|
Dzus Fastener
The Dzus fastener, also known as a turnlock fastener or quick-action panel fastener, is a type of proprietary quarter-turn spiral cam lock fastener often used to secure skin panels on aircraft and other high-performance vehicles. It is named after its inventor William Dzus (). History The fastener was invented and patented by an American engineer of Ukrainian descent William Dzus in the early 1930s. Operation The cowling (10) and fuselage (11) can be quickly fastened together by bringing the cowling (10) to the fuselage (11), placing the shank (13) of the button (12) into the hole in the fuselage (25). The button (12) is turned by a screwdriver in its slot (21) to a position in which the slots (16) will hold the spring (22). As button (12) turns, the walls of its spiral slots (16) act as cams, and pull the intermediate section of the spring (22) from its relaxed position up into the slot's holes (18) past the slot's projections (17). The projection (17) in the slots (16) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fastener
A fastener (US English) or fastening (UK English) is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together. In general, fasteners are used to create non-permanent joints; that is, joints that can be removed or dismantled without damaging the joining components. Welding is an example of creating permanent joints. Steel fasteners are usually made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel. Other alternative methods of joining materials include: crimping, welding, soldering, brazing, taping, gluing, cement, or the use of other adhesives. Force may also be used, such as with magnets, vacuum (like suction cups), or even friction (like sticky pads). Some types of woodworking joints make use of separate internal reinforcements, such as dowels or biscuits, which in a sense can be considered fasteners within the scope of the joint system, although on their own they are not general purpose fasteners. Furniture supplied in flat-pack form often uses c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called '' aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Dzus
William Dzus (5 January 1895, Chernykhivtsi, Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, currently Ukraine - 19 June 1964, New York City, United States) was born Volodymyr Dzhus ( uk, Володимир Джус) and was an American engineer from Eastern Galicia, and the inventor of the Dzus fastener, also known as the quarter-turn fastener. He was also one of the founders of the Ukrainian Institute of America, a cultural foundation, for which he purchased the Harry F. Sinclair House (its current home). Life Dzus was born 1895 in the country of Ukraine to a family of wealthy Ukrainian farmers in the village of in the Austro-Hungarian Empire. In his late teens he moved over from his home country to New York where he quickly established himself as an innovative thinker, developing the first form of the quick‐acting fastener and founding the Dzus Fastener Company in 1934. The fastener was originally designed to fit aircraft - subsequently being used in heavy machinery, automobiles and li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzus Fastener, From US Patent 1955740
Dzus may refer to: * Asteroid 3687 Dzus * Dzus fastener The Dzus fastener, also known as a turnlock fastener or quick-action panel fastener, is a type of proprietary quarter-turn spiral cam lock fastener often used to secure skin panels on aircraft and other high-performance vehicles. It is named afte ... See also * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Screw Drives
At a minimum, a screw drive is a set of shaped cavities and protrusions on the screw head that allows torque to be applied to it. Usually, it also involves a mating tool, such as a screwdriver, that is used to turn it. The following heads are categorized based on frequency, with some of the less-common drives being classified as "tamper-resistant." Most heads come in a range of sizes, typically distinguished by a number, such as "Phillips #00". These sizes do not necessarily describe a particular dimension of the drive shape, but rather are arbitrary designations. Slotted drives Slot Slot screw drives have a single horizontal indentation (the ''slot'') in the fastener head and is driven by a "common blade" or flat-bladed screwdriver. This form was the first type of screw drive to be developed, and for centuries, it was the simplest and cheapest to make. Additionally, it is unique compared to other common drives, due to it being straightforward to manufacture the slot h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
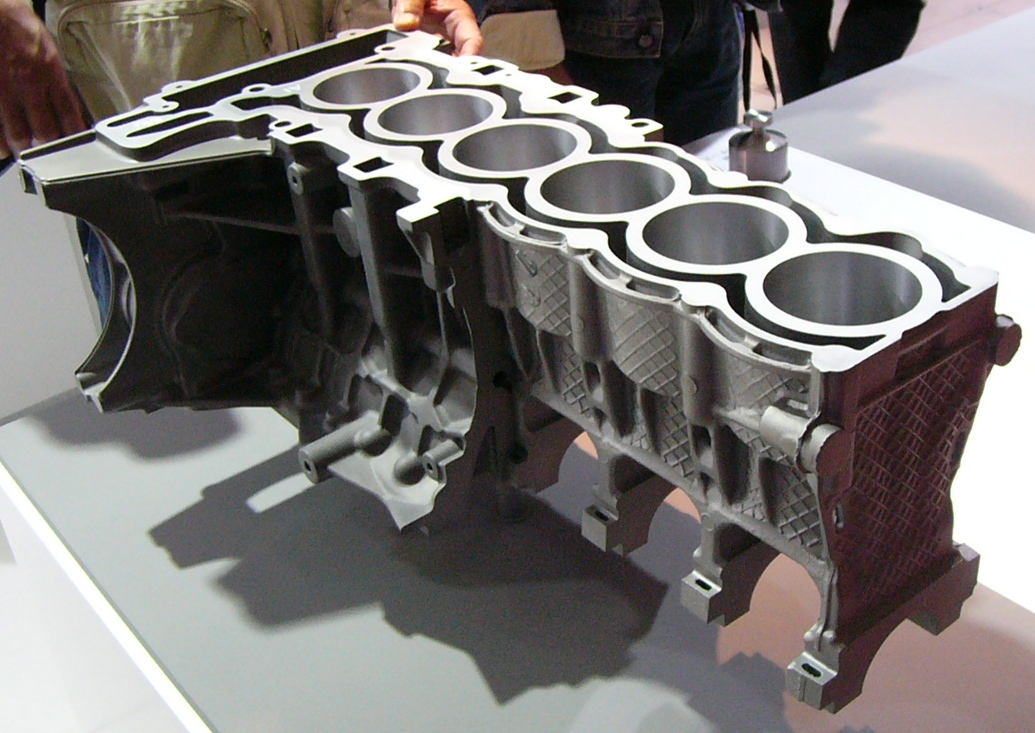
Die Casting
Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used. The casting equipment and the metal dies represent large capital costs and this tends to limit the process to high-volume production. Manufacture of parts using die casting is relatively simple, involving only four main steps, which keeps the incremental cost per item low. It is especially suited for a large quantity of small- to medium-sized castings, which is why die casting produces more castings than any other casting process. Die castings are characterized by a very good surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |