|
Décauville
Decauville () was a manufacturing company which was founded by Paul Decauville (1846–1922), a French pioneer in industrial railways. Decauville's major innovation was the use of ready-made sections of light, narrow gauge track fastened to steel sleepers; this track was portable and could be disassembled and transported very easily. The first Decauville railway used gauge; Decauville later refined his invention and switched to and gauge. History Origins In 1853 Paul Decauville's father, Amand, created a boilermaking workshop on the family farm in order to set up distilleries on the farms to the east of Paris. In 1864, Amand asked his eldest son, Paul, to come and help him following health problems. Very quickly, the latter seeks to improve the functioning of the estate. Very developed under the Second Empire in the northern half of France, the production of sugar beet and its refining into sugar, is linked to that of alcoholic products such as fuel. Amand will therefore en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privately Held Company
A privately held company (or simply a private company) is a company whose shares and related rights or obligations are not offered for public subscription or publicly negotiated in the respective listed markets, but rather the company's stock is offered, owned, traded, exchanged privately, or Over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter. In the case of a closed corporation, there are a relatively small number of shareholders or company members. Related terms are closely-held corporation, unquoted company, and unlisted company. Though less visible than their public company, publicly traded counterparts, private companies have major importance in the world's economy. In 2008, the 441 list of largest private non-governmental companies by revenue, largest private companies in the United States accounted for ($1.8 trillion) in revenues and employed 6.2 million people, according to ''Forbes''. In 2005, using a substantially smaller pool size (22.7%) for comparison, the 339 companies on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire (; officially the French Empire, ), was the 18-year Empire, Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870, between the French Second Republic, Second and the French Third Republic, Third Republic of France. Historians in the 1930s and 1940s often disparaged the Second Empire as a precursor of fascism. That interpretation is no longer widely held, and by the late 20th century they were giving it as an example of a modernising regime. Historians have generally given the Empire negative evaluations on its foreign policy, and somewhat more positive evaluations of domestic policies, especially after Napoleon III liberalised his rule after 1858. He promoted French business and exports. The greatest achievements included a grand History of rail transport in France#Success under the Second Empire, railway network that facilitated commerce and tied the nation together with Paris as its hub. This stimulated economic growth a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
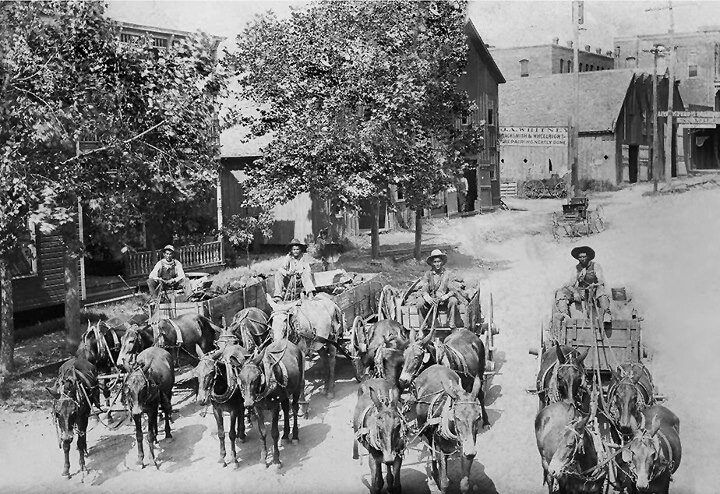
Wagon Du Rail En Soignes
A wagon or waggon is a heavy four-wheeled vehicle pulled by draught animals or on occasion by humans, used for transporting goods, commodities, agricultural materials, supplies and sometimes people. Wagons are immediately distinguished from carts (which have two wheels) and from lighter four-wheeled vehicles primarily for carrying people, such as carriages. Animals such as horses, mules, or oxen usually pull wagons. One animal or several, often in pairs or teams may pull wagons. However, there are examples of human-propelled wagons, such as mining corfs. A wagon was formerly called a wain and one who builds or repairs wagons is a wainwright. More specifically, a wain is a type of horse- or oxen-drawn, load-carrying vehicle, used for agricultural purposes rather than transporting people. A wagon or cart, usually four-wheeled; for example, a haywain, normally has four wheels, but the term has now acquired slightly poetical connotations, so is not always used with technical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tramway De Pithiviers à Toury
The Tramway de Pithiviers à Toury (TPT) was a gauge railway in the Loiret department of France. It was built to carry sugar beet and was long. History Pithiviers and Toury are apart, and sugar beet is a major agricultural product in the area. The Chemin de fer de Paris à Orléans passed through Toury. In 1892, the Société Decauville took a 15-year concession to build and operate a light railway linking Pithiviers and the surrounding villages to Toury. There were sugar refineries at Pithiviers and Toury, and the line connected these. The route of the railway generally followed local roads. The line opened on 25 July 1892. The failure of the Société Decauville in 1898 meant that the operation of the TPT was taken over by the department on 1 January 1899 and later by the ''Ponts et Chaussees'' on 29 March 1901. Traffic grew steadily until the Second World War. A railcar was introduced in 1922, and another followed in 1926, followed by two more acquired second-hand fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manure
Manure is organic matter that is used as organic fertilizer in agriculture. Most manure consists of animal feces; other sources include compost and green manure. Manures contribute to the fertility of soil by adding organic matter and nutrients, such as nitrogen, that are utilised by bacteria, fungi and other organisms in the soil. Higher organisms then feed on the fungi and bacteria in a chain of life that comprises the soil food web. History According to a Byzantine tradition attributed to Cassianus Bassus pig dung was generally not usable as fertilizer, except for almond trees. Similar views recorded by Columella were unrelated to the Islamic taboos of later centuries, though the medieval Andalusian writer Ibn Bassal and some later writers from Yemen also recorded negative effects of pig dung "burning" plants. Ibn Bassal described a sort of mixed manure with straw or sweeping mixed in as ', implying that was not composed of only manure. The sweepings from hot baths inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposition Universelle (1878)
The third Paris World's Fair, called an Exposition Universelle in French, was held from 1 May to 10 November 1878. It celebrated the recovery of France after the 1870–71 Franco-Prussian War. Construction The buildings and the fairgrounds were somewhat unfinished on opening day, as political complications had prevented the French government from paying much attention to the exhibition until six months before it was due to open. However, efforts made in April were prodigious, and by 1 June, a month after the formal opening, the exhibition was finally completed. This exposition was on a far larger scale than any previously held anywhere in the world. It covered over , the main building in the Champ de Mars and the hill of Chaillot, occupying . The Gare du Champ de Mars was rebuilt with four tracks to receive rail traffic occasioned by the exposition. The Pont d'Iéna linked the two exhibition sites along the central allée. The French exhibits filled one-half of the entir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jardin D'Acclimatation Railway
The Jardin d'Acclimatation railway is a minimum gauge park railway, located in the Bois de Boulogne in Paris. It was opened in 1878 and connects Porte Maillot and the Jardin d'Acclimatation (zoological gardens), 800 meters apart. It was the first passenger-carrying narrow gauge railway of France. History The French narrow gauge railway pioneer Paul Decauville wanted to experiment with passenger transport using his portable railways, already successfully introduced in the industry and agriculture. For the 1878 Exposition Universelle he proposed to use his concept for the exhibition by a line Trocadéro - Military Academy passing the Champ-de-Mars, but permission was denied. He then offered the same facility at the Zoological Gardens, which was accepted. Two kilometers of railway line at the track gauge of was constructed for the transportation of the exhibit visitors over a circular track, having a maximum speed of 15 km/h. The line carried up to 3000 passengers on some Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Railway History
''Australian Railway History'' is a monthly magazine covering railway history in Australia, published by the New South Wales Division of the Australian Railway Historical Society on behalf of its state and territory Divisions. Australian Railway Historical Society History and profile It was first published in 1937 as the ''Australasian Railway and Locomotive Historical Society Bulletin'', being renamed ''ARHS Bulletin'' in 1952. In January 2004, the magazine was re-branded as ''Australian Railway History''. Historically, the magazine had a mix of articles dealing with historical material and items on current events drawn from its affiliate publications. Today, it contains only historical articles, two or three of them being in-depth.Parameters * Size : A4; ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the ''metropole, metropolitan state'' (or "mother country"). This administrative colonial separation makes colonies neither incorporated territories nor client states. Some colonies have been organized either as dependent territory, dependent territories that are Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter, not sufficiently self-governed, or as self-governing colony, self-governed colonies controlled by settler colonialism, colonial settlers. The term colony originates from the ancient rome, ancient Roman ''colonia (Roman), colonia'', a type of Roman settlement. Derived from ''colon-us'' (farmer, cultivator, planter, or settler), it carries with it the sense of 'farm' and 'landed estate'. Furthermore the term was used to refer to the older Greek ''apoikia'' (), which w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sled
A sled, skid, sledge, or sleigh is a land vehicle that slides across a surface, usually of ice or snow. It is built with either a smooth underside or a separate body supported by two or more smooth, relatively narrow, longitudinal runners similar in principle to skis. This reduces the amount of friction, which helps to carry heavy loads. Some designs are used to transport passengers or cargo across relatively level ground. Others are designed to go downhill for recreation, particularly by children, or competition. (Compare cross-country skiing with its downhill cousin.) Shades of meaning differentiating the three terms often reflect regional variations depending on historical uses and prevailing climate. In British English, ''sledge'' is the general term, and more common than ''sled''. ''Toboggan'' is sometimes used synonymously with ''sledge'' but more often to refer to a particular type of sledge without runners. ''Sleigh'' refers to a moderate to large-sized, usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumper
A dumper or dumper truck (British English) or dump truck (North American English) is a truck designed for carrying bulk material, often on building sites. A dumper has a body which tilts or opens at the back for unloading and is usually an open 4-wheeled vehicle with the load skip in front of the driver. The skip can tip to dump the load; this is where the name "dumper" comes from. They are normally diesel powered. A towing eye is fitted for secondary use as a site tractor. Dumpers with rubber tracks are used in special circumstances and provide a more even distribution of weight compared to tires. Continuous tracks allow the operator to carry heavier payload on slick, snowy, or muddy surfaces, and are popular in some countries. Background One of the earliest British dumpers was the Muir-Hill, which was based on the Fordson tractor with 2 cubic yard bucket, driving on the front axle and steered by the back wheels. Devised in 1927, and on sale by 1931, it gained a lot of versatil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemins De Fer De Paris à Lyon Et à La Méditerranée
The Compagnie des chemins de fer de Paris à Lyon et à la Méditerranée ("Railway Company of Paris to Lyon and the Mediterranean"), also known as the Chemins de fer Paris-Lyon-Méditerranée or simply PLM, established in 1857, was one of France’s main railway companies until the nationalization of all French railways and establishment of the Société nationale des chemins de fer français (SNCF) on . History Established on 3 July 1857, the PLM grew between 1858 and 1862 from the amalgamation of the earlier Paris–Lyon and Lyon–Méditerranée companies, as well as subsequently incorporating a number of smaller railways. The PLM operated chiefly in the Southeast of France, with a main line which connected Paris to the French Riviera by way of Dijon, Lyon and Marseille. The company was also the operator of railways in Algeria. The PLM was absorbed in 1938 into the majority state-owned Société nationale des chemins de fer français, and its network became the southeaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |