|
Dzungar Conquest Of Altishahr
The Dzungar conquest of Altishahr resulted in the Tibetan Buddhist Dzungar Khanate in Dzungaria conquering and subjugating the Genghisid-ruled Chagatai Khanate in Altishahr (the Tarim Basin). It put a final end to the independence of the Chagatai Khanate. Conquest The Turkic Muslim sedentary people of the Tarim Basin were originally ruled by the Chagatai Khanate while the nomadic Oirat Dzungar Buddhists in Dzungaria ruled over the Dzungar Khanate. The Dzungar Oirats led by Sengge attacked the Chagatai Khanate during the reign of Abdullah Khan. The Naqshbandi Sufi Khojas, descendants of the Prophet Muhammad, had replaced the Chagatayid Khans as the ruling authority of the Tarim Basin in the early 17th century. There was a struggle between two factions of Khojas, the Afaqi (White Mountain) faction and the Ishaqi (Black Mountain) faction. The Ishaqi defeated the Afaqi, which resulted in the Afaqi Khoja inviting the 5th Dalai Lama, the leader of the Tibetan Buddhists, to int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
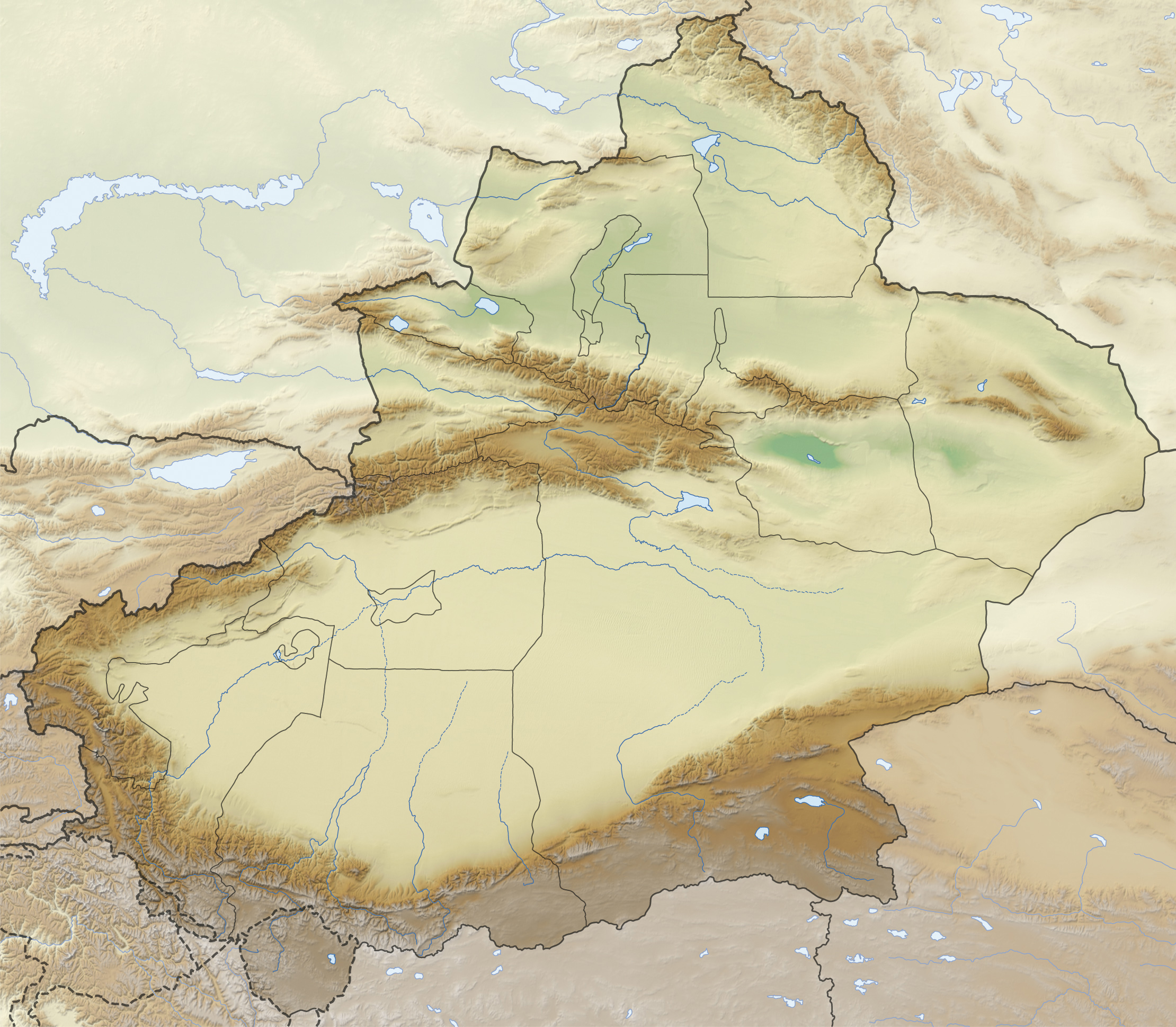
Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydrological Processes 20.10 (2006): 2207–2216.online 426 KB) Located in China's Xinjiang region, it is sometimes used synonymously to refer to the southern half of the province, or Nanjiang (), as opposed to the northern half of the province known as Dzungaria or Beijiang. Its northern boundary is the Tian Shan mountain range and its southern boundary is the Kunlun Mountains on the edge of the Tibetan Plateau. The Taklamakan Desert dominates much of the basin. The historical Uyghur name for the Tarim Basin is Altishahr ( Traditional spelling: 六城 or ), which means 'six cities' in Uyghur. Geography and relation to Xinjiang Xinjiang consists of two main geographically, historically, and ethnically distinct regions with different h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Xinjiang
Xinjiang historically consisted of two main geographically, historically, and ethnically distinct regions with different historical names: Dzungaria north of the Tianshan Mountains; and the Tarim Basin south of the Tianshan Mountains, currently mainly inhabited by the Uyghurs. They were renamed Xinjiang () in 1884, meaning "new frontier," when both regions were conquered by the Manchu Qing dynasty after the Dungan revolt (1862–1877). The first inhabitants of Xinjiang, specifically from southern and western Xinjiang formed from admixture between locals of Ancient North Eurasian and Northeast Asians descent. The oldest Tarim mummies, found in the Tarim Basin, are dated to the 2nd millennium BCE. In the first millennium BCE Indo-European-speaking Yuezhi nomads migrated into parts of Xinjiang. In the second century BCE the region became part of the Xiongnu empire, a confederation of nomads centered on present-day Mongolia, which forced the Yuezhi out of Xinjiang. Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawachi
Dawachi (; mn, Даваач; died 1759) was the last khan of the Dzungar Khanate from 1753 until his defeat at the hands of Qing and Mongol forces at Ili in 1755. Dawachi belonged to the highest rank of Dzungar aristocracy. He traced his ancestry back directly to Erdeni Batur (died 1635), the founder of the Dzungar Khanate. His grandfather was Tsering Dondup. His brother, Tsewang Rabtan (1643-1727), led the Dzungar invasion and occupation of Tibet in 1717. His father was the second cousin of Galdan Tseren, the Khong Tayiji of the Dzungar Khanate from 1727 to 1745. Background Dawachi, whose pasture lands were centered in the Tarbagatai region first came to prominence when he and his Khoit- Oirat ally Amursana opposed the rule of Lama Dorji (1728-1753), who had seized the Dzungar throne after assassinating his brother Tsewang Dorji Namjal in 1750. The reign of Lama Dorji's father, Galdan Tseren, represented a resurgence of the Dzungar Khanate's political, military and economic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Jao Modo
The Battle of Jao Modo ( mn, Зуунмод-Тэрэлжийн тулалдаан; ) also known as the Battle of Zuunmod (literally "Battle of the Hundred Trees"), was fought on June 12, 1696 on the banks of the upper Terelj river east of the modern-day Mongolian capital Ulaanbaatar. A Dzungar-Mongol army under the command of Galdan Boshugtu Khan was defeated by Qing armies personally led by the Kangxi Emperor. This decisive Qing victory in the early stages of the Dzungar–Qing Wars (1687–1758) effectively incorporated Khalkha Mongolia under Qing rule and relegated Dzungar Mongol forces to Inner Asia until they were finally defeated in 1758. Background Attempts by the Qing court to maintain an uneasy peace between the eastern Khalkha and western Dzungar-Oirat Mongols ultimately collapsed when in 1687 forces loyal to the Khalkha Tüsheet Khan killed the brother of the Dzungar Mongol leader Galdan Boshugtu Khan in battle as he attempted to support the rival Zasaghtu Khalkha t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jizyah
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Islamic law. The jizya tax has been understood in Islam as a fee for protection provided by the Muslim ruler to non-Muslims, for the exemption from military service for non-Muslims, for the permission to practice a non-Muslim faith with some communal autonomy in a Muslim state, and as material proof of the non-Muslims' submission to the Muslim state and its laws. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Social Sciences'' 24:4, Oxford; pp. 99–100. and the application of jizya varied in the course of Islamic history. However, scholars largely agree that early Muslim rulers adapted existing systems of taxation and tribute that were established under previous rulers of the conquered lands, such as those of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsewang Rabtan
Tsewang Rabtan (from ''Tsewang Rapten''; ; ; 1643–1727) was a Choros (Oirats) prince and the Khong Tayiji of the Dzungar Khanate from 1697 (following the death of his uncle and rival Galdan Boshugtu Khan) until his death in 1727. He was married to Lha-bzang Khan's sister. Political and military action Tsewang Rabtan married his daughter, Boitalak (), to Danjung (), the eldest son of Lha-bzang Khan in 1714. He used the occasion to destroy some of Lha-bzang's troops in preparation for an invasion of Tibet. He consolidated Dzungar power by 1715, and in 1717 sent one army of 300 into Amdo to retrieve the 7th Dalai Lama, planning to consolidate Tibetan support by bringing him to Lhasa, and another army of 6000, led by his brother Tseren Dondub, that successfully took Lhasa from the Khoshut and killed Lha-bzang Khan. However, the first army failed to acquire the Dalai Lama, having been defeated by Qing troops at Kumbum. Dzungar troops went on the rampage through Lhasa and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galdan Tseren
Galdan Tseren (; ?–1745) was a Choros (Oirats) prince and the '' Khong Tayiji'' of the Dzungar Khanate from 1727 until his death in 1745. Galdan Tseren was the eldest son of Tsewang Rabtan. After the assassination of his father by rival factions, a civil war followed between his sons of which Galdan Tseren emerged victorious and crowned himself the new Dzungar Khan. Galdan Tseren continued his fathers policies of confrontation with the Qing dynasty. He refused to surrender Lubsan Danjin, the leader of the revolt of the Kokonor (Qinghai) Khoshuts of 1723, and he initiated a policy of harassment of the Khalkha Mongols, the Manchu's allies. In the spring of 1729, war broke out against the Qing dynasty and Galdan Tseren's forces obtained numerous victories against the Qing. The war dragged on until 1737. Peace negotiations had already started in 1734. In 1737 both sides finally made peace and the Galdan Tseren accepted the condition of tributary. Galdan Tseren not only view ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akbash Khan
Akbash Khan ( literally ''White Head Khan'' in Uyghur) of the Yarkent Khanate was a Central Asian Khan in the beginning of 18th century. He was the last Khan of Yarkent Khanate. He is known as one of the "later Chagatai princes"(察合台後王) in China. Origin Akbash Khan's name was Muhammad Mumin. He descended from the second son of Genghis Khan, Chagatai. He was a member of the Borjigin clan by blood. His father was Said Baba Khan of Eastern Khanate (Uyghurstan) and his grandfather was Ismail Khan. He had two brothers who were also at one point Khans of Yarkent Khanate (Abd ar-Rashid Khan II and Muhammad Imin Khan respectively). Reign In 1678, Galdan Boshugtu Khan of Dzungar invaded Yarkent Khanate on the invitation of Afak Khoja, who previously was exiled from the country by Ismail Khan, conquered eastern part of Yarkent Khanate, captured Ismail Khan in Yarkand and set up Abd ar-Rashid Khan II as a puppet. Instead of Afaq Khoja of the Naqshbandi order, Galdan appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Amin Khan
Muhammad Amin Khan was Khan of Turpan from 1682 to 1694. He was the younger brother of Abd ar-Rashid Khan II and the grandson of Ismail Khan (Moghul khan). Revival of the Khanship Muhammad Amin Khan tried to re-established his authority as khan and sought external support. He twice sent tribute to the Qing government in the name of khan of Turpan, and sent an embassy to the Mughal Court in India in 1690. The next year he dispatched an embassy to Subhan Quli, the Uzbek Khan of Bukhara (1680–1720), seeking help against "Qirkhiz infidels" (meaning the Dzungars), who "had acquired dominance over the country". War against the Dzungars In 1693-94 Muhammad Amin Khan led an expedition against Yining, the Dzungar capital, capturing over 30,000 Kalmyks and Oirats. Death The Khan was overthrown and killed during a revolt by Afaq Khoja's followers in 1694. Afaq khoja's son Yahya Khoja Yahya may refer to: * Yahya (name), a common Arabic male given name * Yahya (Zaragoza), 11th-century ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Ar-Rashid Khan II
{{unreferenced, date=August 2014 Abd ar-Rashid Khan II was Khan of Yarkand and Turpan from 1680–1682. He was son of Baba Khan or Babak Khan. Baba Khan was son of Ismail Khan (Moghul khan). Dzungar's appointment of the khan After Galdan Boshugtu Khan occupied Yarkand, he did not hand over power to Afaq Khoja, who had rendered outstanding service to him but appointed one of the members of the old chaghatai family, Abdul ar-Rashid Khan II, son of Baba Khan of Turpan, as Khan and made him his vassal. Conflict between Khan and Afaq Khoja Discord soon arose between Khan and Afaq Khoja, however, with the latter fleeing the region once again. In 1682 riots erupted in Yarkand and the khan fled to Ili, his younger brother Muhammad Amin Khan thereafter became khan. See also *List of Chagatai khans The Chagatai Khans were the monarchs of the Chagatai Khanate from Chagatai Khan's inheritance of the state in 1227 to their removal from power by the Dzungars and their vassals in 1687. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ismail Khan (Moghul Khan)
Ismail Khan was Khan of Yarkand and Kashgar between 1666 and 1669. He was replaced by Ilbars Khan from 1669–1670. His khanship was restored from 1670–1680. War with Dzungars In 1680 Galdan Boshugtu Khan led 120,000 Dzungar cavalry into the Tarim Basin through Aksu and Turpan towards Kashgar and Yarkand with the help of Afaq Khoja of the {{Interlanguage link multi, White Mountain Khoja, zh, 3=白山派s and his followers. The army made good progress in their advance. The Chagatai ruler Ismail Khan's son Babak Sultan led his troops and offered fierce resistance only to perish in battle. Having occupied Kashgar, the Dzungar army immediately advanced upon Yarkand. The general Yiwazibo (Iwaz Beg), sent to oppose their advance was killed, and the Dzungar occupied Yarkand and took Ismail Khan and his family as prisoners to Ili.Page 191,192, Studied by Dr Abdul Rauf Mughal See also *List of Chagatai khans The Chagatai Khans were the monarchs of the Chagatai Khanate from Chagatai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |