through his mentor S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoph Bernhard
Christoph Bernhard (1 January 1628 – 14 November 1692) was born in Kolberg, Pomerania, and died in Dresden. He was a German Baroque composer and musician. He studied with former Sweelinck-pupil Paul Siefert in Danzig (now Gdańsk) and in Warsaw. By the age of 20, he was singing at the electoral court in Dresden under Heinrich Schütz and composed some of the music for the Master's funeral. He then spent a year in Copenhagen to study singing with Agostino Fontana. After his appointment as assistant '' kapellmeister'' in Dresden in 1655, Bernhard made two sojourns to Italy to further his musical education. When he was 35, he moved to Hamburg to work as the director of music for the Johanneum and for civic musical events. The next ten years were a golden age in the musical tradition of Hamburg: Bernhard and his good friend Matthias Weckmann performed together and directed the latest compositions from Italy and Vienna, as well as composing an important collection of music in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudio Monteverdi
Claudio Giovanni Antonio Monteverdi (baptized 15 May 1567 – 29 November 1643) was an Italian composer, choirmaster and string instrument, string player. A composer of both Secular music, secular and Church music, sacred music, and a pioneer in the Origins of opera, development of opera, he is considered a crucial Transition from Renaissance to Baroque in instrumental music, transitional figure between the Renaissance music, Renaissance and Baroque music, Baroque periods of music history. Born in Cremona, where he undertook his first musical studies and compositions, Monteverdi developed his career first at the court of Mantua () and then until his death in the Republic of Venice where he was ''maestro di cappella'' at the basilica of St Mark's Basilica, San Marco. His surviving letters give insight into the life of a professional musician in Italy of the period, including problems of income, patronage and politics. Much of List of compositions by Claudio Monteverdi, Monteve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |