|
Département Du Nord
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivity, territorial collectivities"), between the Regions of France, administrative regions and the Communes of France, communes. There are a total of 101 departments, consisting of ninety-six departments in metropolitan France, and five Overseas department and region, overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 333 Arrondissements of France, arrondissements and 2,054 Cantons of France, cantons (as of 2023). These last two levels of government have no political autonomy, instead serving as the administrative basis for the local organisation of police, fire departments, and, in certain cases, elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council (France), departmental council ( , ). From 1800 to April 2015, these were called gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France Maximale
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Territorial Collectivity
A territorial collectivity (, previously '), or territorial authority, in many francophone countries, is a Legal person, legal entity governed by public law that exercises within its territory certain powers devolved to it by the State as part of a decentralization process. In France, it also refers to a chartered administrative division of France with recognized governing authority. It is the generic name for any territory with an elective form of local government and local regulatory authority. The nature of a French territorial collectivity is set forth in Article 72 of the Constitution of France (1958), which provides for local autonomy within limits prescribed by law. Overview Use of the term The term ''collectivité territoriale'' is used in Burkina Faso, in France by its legislation and the Constitution, in Mali and in Morocco. In Algeria and Senegal, they refer to it as ''collectivité locale''. However, in France, it is also used by the State administration: the ''Dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1833 Territorial Division Of Spain
The 1833 territorial division of Spain divided the country into provinces, in turn classified into "historic regions" ().''Real Decreto de 30 de noviembre de 1833'' on Wikisource; ''Real Decreto de 30 de noviembre de 1833'' on the official web site of the government of the Canary Islands. Retrieved 31 December 2009. Original announcement in th ''Gaceta num. 154.'' on th [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trienio Liberal
The , () or Three Liberal Years, was a period of three years in Spain between 1820 and 1823 when a liberal government ruled Spain after a military uprising in January 1820 by the lieutenant-colonel Rafael del Riego against the absolutist rule of Ferdinand VII. It ended in 1823 when, with the approval of the crowned heads of Europe, a French army invaded Spain and reinstated the King's absolute power. This invasion is known in France as the "Spanish Expedition" () and in Spain as the " Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis." Revolution of Cabezas de San Juan King Ferdinand VII provoked widespread unrest, particularly in the army, by refusing to accept the liberal Spanish Constitution of 1812. The King sought to reclaim the Spanish colonies in the Americas that had recently revolted successfully, consequently depriving Spain of an essential source of revenue. In January 1820, soldiers assembled at Cádiz for an expedition to South America, angry over infrequent pay, bad foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Thousand Sons Of Saint Louis
The "Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis" was the popular name for a French army mobilized in 1823 by the Bourbon King of France, Louis XVIII, to help the Spanish Bourbon royalists restore King Ferdinand VII of Spain to the absolute power of which he had been deprived during the Liberal Triennium. Despite the name, the actual number of troops was between 60,000 and 90,000. A minor campaign, the force comprised some five army corps (the bulk of the French regular army) and was led by the Duke of Angoulême, nephew of Louis XVIII and son of future King Charles X. The French name of the conflict is ''l'Expédition d'Espagne'' ("the Expedition of Spain"). Context In 1822, Ferdinand VII applied the terms of the Congress of Vienna, lobbied for the assistance of the other absolute monarchs of Europe, in the process joining the Holy Alliance formed by Russia, Prussia, Austria and France to restore absolutism. In France, the ultra-royalists pressured Louis XVIII to intervene. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1822 Territorial Division Of Spain
The 1822 territorial division of Spain was a rearrangement of the territory of Spain into various provinces, enacted briefly during the '' Trienio Liberal'' of 1820–1823. It is remembered today largely as a precursor to the similar 1833 territorial division of Spain; the provinces established in the latter remain, by and large, the basis for the present-day division of Spain into provinces. Eduardo BarrenecheaLos 'gibraltares' de unas regiones en otras: Treviño, Llivia, Rincón de Ademuz... '' El País'', 1983-02-08. Accessed online 2000-12-30. This article comments on the persistence of the 1833 territorial division, in the context of a discussion of the remaining exclaves of various provinces.Daniele ConversiThe Spanish Federalist Tradition and the 1978 Constitution, p. 12, footnote 63. Accessed online 2000-12-31. Background After the uprising led by liberal general Rafael del Riego of 1820 led to the '' Trienio Liberal'' (three years of government by the Spanish liberal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Louis De Voyer De Paulmy D'Argenson
René ('' born again'' or ''reborn'' in French) is a common first name in French-speaking, Spanish-speaking, and German-speaking countries. It derives from the Latin name Renatus. René is the masculine form of the name ( Renée being the feminine form). In some non-Francophone countries, however, there exists the habit of giving the name René (sometimes spelled without an accent) to girls as well as boys. In addition, both forms are used as surnames (family names). René as a first name given to boys in the United States reached its peaks in popularity in 1969 and 1983 when it ranked 256th. Since 1983 its popularity has steadily declined and it ranked 881st in 2016. René as a first name given to girls in the United States reached its peak in popularity in 1962 when it ranked 306th. The last year for which René was ranked in the top 1000 names given to girls in the United States was 1988. Persons with the given name * René, Duke of Anjou (1409–1480), titular king of Nap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbé Sieyès
''Abbé'' (from Latin , in turn from Greek , , from Aramaic ''abba'', a title of honour, literally meaning "the father, my father", emphatic state of ''abh'', "father") is the French word for an abbot. It is also the title used for lower-ranking Catholic clergy in France who are not members of religious orders. History A concordat between ... between Pope Leo X and King François I of France (1516) cites III under Kinds of Abbot gave the monarchs of France the right to nominate 255 commendatory abbot">Francis I of France">King François I of France (1516) cites III under Kinds of Abbot gave the monarchs of France the right to nominate 255 commendatory abbots () for almost all French abbeys, who received income from a monastery without needing to render service, creating, in essence, a sinecure. From the mid-16th century, the title of ''abbé'' has been used in France for all young clergy, with or without consecration. Their clothes consisted of black or dark violet robes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
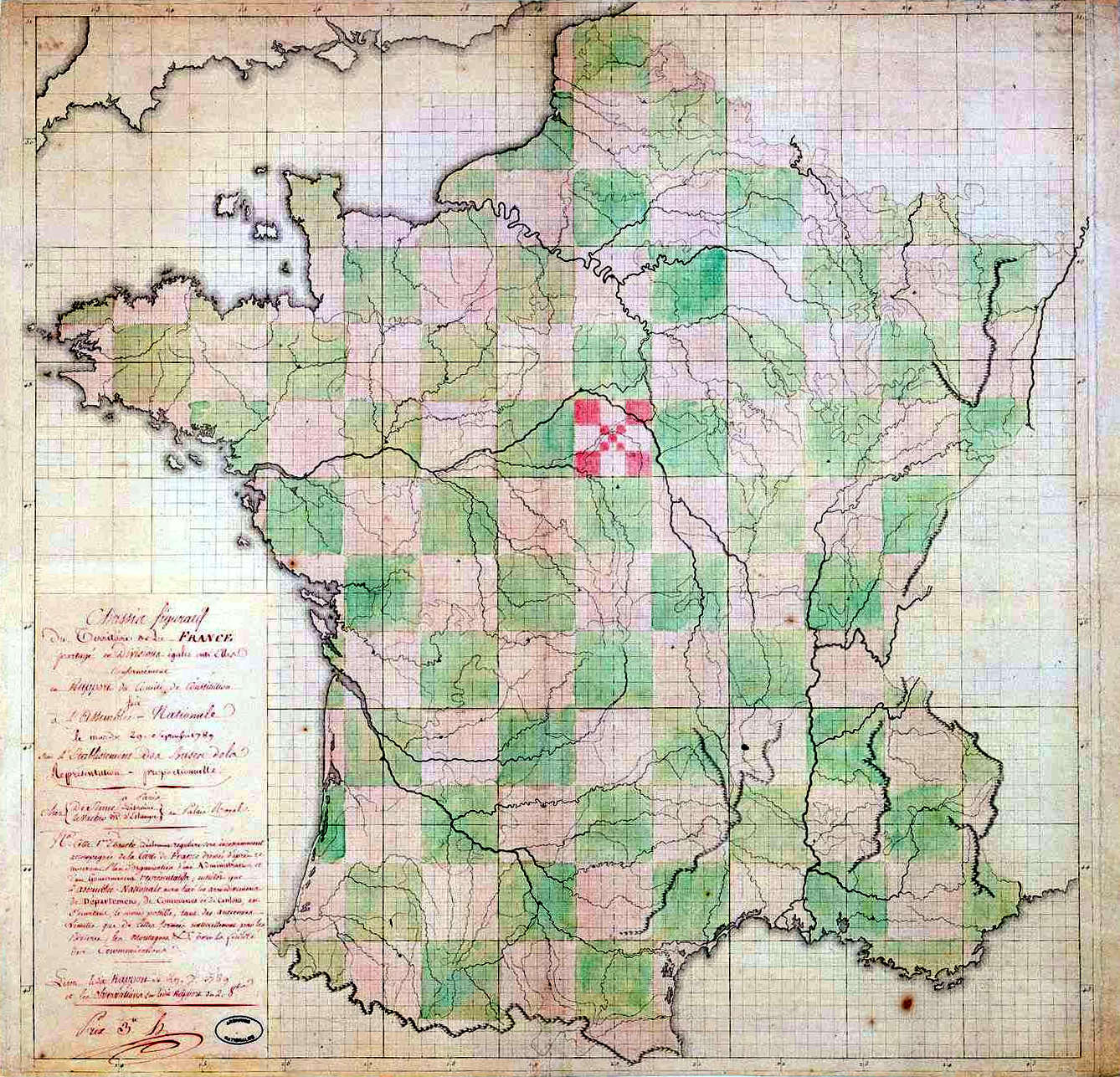
Provinces Of France
Under the Ancien Régime, the Kingdom of France was subdivided in multiple different ways (judicial, military, ecclesiastical, etc.) into several administrative units, until the National Constituent Assembly adopted a more uniform division into departments (''départements'') and districts in late 1789. The provinces () continued to exist administratively until 21 September 1791. The country was subdivided ecclesiastically into dioceses, judicially into ''généralités'', militarily into general governments. None of these entities was called "province" by their contemporaries. However, later interpretations confused the term of "general government" (a military division) with that of a cultural province, since the general governments often used the names and borders of a province. It was not always the case, which causes confusion as to the borders of some provinces. Today, the term "province" is used to name the resulting regional areas, which retain a cultural and linguistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to * the French word for " ancient, old" ** Société des anciens textes français * the French for "former, senior" ** Virelai ancien ** Ancien Régime ** Ancien Régime in France {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
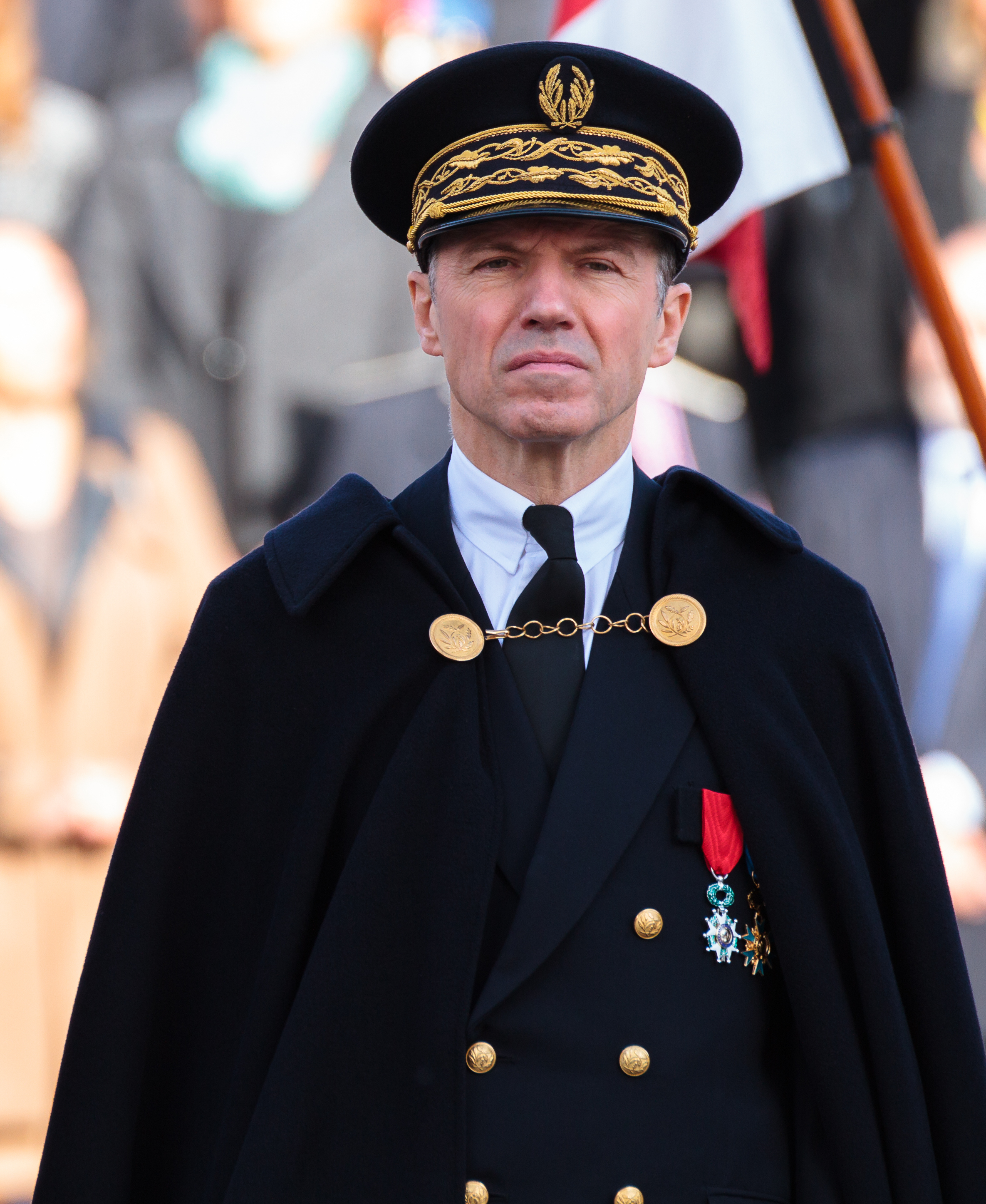
Prefect (France)
A prefect (, plural , both ) in France is the State's representative in a Departments of France, department or Regions of France, region. Regional prefects are ''ex officio'' the departmental prefects of the regional Prefectures in France, prefecture. Prefects are tasked with upholding the law in the department they serve in, including controlling the actions of local authorities. Prefects are appointed by decree by the President of France when presiding over the Government of France, government's Council of Ministers, following a proposal by the Prime Minister of France, Prime Minister and the Minister of the Interior (France), Minister of the Interior. They serve at the government's discretion and can be replaced at any meeting of the Council of Ministers. To uphold the law, they are authorised to undertake a wide variety of actions, such as coordinating police forces, enforcing immigration rules, controlling authorities' finances, as well as suing local collectivities in the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Education In France
In France, secondary education is in two stages: * ''Collèges'' () cater for the first four years of secondary education from the ages of 11 to 14. * ''Lycées'' () provide a three-year course of further secondary education for students between the ages of 15 and 19. Pupils are prepared for the '' baccalauréat'' (; baccalaureate, colloquially known as ''bac'', previously ''bachot''), which can lead to higher education studies or directly to professional life. There are three main types of ''baccalauréat'': the ''baccalauréat général'', ''baccalauréat technologique'' and ''baccalauréat professionnel''. School year The school year starts in early September and ends in early July. Metropolitan French school holidays are scheduled by the Ministry of Education by dividing the country into three zones (A, B, and C) to prevent overcrowding by family holidaymakers of tourist destinations, such as the Mediterranean coast and ski resorts. Lyon, for example, is in zone A, Mars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |