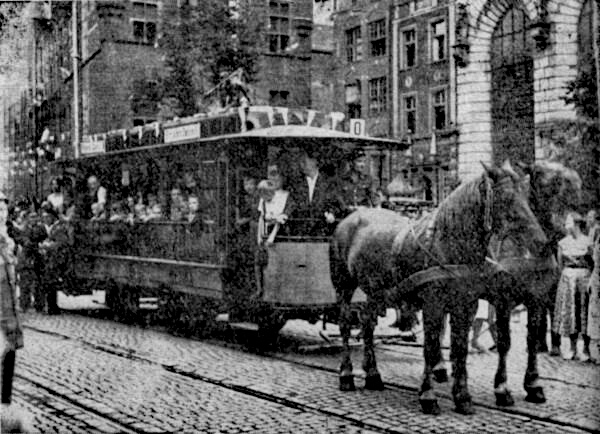|
Döbeln Tramway
The Döbeln Tramway or ''Döbelner Straßenbahn'' is a tramway in the German town of Döbeln. It is the only horse-drawn tram line to operate on its original urban route in Germany, and one of only a handful in the world. The Döbeln Tramway was built in 1892 and connected the town's railway station with its market square until 1926, when it was replaced by a bus. Throughout its period of operation it remained horse-drawn, and was one of the last such of such lines to remain in operation in Germany. Even after it ceased operation, some of its tram track remained in place and served as a reminder of the old line. Occasional suggestions to restore the line surfaced over the years of closure but, until the beginning of the 21st century, no action was taken. In 2002 flooding in the centre of Döbeln caused serious damage and required significant restoration work to restore the town's streets. As part of this work, the opportunity was taken to relay of track from Obermarkt to Thea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
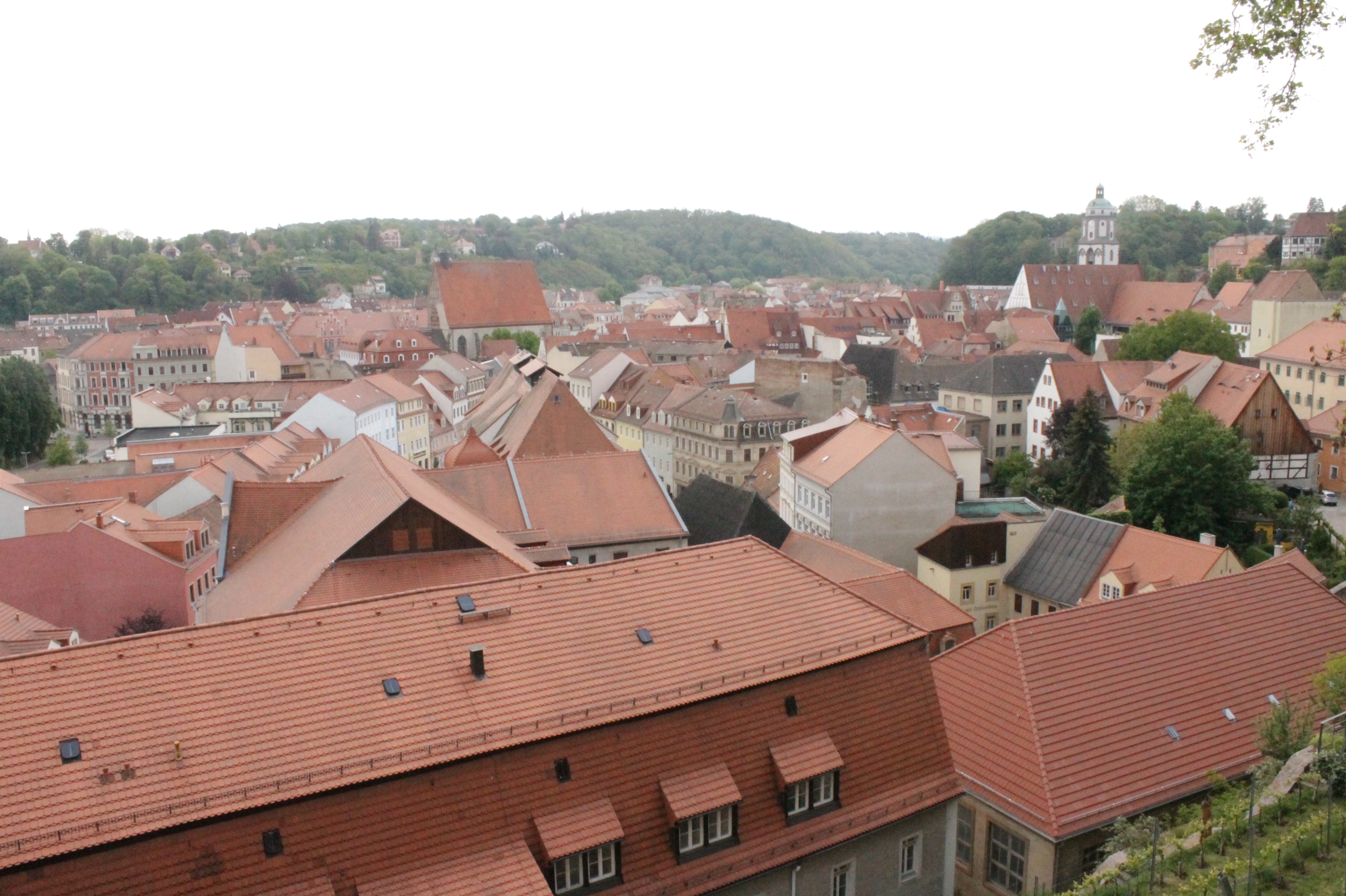
Meißen
Meissen (in German orthography: ''Meißen'', ) is a town of approximately 30,000 about northwest of Dresden on both banks of the Elbe river in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. Meissen is the home of Meissen porcelain, the Albrechtsburg castle, the Gothic Meissen Cathedral and the Meissen Frauenkirche. The ''Große Kreisstadt'' is the capital of the Meissen district. Names * german: Meißen * french: Meissen, ou, selon l'orthographe allemande: ''Meißen''; en français suranné: ''Misnie'' * la, Misnia, Misena, Misnensium * pl, Miśnia * cs, Míšeň * hsb, Mišno * dsb, Mišnjo * zh, 迈森 (pinyin: ) History Meissen is sometimes known as the "cradle of Saxony". It grew out of the early West Slavic settlement of ''Misni'' inhabited by Glomatians and was founded as a German town by King Henry the Fowler in 929. In 968, the Diocese of Meissen was founded, and Meissen became the episcopal see of a bishop. The Catholic bishopric was suppressed in 1581 after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Lines Opened In 1892
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in Track (rail transport), tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on Railroad tie, sleepers (ties) set in track ballast, ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower friction, frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The rail transport operations, operation is carried out by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre Gauge Railways In Germany
The metre (British spelling) or meter (American spelling; see spelling differences) (from the French unit , from the Greek noun , "measure"), symbol m, is the primary unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), though its prefixed forms are also used relatively frequently. The metre was originally defined in 1793 as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's circumference is approximately km. In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar (the actual bar used was changed in 1889). In 1960, the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the path travelled by light in a vacuum in of a second. After the 2019 redefiniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse-drawn Trams In Operation
A horse-drawn vehicle is a mechanized piece of equipment pulled by one horse or by a team of horses. These vehicles typically had two or four wheels and were used to carry passengers and/or a load. They were once common worldwide, but they have mostly been replaced by automobiles and other forms of self-propelled transport. General Horses were domesticated circa 3500 BCE. Prior to that oxen were used. Historically a wide variety of arrangements of horses and vehicles have been used, from chariot racing, which involved a small vehicle and four horses abreast, to horsecars or trollies, which used two horses to pull a car that was used in cities before electric trams were developed. A two-wheeled horse-drawn vehicle is a cart (see various types below, both for carrying people and for goods). Four-wheeled vehicles have many names – one for heavy loads is most commonly called a wagon. Very light carts and wagons can also be pulled by donkeys (much smaller than horses), ponies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse-drawn Railways
Wagonways (also spelt Waggonways), also known as horse-drawn railways and horse-drawn railroad consisted of the horses, equipment and tracks used for hauling wagons, which preceded steam-powered railways. The terms plateway, tramway, dramway, were used. The advantage of wagonways was that far bigger loads could be transported with the same power. Ancient systems The earliest evidence is of the 6 to 8.5 km long '' Diolkos'' paved trackway, which transported boats across the Isthmus of Corinth in Greece from around 600 BC. Wheeled vehicles pulled by men and animals ran in grooves in limestone, which provided the track element, preventing the wagons from leaving the intended route. The Diolkos was in use for over 650 years, until at least the 1st century AD. Paved trackways were later built in Roman Egypt. Wooden rails Such an operation was illustrated in Germany in 1556 by Georgius Agricola (image right) in his work De re metallica. This line used "Hund" carts w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritage Streetcar Systems
Heritage may refer to: History and society * A heritage asset is a preexisting thing of value today ** Cultural heritage is created by humans ** Natural heritage is not * Heritage language Biology * Heredity, biological inheritance of physical characteristics * Kinship, the relationship between entities that share a genealogical origin Arts and media Music * ''Heritage'' (Earth, Wind & Fire album), 1990 * ''Heritage'' (Eddie Henderson album), 1976 * ''Heritage'' (Opeth album), 2011, and the title song * Heritage Records (England), a British independent record label * Heritage (song), a 1990 song by Earth, Wind & Fire Other uses in arts and media * ''Heritage'' (1935 film), a 1935 Australian film directed by Charles Chauvel * ''Heritage'' (1984 film), a 1984 Slovenian film directed by Matjaž Klopčič * ''Heritage'' (2019 film), a 2019 Cameroonian film by Yolande Welimoum * ''Heritage'' (novel), a ''Doctor Who'' novel Organizations Political parties * Heritage (Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicken Coop
Poultry farming is the form of animal husbandry which raises domesticated birds such as chickens, ducks, turkeys and geese to produce meat or eggs for food. Poultry – mostly chickens – are farmed in great numbers. More than 60 billion chickens are killed for consumption annually. Chickens raised for eggs are known as layers, while chickens raised for meat are called broilers. In the United States, the national organization overseeing poultry production is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In the UK, the national organisation is the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra). Intensive and alternative According to the World Watch Institute, 74 percent of the world's poultry meat, and 68 percent of eggs are produced intensively.''State of the World 2006'' World "atch Institute, p. 26 One alternative to intensive poultry farming is free-range farming using lower stocking densities. Poultry producers routinely use nationally approved medications, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tramways & Urban Transit
''Tramways & Urban Transit'' ''(TAUT'' or ''T&UT)'', also known as ''Modern Tramway'', is a British monthly magazine about tramways and light rail transport, published continuously since 1938. Its content is orientated both to tramway enthusiasts and to persons working in the tram transport field or studying tramways. It has been issued monthly from the beginning.Claydon, Geoffrey (June 1997). "Sixty Years of the LRTA". ''Light Rail & Modern Tramway'', pp. 227–228. Although published in Britain, the magazine's coverage is international, and its regular "World News" column includes detailed news on electric trams (called streetcars or trolleys in American English) and light rail worldwide.Saitta, Joseph P. (Ed.) (1981). Review of ''Modern Tramway'' in ''Traction Yearbook '81'', p. 230. Merrick, NY (US): Traction Slides International. Quote: "Necessary reading for those wishing to keep abreast of light rail progress." From 1938 until 2007 the magazine was published by the Ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Döbeln Hauptbahnhof
Döbeln Hauptbahnhof is the largest station in Döbeln in the German state of Saxony. Now an unstaffed halt, it was built as a Keilbahnhof ("wedge-shaped station"). The station is listed by the rail authorities with the abbreviation of DDE. The diesel-worked Borsdorf–Coswig and electrified Riesa–Chemnitz lines cross in Döbeln Hbf. From 1884 to 1964 Döbeln Hbf was also the terminus of the 750 mm gauge railway from Oschatz. History Although Döbeln had already been connected to the Riesa-Chemnitz route since 1847 with the nearby Großbauchlitz station, this station was opened with the opening of the Döbeln–Leisnig section of the Borsdorf–Coswig railway 2 June 1868 as ''Station Döbeln'', which "interimistically" had only a "passenger entrance shed". On 25 October 1868, the ''Döbeln Ost'' (east) station came into operation on the route to Meißen, and Döbeln station received the designation of ''Hauptbahnhof'' (main or central station). Two years later, on 1&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsecar
A horsecar, horse-drawn tram, horse-drawn streetcar (U.S.), or horse-drawn railway (historical), is an animal-powered (usually horse) tram or streetcar. Summary The horse-drawn tram (horsecar) was an early form of public rail transport, which developed out of industrial haulage routes that had long been in existence, and from the omnibus routes that first ran on public streets in the 1820s{{{citation needed, date=February 2022, using the newly improved iron or steel rail or ' tramway'. They were local versions of the stagecoach lines and picked up and dropped off passengers on a regular route, without the need to be pre-hired. Horsecars on tramlines were an improvement over the omnibus, because the low rolling resistance of metal wheels on iron or steel rails (usually grooved from 1852 on) allowed the animals to haul a greater load for a given effort than the omnibus, and gave a smoother ride. The horse-drawn streetcar combined the low cost, flexibility, and safety of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |