|
Działowski D.K.D.1
The Działowski D.K.D.1 was the first powered aircraft designed by . It was a low-power high-wing monoplane with a cabin for one passenger. After attending an aviation exhibition in Warsaw in 1927 it was badly damaged when the engine failed as it left and it did not fly again. Design and development In the early 1920s Stanisław Działowski was head of aircraft assembly at the military flying school at Bydgoszcz. He and his brother Mieczysław began aircraft design with a glider, the Bydgoszczanka, which flew at the 1925 Second Polish Glider Contest. In the same year they began work on the D.K.D.1. The surname initials D.K.D were those of the two brothers and of Jan Kruger, a local shoemaker who provided some funding and also bought the Gabriel brothers the Haacke engine that had been used in the Gabriel P 5 and P 6. The wing was built in the military workshop but they were later forced out to a cellar in the town. The D.K.D.1 was a high wing aircraft with an enclosed cabin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
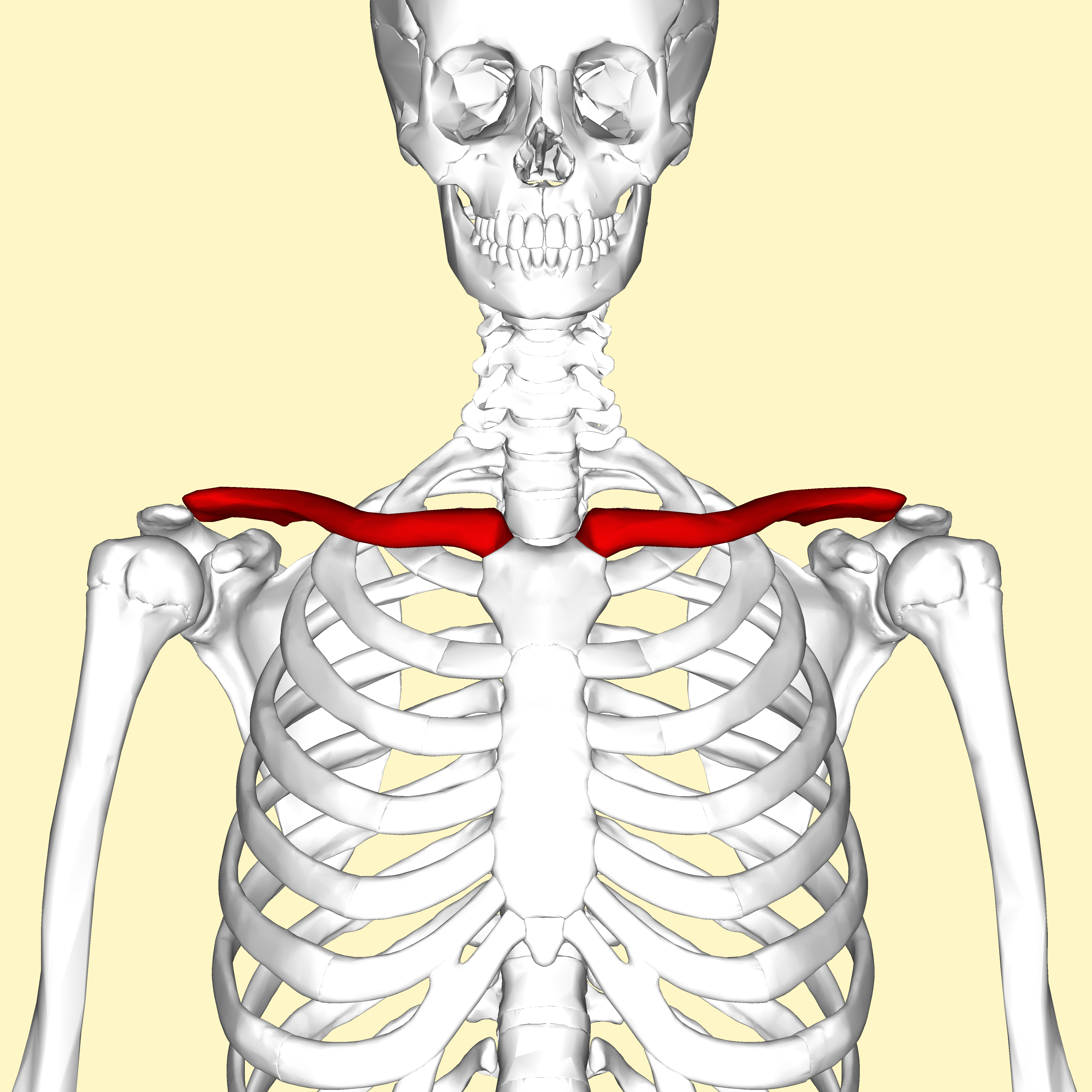
Strut
A strut is a structural component commonly found in engineering, aeronautics, architecture and anatomy. Struts generally work by resisting longitudinal compression, but they may also serve in tension. A stay is sometimes used as a synonym for strut, but some sources distinguish that struts are braces for holding compressive forces apart, while stays are braces for keeping stretching forces together. Human anatomy Part of the functionality of the clavicle is to serve as a strut between the scapula and sternum, resisting forces that would otherwise bring the upper limb close to the thorax. Keeping the upper limb away from the thorax is vital for its range of motion. Complete lack of clavicles may be seen in cleidocranial dysostosis, and the abnormal proximity of the shoulders to the median plane in cases of this genetic condition exemplifies the clavicle's importance as a strut. Architecture and construction Strut is a common name in timber framing for a support or brace of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 (2023), with approximately 8 million additional people living within a radius. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596, and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Kraków Old Town, Old Town was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1978, one of the world's first sites granted the status. The city began as a Hamlet (place), hamlet on Wawel Hill and was a busy trading centre of Central Europe in 985. In 1038, it became the seat of King of Poland, Polish monarchs from the Piast dynasty, and subsequently served as the centre of administration under Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellonian kings and of the Polish–Lithuan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toruń
Toruń is a city on the Vistula River in north-central Poland and a World Heritage Sites of Poland, UNESCO World Heritage Site. Its population was 196,935 as of December 2021. Previously, it was the capital of the Toruń Voivodeship (1975–1998) and the Pomeranian Voivodeship (1919–1939), Pomeranian Voivodeship (1921–1945). Since 1999, Toruń has been a seat of the local government of the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship and is one of its two capitals, together with Bydgoszcz. The cities and neighboring counties form the Bydgoszcz–Toruń twin city metropolitan area. Toruń is one of the oldest cities in Poland; it was first settled in the 8th century and in 1233 was expanded by the Teutonic Knights. For centuries it was home to people of diverse backgrounds and religions. From 1264 until 1411, Toruń was part of the Hanseatic League and by the 17th century a leading trading point, which greatly affected the city's architecture, ranging from Brick Gothic to Mannerism, Mann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landing Gear
Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for taxiing, takeoff or landing. For aircraft, it is generally needed for all three of these. It was also formerly called ''alighting gear'' by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Martin Company. For aircraft, Stinton makes the terminology distinction ''undercarriage (British) = landing gear (US)''. For aircraft, the landing gear supports the craft when it is not flying, allowing it to take off, land, and taxi without damage. Wheeled landing gear is the most common, with skis or Seaplane, floats needed to operate from snow/ice/water and skids for vertical operation on land. Retractable undercarriages fold away during flight, which reduces drag (physics), drag, allowing for faster airspeeds. Landing gear must be strong enough to support the aircraft and its design affects the weight, balance and performance. It often comprises three wheels, or wheel-sets, giving a tripod effect. Some unusual land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevator (aeronautics)
Elevators are flight control surfaces, usually at the rear of an aircraft, which control the aircraft's flight dynamics, pitch, and therefore the angle of attack and the lift of the wing. The elevators are usually hinged to the tailplane or horizontal stabilizer (aircraft), stabilizer. They may be the only pitch control surface present, and are sometimes located at the front of the aircraft (early airplanes and canard (aeronautics), canards) or integrated into a rear "all-moving tailplane", also called a slab elevator or stabilator. Elevator control effectiveness The elevator is a usable up and down system that controls the plane, horizontal stabilizer usually creates a ''downward'' force which balances the nose down moment (physics), moment created by the wing lift force, which typically applies at a point (the wing center of lift) situated aft of the airplane's center of gravity. The effects of drag (physics), drag and changing the engine thrust may also result in pitch mome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailplane
A tailplane, also known as a horizontal stabilizer, is a small lift (force), lifting surface located on the tail (empennage) behind the main lifting surfaces of a fixed-wing aircraft as well as other non-fixed-wing aircraft such as helicopters and gyroplanes. Not all fixed-wing aircraft have tailplanes. Canard (aeronautics), Canards, tailless aircraft, tailless and flying wing aircraft have no separate tailplane, while in V-tail aircraft the vertical stabilizer, rudder, and the tail-plane and elevator are combined to form two diagonal surfaces in a V layout. The function of the tailplane is to provide stability and control. In particular, the tailplane helps adjust for changes in position of the center of pressure (fluid mechanics), centre of pressure or centre of gravity caused by changes in speed and attitude, fuel consumption, or dropping cargo or payload. Tailplane types The tailplane comprises the tail-mounted fixed horizontal stabilizer and movable Elevator (aeronautics), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fin (aeronautics)
An aircraft stabilizer is an aerodynamic surface, typically including one or more movable control surfaces, that provides longitudinal (pitch) and/or directional (yaw) stability and control. A stabilizer can feature a fixed or adjustable structure on which any movable control surfaces are hinged, or it can itself be a fully movable surface such as a stabilator. Depending on the context, "stabilizer" may sometimes describe only the front part of the overall surface. In the conventional aircraft configuration, separate vertical (fin) and horizontal (tailplane) stabilizers form an empennage positioned at the tail of the aircraft. Other arrangements of the empennage, such as the V-tail configuration, feature stabilizers which contribute to a combination of longitudinal and directional stabilization and control. Longitudinal stability and control may be obtained with other wing configurations, including canard, tandem wing and tailless aircraft. Some types of aircraft are stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plywood
Plywood is a composite material manufactured from thin layers, or "plies", of wood veneer that have been stacked and glued together. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured boards, which include plywood, medium-density fibreboard (MDF), oriented strand board (OSB), and particle board (or chipboard). All plywoods bind resin and wood fibre sheets (cellulose cells are long, strong and thin) to form a composite material. The sheets of wood are stacked such that each layer has its grain set typically (see below) perpendicular to its adjacent layers. This alternation of the grain is called ''cross-graining'' and has several important benefits: it reduces the tendency of wood to split when nailed at the edges; it reduces thickness swelling and shrinkage, providing improved dimensional stability; and it makes the strength of the panel consistent across all directions. There is usually an odd number of plies, so that the sheet is balanced, that is, the surface layers ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duralumin
Duralumin (also called duraluminum, duraluminium, duralum, dural(l)ium, or dural) is a trade name for one of the earliest types of age hardening, age-hardenable aluminium–copper alloys. The term is a combination of ''Düren'' and ''aluminium'' . Its use as a trade name is obsolete. Today the term mainly refers to aluminium-copper alloys, designated as the 2000 series by the international alloy designation system (IADS), as with 2014 aluminium alloy, 2014 and 2024 aluminium alloy, 2024 alloys used in airframe fabrication. Duralumin was developed in 1909 in Germany. Duralumin is known for its strength and hardness, making it suitable for various applications, especially in the aviation and aerospace industry. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, which can be mitigated by using alclad-duralum materials. History Duralumin was developed by the German metallurgist Alfred Wilm at private military-industrial laboratory (Center for Scientific-Technical Research) in Neubabelsberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Twin Engine
A flat-twin engine is a two-cylinder internal combustion engine with the cylinders on opposite sides of the crankshaft. The most common type of flat-twin engine is the boxer-twin engine, where both pistons move inwards and outwards at the same time. The flat-twin design was patented by Karl Benz in 1896 and the first production flat-twin engine was used in the ''Lanchester 8 hp Phaeton'' car released in 1900. The flat-twin engine was used in several other cars since, however a more common usage is in motorcycles; early models oriented the cylinders in line with the frame, however later models switched to the cylinders being perpendicular to the frame to provide even cooling across both cylinders. Flat-twin engines were also used in several aircraft up until the 1930s and in various stationary applications from the 1930s to the 1960s. The Australian lawnmower manufacturer Victa also produced a flat-twin engine push mower from August 1975 to 1980 dubbed the ‘Twin 500’, and lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haacke HFM-2
The Haacke HFM-2 was a German two cylinder flat engine built in the early 1920s. Variants From Flight * HFM-2 () * HFM-2a (); as HFM-2 apart from bore Applications * Albatros L.66 * Dietrich-Gobiet DP.VII * Działowski D.K.D.1 The Działowski D.K.D.1 was the first powered aircraft designed by . It was a low-power high-wing monoplane with a cabin for one passenger. After attending an aviation exhibition in Warsaw in 1927 it was badly damaged when the engine failed as it ... * Dobi-I * Gabriel P 5 * Karhu 3 * Mayenberger amphibian * Rieseler R.I * Rieseler R.II * Rieseler R.III * Silesia S-3 * Silesia S-4 * Udet U.1 * Udet U.2 Engines on display * Finnish Airforce Museum Specifications (HFM-2) See also References {{reflist, 2, refs= 1920s aircraft piston engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |